Would you like to explore a topic?
- LEARNING OUTSIDE OF SCHOOL

Or read some of our popular articles?
Free downloadable english gcse past papers with mark scheme.
- 19 May 2022
The Best Free Homeschooling Resources UK Parents Need to Start Using Today
- Joseph McCrossan
- 18 February 2022
How Will GCSE Grade Boundaries Affect My Child’s Results?
- Akshat Biyani
- 13 December 2021
How to Write the Perfect Essay: A Step-By-Step Guide for Students
- June 2, 2022

- What is an essay?
What makes a good essay?
Typical essay structure, 7 steps to writing a good essay, a step-by-step guide to writing a good essay.
Whether you are gearing up for your GCSE coursework submissions or looking to brush up on your A-level writing skills, we have the perfect essay-writing guide for you. 💯
Staring at a blank page before writing an essay can feel a little daunting . Where do you start? What should your introduction say? And how should you structure your arguments? They are all fair questions and we have the answers! Take the stress out of essay writing with this step-by-step guide – you’ll be typing away in no time. 👩💻

What is an essay?
Generally speaking, an essay designates a literary work in which the author defends a point of view or a personal conviction, using logical arguments and literary devices in order to inform and convince the reader.
So – although essays can be broadly split into four categories: argumentative, expository, narrative, and descriptive – an essay can simply be described as a focused piece of writing designed to inform or persuade. 🤔
The purpose of an essay is to present a coherent argument in response to a stimulus or question and to persuade the reader that your position is credible, believable and reasonable. 👌
So, a ‘good’ essay relies on a confident writing style – it’s clear, well-substantiated, focussed, explanatory and descriptive . The structure follows a logical progression and above all, the body of the essay clearly correlates to the tile – answering the question where one has been posed.
But, how do you go about making sure that you tick all these boxes and keep within a specified word count? Read on for the answer as well as an example essay structure to follow and a handy step-by-step guide to writing the perfect essay – hooray. 🙌
Sometimes, it is helpful to think about your essay like it is a well-balanced argument or a speech – it needs to have a logical structure, with all your points coming together to answer the question in a coherent manner. ⚖️
Of course, essays can vary significantly in length but besides that, they all follow a fairly strict pattern or structure made up of three sections. Lean into this predictability because it will keep you on track and help you make your point clearly. Let’s take a look at the typical essay structure:
#1 Introduction
Start your introduction with the central claim of your essay. Let the reader know exactly what you intend to say with this essay. Communicate what you’re going to argue, and in what order. The final part of your introduction should also say what conclusions you’re going to draw – it sounds counter-intuitive but it’s not – more on that below. 1️⃣
Make your point, evidence it and explain it. This part of the essay – generally made up of three or more paragraphs depending on the length of your essay – is where you present your argument. The first sentence of each paragraph – much like an introduction to an essay – should summarise what your paragraph intends to explain in more detail. 2️⃣
#3 Conclusion
This is where you affirm your argument – remind the reader what you just proved in your essay and how you did it. This section will sound quite similar to your introduction but – having written the essay – you’ll be summarising rather than setting out your stall. 3️⃣
No essay is the same but your approach to writing them can be. As well as some best practice tips, we have gathered our favourite advice from expert essay-writers and compiled the following 7-step guide to writing a good essay every time. 👍
#1 Make sure you understand the question
#2 complete background reading.
#3 Make a detailed plan
#4 Write your opening sentences
#5 flesh out your essay in a rough draft, #6 evidence your opinion, #7 final proofread and edit.
Now that you have familiarised yourself with the 7 steps standing between you and the perfect essay, let’s take a closer look at each of those stages so that you can get on with crafting your written arguments with confidence .
This is the most crucial stage in essay writing – r ead the essay prompt carefully and understand the question. Highlight the keywords – like ‘compare,’ ‘contrast’ ‘discuss,’ ‘explain’ or ‘evaluate’ – and let it sink in before your mind starts racing . There is nothing worse than writing 500 words before realising you have entirely missed the brief . 🧐
Unless you are writing under exam conditions , you will most likely have been working towards this essay for some time, by doing thorough background reading. Re-read relevant chapters and sections, highlight pertinent material and maybe even stray outside the designated reading list, this shows genuine interest and extended knowledge. 📚
#3 Make a detailed plan
Following the handy structure we shared with you above, now is the time to create the ‘skeleton structure’ or essay plan. Working from your essay title, plot out what you want your paragraphs to cover and how that information is going to flow. You don’t need to start writing any full sentences yet but it might be useful to think about the various quotes you plan to use to substantiate each section. 📝
Having mapped out the overall trajectory of your essay, you can start to drill down into the detail. First, write the opening sentence for each of the paragraphs in the body section of your essay. Remember – each paragraph is like a mini-essay – the opening sentence should summarise what the paragraph will then go on to explain in more detail. 🖊️
Next, it's time to write the bulk of your words and flesh out your arguments. Follow the ‘point, evidence, explain’ method. The opening sentences – already written – should introduce your ‘points’, so now you need to ‘evidence’ them with corroborating research and ‘explain’ how the evidence you’ve presented proves the point you’re trying to make. ✍️
With a rough draft in front of you, you can take a moment to read what you have written so far. Are there any sections that require further substantiation? Have you managed to include the most relevant material you originally highlighted in your background reading? Now is the time to make sure you have evidenced all your opinions and claims with the strongest quotes, citations and material. 📗
This is your final chance to re-read your essay and go over it with a fine-toothed comb before pressing ‘submit’. We highly recommend leaving a day or two between finishing your essay and the final proofread if possible – you’ll be amazed at the difference this makes, allowing you to return with a fresh pair of eyes and a more discerning judgment. 🤓
If you are looking for advice and support with your own essay-writing adventures, why not t ry a free trial lesson with GoStudent? Our tutors are experts at boosting academic success and having fun along the way. Get in touch and see how it can work for you today. 🎒

Popular posts

- By Guy Doza

- By Joseph McCrossan
- In LEARNING TRENDS

- By Akshat Biyani

What are the Hardest GCSEs? Should You Avoid or Embrace Them?
- By Clarissa Joshua

4 Surprising Disadvantages of Homeschooling
- By Andrea Butler
Want to try tutoring? Request a free trial session with a top tutor.
More great reads:.

Benefits of Reading: Positive Impacts for All Ages Everyday
- May 26, 2023

15 of the Best Children's Books That Every Young Person Should Read
- By Sharlene Matharu
- March 2, 2023

Ultimate School Library Tips and Hacks
- By Natalie Lever
- March 1, 2023
Book a free trial session
Sign up for your free tutoring lesson..
Academic Editing and Proofreading
- Tips to Self-Edit Your Dissertation
- Guide to Essay Editing: Methods, Tips, & Examples
- Journal Article Proofreading: Process, Cost, & Checklist
- The A–Z of Dissertation Editing: Standard Rates & Involved Steps
- Research Paper Editing | Guide to a Perfect Research Paper
- Dissertation Proofreading | Definition & Standard Rates
- Thesis Proofreading | Definition, Importance & Standard Pricing
- Research Paper Proofreading | Definition, Significance & Standard Rates
- Essay Proofreading | Options, Cost & Checklist
- Top 10 Paper Editing Services of 2024 (Costs & Features)
- Top 10 Essay Checkers in 2024 (Free & Paid)
- Top 10 AI Proofreaders to Perfect Your Writing in 2024
- Top 10 English Correctors to Perfect Your Text in 2024
- Top 10 Essay Editing Services of 2024
- 10 Advanced AI Text Editors to Transform Writing in 2024
- Personal Statement Editing Services: Craft a Winning Essay
- Top 10 Academic Proofreading Services & How They Help
- College Essay Review: A Step-by-Step Guide (With Examples)
Academic Research
- Research Paper Outline: Free Templates & Examples to Guide You
- How to Write a Research Paper: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Write a Lab Report: Examples from Academic Editors
- Research Methodology Guide: Writing Tips, Types, & Examples
- The 10 Best Essential Resources for Academic Research
- 100+ Useful ChatGPT Prompts for Thesis Writing in 2024
- Best ChatGPT Prompts for Academic Writing (100+ Prompts!)
- Sampling Methods Guide: Types, Strategies, and Examples
- Independent vs. Dependent Variables | Meaning & Examples
Academic Writing & Publishing
- Difference Between Paper Editing and Peer Review
- What are the different types of peer review?
- How to Handle Journal Rejection: Essential Tips
- Editing and Proofreading Academic Papers: A Short Guide
- How to Carry Out Secondary Research
- The Results Section of a Dissertation
- Checklist: Is my Article Ready for Submitting to Journals?
- Types of Research Articles to Boost Your Research Profile
- 8 Types of Peer Review Processes You Should Know
- The Ethics of Academic Research
- How does LaTeX based proofreading work?
- How to Improve Your Scientific Writing: A Short Guide
- Chicago Title, Cover Page & Body | Paper Format Guidelines
- How to Write a Thesis Statement: Examples & Tips
- Chicago Style Citation: Quick Guide & Examples
- The A-Z Of Publishing Your Article in A Journal
- What is Journal Article Editing? 3 Reasons You Need It
- 5 Powerful Personal Statement Examples (Template Included)
- Complete Guide to MLA Format (9th Edition)
- How to Cite a Book in APA Style | Format & Examples
- How to Start a Research Paper | Step-by-step Guide
- APA Citations Made Easy with Our Concise Guide for 2024
- A Step-by-Step Guide to APA Formatting Style (7th Edition)
- Top 10 Online Dissertation Editing Services of 2024
- Academic Writing in 2024: 5 Key Dos & Don’ts + Examples
- What Are the Standard Book Sizes for Publishing Your Book?
- MLA Works Cited Page: Quick Tips & Examples
- 2024’s Top 10 Thesis Statement Generators (Free Included!)
- Top 10 Title Page Generators for Students in 2024
- What Is an Open Access Journal? 10 Myths Busted!
- Primary vs. Secondary Sources: Definition, Types & Examples
- How To Write a College Admissions Essay That Stands Out
- How to Write a Dissertation & Thesis Conclusion (+ Examples)
- APA Journal Citation: 7 Types, In-Text Rules, & Examples
- What Is Predatory Publishing and How to Avoid It!
- What Is Plagiarism? Meaning, Types & Examples
- How to Write a Strong Dissertation & Thesis Introduction
- How to Cite a Book in MLA Format (9th Edition)
- How to Cite a Website in MLA Format | 9th Edition Rules
- 10 Best AI Conclusion Generators (Features & Pricing)
- Top 10 Academic Editing Services of 2024 [with Pricing]
- 100+ Writing Prompts for College Students (10+ Categories!)
- How to Create the Perfect Thesis Title Page in 2024
- Additional Resources
- Preventing Plagiarism in Your Thesis: Tips & Best Practices
- Final Submission Checklist | Dissertation & Thesis
- 7 Useful MS Word Formatting Tips for Dissertation Writing
- How to Write a MEAL Paragraph: Writing Plan Explained in Detail
- Em Dash vs. En Dash vs. Hyphen: When to Use Which
- The 10 Best Citation Generators in 2024 | Free & Paid Plans!
- 2024’s Top 10 Self-Help Books for Better Living
- The 10 Best Free Character and Word Counters of 2024
- Know Everything About How to Make an Audiobook
- Mastering Metaphors: Definition, Types, and Examples
- Citation and Referencing
- Citing References: APA, MLA, and Chicago
- How to Cite Sources in the MLA Format
- MLA Citation Examples: Cite Essays, Websites, Movies & More
- Citations and References: What Are They and Why They Matter
- APA Headings & Subheadings | Formatting Guidelines & Examples
- Formatting an APA Reference Page | Template & Examples
- Research Paper Format: APA, MLA, & Chicago Style
- How to Create an MLA Title Page | Format, Steps, & Examples
- How to Create an MLA Header | Format Guidelines & Examples
- MLA Annotated Bibliography | Guidelines and Examples
- APA Website Citation (7th Edition) Guide | Format & Examples
- APA Citation Examples: The Bible, TED Talk, PPT & More
- APA Header Format: 5 Steps & Running Head Examples
- APA Title Page Format Simplified | Examples + Free Template
- How to Write an Abstract in MLA Format: Tips & Examples
- 10 Best Free Plagiarism Checkers of 2024 [100% Free Tools]
- 5 Reasons to Cite Your Sources Properly | Avoid Plagiarism!
- Dissertation Writing Guide
- Writing a Dissertation Proposal
- The Acknowledgments Section of a Dissertation
- The Table of Contents Page of a Dissertation
- The Introduction Chapter of a Dissertation
- The Literature Review of a Dissertation
- The Only Dissertation Toolkit You’ll Ever Need!
- 5 Thesis Writing Tips for Master Procrastinators
- How to Write a Dissertation | 5 Tips from Academic Editors
- The 5 Things to Look for in a Dissertation Editing Service
- Top 10 Dissertation Editing & Proofreading Services
- Why is it important to add references to your thesis?
- Thesis Editing | Definition, Scope & Standard Rates
- Expert Formatting Tips on MS Word for Dissertations
- A 7-Step Guide on How to Choose a Dissertation Topic
- 350 Best Dissertation Topic Ideas for All Streams in 2024
- A Guide on How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper
- Dissertation Defense: What to Expect and How to Prepare
- Creating a Dissertation Title Page (Examples & Templates)
- Essay Writing Guide
- Essential Research Tips for Essay Writing
- What Is a Mind Map? Free Mind Map Templates & Examples
- How to Write an Essay Outline: 5 Examples & Free Template
- How to Write an Essay Header: MLA and APA Essay Headers
- What Is an Essay? Structure, Parts, and Types
How to Write an Essay in 8 Simple Steps (Examples Included)
- 8 Types of Essays | Quick Summary with Examples
- Expository Essays | Step-by-Step Manual with Examples
- Narrative Essay | Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
- How to Write an Argumentative Essay (Examples Included)
- Guide to a Perfect Descriptive Essay [Examples & Outline Included]
- How to Start an Essay: 4 Introduction Paragraph Examples
- How to Write a Conclusion for an Essay (Examples Included!)
- How to Write an Impactful Personal Statement (Examples Included)
- Literary Analysis Essay: 5 Steps to a Perfect Assignment
- Compare and Contrast Essay | Quick Guide with Examples
- Top AI Essay Writers in 2024: 10 Must-Haves
- 100 Best College Essay Topics & How to Pick the Perfect One!
- College Essay Format: Tips, Examples, and Free Template
- Structure of an Essay: 5 Tips to Write an Outstanding Essay
- 10 Best AI Essay Outline Generators of 2024
- The Best Essay Graders of 2024 That You Can Use for Free!
- Top 10 Free Essay Writing Tools for Students in 2024
Still have questions? Leave a comment
Add Comment
Checklist: Dissertation Proposal
Enter your email id to get the downloadable right in your inbox!
Examples: Edited Papers
Need editing and proofreading services.

- Tags: Academic Writing , Essay , Essay Writing
Knowing how to write an essay can help you out significantly in both, your academic and professional life. An essay is a highly versatile nonfiction piece of writing that not only tests your knowledge of a topic but also your literary and argumentative skills.
Each essay requires the same basic process of planning, writing, and editing. Naturally, we’ve used these stages to group our steps on how to write an essay. So w ithout further ado, let’s get into it! Here are the eight steps to write an essay:
Stage 1: Planning
1. Pick an appropriate research topic
In certain cases, your teacher or professor may assign you a topic. However, in many cases, students have the freedom to select a topic of their choice. Make sure you choose a topic that you’re well versed in and have significant knowledge of.
Having prior knowledge of the topic will help you determine the subsequent steps to write an essay. It will also make your research process considerably easier.
2. Form an appropriate thesis statement
A thesis statement is the central idea or premise your essay is based on. It is usually a sentence or two long and is included in the introduction of the essay. The scope of your thesis statement depends on the type of your essay and its length.
For instance, the scope of the thesis statement for a 500–1000 word school essay will be narrower than a 1000–5000 word college essay. A rule of thumb is that your essay topic should be broad enough to gather enough information, but narrow enough to address specific points and not be vague. Here’s an example:
The invention of the airplane by the Wright Brothers in 1903 revolutionized transportation and paved the way for modern aviation. It represents a monumental achievement in human history that forever changed the course of human civilization.
3. Create an essay outline
Creating a well-organized essay outline not only gives structure and flow to your essay but also makes it more impactful and easy to understand. The idea is to collect the main points of information that support or elaborate on your thesis statement. You can also include references or examples under these main points.
For example, if your thesis statement revolves around the invention of the airplane, your main points will include travel before the invention of the airplane, how it was invented, and its effects on modern-day travel. Take a look:
The Wright Brothers’ invention had a massive impact on modern-day travel. The subsequent growth of the aviation industry led to increased accessibility of air travel to the general public.
Stage 2: Writing
4. Write a comprehensive introduction
After creating the basic outline, it is important to know how to write an essay. Begin your essay by introducing your voice and point of view to the reader. An introduction is usually a paragraph or two long and consists of three main parts:
- Background information
- Thesis statement
Let’s better understand this with the help of an example:
The Wright Brothers’ invention of the airplane in 1903 revolutionized the way humans travel and explore the world. Prior to this invention, transportation relied on trains, boats, and cars, which limited the distance and speed of travel. However, the airplane made air travel a reality, allowing people to reach far-off destinations in mere hours. This breakthrough paved the way for modern-day air travel, transforming the world into a smaller, more connected place. In this essay, we will explore the impact of the Wright Brothers’ invention on modern-day travel, including the growth of the aviation industry, increased accessibility of air travel to the general public, and the economic and cultural benefits of air travel.
Let’s understand how to construct each of these sections in more detail.
A. Construct an attractive hook
The opening sentence of an essay, also known as the hook, should include a powerful or startling statement that captures the reader’s attention. Depending on the type of your essay, it can be an interesting fact, a surprising statistic, or an engaging anecdote.
B. Provide relevant background information
While writing the introduction, it’s important to provide context or background information before including the thesis statement. The background information may include the time before a groundbreaking invention, the pros and cons of a significant discovery, or the short- and long-term effects of an event.
C. Edit the thesis statement
If you’ve constructed your thesis statement during the outlining stage, it’s time to edit it based on the background information you’ve provided. Observe the slight changes we’ve made to the scope of the thesis statement in the example above. This accommodates the bits of information we’ve provided in the background history.
5. Form relevant body paragraphs
Body paragraphs play a crucial role in supporting and expanding the central argument presented in the thesis statement. The number of body paragraphs depends on the type of essay as well as the scope of the thesis statement.
Most school-level essays contain three body paragraphs while college-level essays can vary in length depending on the assignment.
A well-crafted body paragraph consists of the following parts:
- A topic sentence
- Supporting information
- An analysis of the information
- A smooth transition to the next paragraph
Let’s understand this with the help of an example.
The Wright Brothers’ invention of the airplane revolutionized air travel. They achieved the first-ever successful powered flight with the Wright Flyer in 1903, after years of conducting experiments and studying flight principles. Despite their first flight lasting only 12 seconds, it was a significant milestone that paved the way for modern aviation. The Wright Brothers’ success can be attributed to their systematic approach to problem-solving, which included numerous experiments with gliders, the development of a wind tunnel to test their designs, and meticulous analysis and recording of their results. Their dedication and ingenuity forever changed the way we travel, making modern aviation possible.
Here’s a detailed overview of how to construct each of these sections.
A. Construct appropriate topic sentences
A topic sentence is the title of the body paragraph that elaborates on the thesis statement. It is the main idea on which the body paragraph is developed. Ensure that each topic sentence is relevant to the thesis statement and makes the essay flow seamlessly.
The order of topic sentences is key in creating an impactful essay. This order varies depending on the type of essay you choose to write. These sentences may be arranged chronologically, in the order of importance, or in a cause-and-effect format.
B. Provide supporting information
It is necessary to provide relevant supporting information and evidence to validate your topic statement. This may include examples, relevant statistics, history, or even personal anecdotes.
You should also remember to cite your sources wherever you use them to substantiate your arguments. Always give researchers and authors credit for their work!
C. Analyze the supporting information
After presenting the appropriate evidence, the next step is to conduct an in-depth analysis. Establish connections and provide additional details to strengthen the link between your topic sentence and the supporting information.
Depending on the type of essay, this step may also involve sharing your subjective opinions and key takeaways.
D. Create a smooth transition
In case you plan to create multiple body paragraphs, it is crucial to create a seamless transition between them. Transitional statements not only make the essay less jarring to read but also guide the reader in the right direction.
However, these statements need not be too lengthy and complicated. Use words such as “however”, “in addition to”, and “therefore” to convey transitions.
6. Construct an impactful conclusion
An impactful conclusion creates a lasting impression on the mind of the reader. Although it varies in length depending on the specific essay, the conclusion is typically a paragraph long.
It consists of
- A restated thesis statement
- Summary of the main points
- The broader implications of the thesis statement
Here’s an example of a well-structured conclusion:
The Wright Brothers’ invention of the airplane forever changed history by paving the way for modern aviation and countless aerospace advancements. Their persistence, innovation, and dedication to problem-solving led to the first successful powered flight in 1903, sparking a revolution in transportation that transformed the world. Today, air travel remains an integral part of our globalized society, highlighting the undeniable impact of the Wright Brothers’ contribution to human civilization.
Let’s take a closer look at how to construct each of these sections.
A. Restate the thesis statement
Your conclusion should call back to your original argument or thesis statement.
However, this does not mean repeating the thesis statement as is. The essence of your argument should remain the same, but it should also be modified and evolved as per the information presented in your essay.
B. Summarize important points
A powerful conclusion not only lingers in the reader’s mind but also provokes thought. You can create a strong impression on the reader by highlighting the most impactful points of your essay.
C. State the greater implications
End your essay with the most powerful and impactful part: the larger perspective. This can include a question you’d like to leave the reader with, the broader implications and impact of your thesis statement, or the long-term, lingering effects of your experience.
Make sure to include no new evidence or arguments, or to undermine your findings in any way.
Stage 3: Editing
7. Review your essay
Knowing how to write an essay is just one part of essay writing. Properly reviewing and editing your essay is just as important. Make sure to spend enough time going over your essay and adding any bits of information that you’ve missed.
This is also a good time to make minor structural changes in your essay.
8. Thoroughly proofread your essay
After making the necessary structural changes, recheck your essay word by word. It is important to not only correct major grammatical and spelling errors but also minor errors regarding the phrasing or tone of voice.
You can either choose to do this by yourself, ask a friend for assistance, or hire an essay proofreading service to go over your writing. To construct a fool-proof, error-free essay, it is helpful to have a trained pair of eyes go over it. Professional proofreaders can spot errors that are not visible to most people and set the right tone for your essay.
Now that you know the basics of how to write an essay, it’s time to learn about the specifics. Feel free to dig into the articles below and keep reading!
- How to Write an Essay Header in 4 Steps
- How to Write an Essay Outline
- What is an Expository Essay?
- How to Start an Essay
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the steps to write an essay, what is the best essay writing style, how do i start an essay introduction, what are the tips for effective essay writing, what makes a good essay.
Found this article helpful?
2 comments on “ How to Write an Essay in 8 Simple Steps (Examples Included) ”
This is really help ful
Great insights on essay writing! In our time, artificial intelligence can significantly ease the writing process.
Leave a Comment: Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
Your vs. You’re: When to Use Your and You’re
Your organization needs a technical editor: here’s why, your guide to the best ebook readers in 2024, writing for the web: 7 expert tips for web content writing.
Subscribe to our Newsletter
Get carefully curated resources about writing, editing, and publishing in the comfort of your inbox.
How to Copyright Your Book?
If you’ve thought about copyrighting your book, you’re on the right path.
© 2024 All rights reserved
- Terms of service
- Privacy policy
- Self Publishing Guide
- Pre-Publishing Steps
- Fiction Writing Tips
- Traditional Publishing
- Academic Writing and Publishing
- Partner with us
- Annual report
- Website content
- Marketing material
- Job Applicant
- Cover letter
- Resource Center
- Case studies
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write an Essay
Last Updated: July 22, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Christopher Taylor, PhD and by wikiHow staff writer, Megaera Lorenz, PhD . Christopher Taylor is an Adjunct Assistant Professor of English at Austin Community College in Texas. He received his PhD in English Literature and Medieval Studies from the University of Texas at Austin in 2014. There are 18 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 7,988,824 times.
An essay is a common type of academic writing that you'll likely be asked to do in multiple classes. Before you start writing your essay, make sure you understand the details of the assignment so that you know how to approach the essay and what your focus should be. Once you've chosen a topic, do some research and narrow down the main argument(s) you'd like to make. From there, you'll need to write an outline and flesh out your essay, which should consist of an introduction, body, and conclusion. After your essay is drafted, spend some time revising it to ensure your writing is as strong as possible.
Understanding Your Assignment

- The compare/contrast essay , which focuses on analyzing the similarities and differences between 2 things, such as ideas, people, events, places, or works of art.
- The narrative essay , which tells a story.
- The argumentative essay , in which the writer uses evidence and examples to convince the reader of their point of view.
- The critical or analytical essay, which examines something (such as a text or work of art) in detail. This type of essay may attempt to answer specific questions about the subject or focus more generally on its meaning.
- The informative essay , that educates the reader about a topic.

- How long your essay should be
- Which citation style to use
- Formatting requirements, such as margin size , line spacing, and font size and type
Christopher Taylor, PhD
Christopher Taylor, Professor of English, tells us: "Most essays will contain an introduction, a body or discussion portion, and a conclusion. When assigned a college essay, make sure to check the specific structural conventions related to your essay genre , your field of study, and your professor's expectations."

- If you're doing a research-based essay , you might find some inspiration from reading through some of the major sources on the subject.
- For a critical essay, you might choose to focus on a particular theme in the work you're discussing, or analyze the meaning of a specific passage.

- If you're having trouble narrowing down your topic, your instructor might be able to provide guidance or inspiration.
Planning and Organizing Your Essay

- Academic books and journals tend to be good sources of information. In addition to print sources, you may be able to find reliable information in scholarly databases such as JSTOR and Google Scholar.
- You can also look for primary source documents, such as letters, eyewitness accounts, and photographs.
- Always evaluate your sources critically. Even research papers by reputable academics can contain hidden biases, outdated information, and simple errors or faulty logic.
Tip: In general, Wikipedia articles are not considered appropriate sources for academic writing. However, you may be able to find useful sources in the “References” section at the end of the article.

- You might find it helpful to write your notes down on individual note cards or enter them into a text document on your computer so you can easily copy, paste , and rearrange them however you like.
- Try organizing your notes into different categories so you can identify specific ideas you'd like to focus on. For example, if you're analyzing a short story , you might put all your notes on a particular theme or character together.

- For example, if your essay is about the factors that led to the end of the Bronze Age in the ancient Middle East, you might focus on the question, “What role did natural disasters play in the collapse of Late Bronze Age society?”

- One easy way to come up with a thesis statement is to briefly answer the main question you would like to address.
- For example, if the question is “What role did natural disasters play in the collapse of Late Bronze Age society?” then your thesis might be, “Natural disasters during the Late Bronze Age destabilized local economies across the region. This set in motion a series of mass migrations of different peoples, creating widespread conflict that contributed to the collapse of several major Bronze Age political centers.”

- When you write the outline, think about how you would like to organize your essay. For example, you might start with your strongest arguments and then move to the weakest ones. Or, you could begin with a general overview of the source you're analyzing and then move on to addressing the major themes, tone, and style of the work.
- Introduction
- Point 1, with supporting examples
- Point 2, with supporting examples
- Point 3, with supporting examples
- Major counter-argument(s) to your thesis
- Your rebuttals to the counter-argument(s)
Drafting the Essay

- For example, if you're writing a critical essay about a work of art, your introduction might start with some basic information about the work, such as who created it, when and where it was created, and a brief description of the work itself. From there, introduce the question(s) about the work you'd like to address and present your thesis.
- A strong introduction should also contain a brief transitional sentence that creates a link to the first point or argument you would like to make. For example, if you're discussing the use of color in a work of art, lead-in by saying you'd like to start with an overview of symbolic color use in contemporary works by other artists.
Tip: Some writers find it helpful to write the introduction after they've written the rest of the essay. Once you've written out your main points, it's easier to summarize the gist of your essay in a few introductory sentences.

- For example, your topic sentence might be something like, “Arthur Conan Doyle's Sherlock Holmes stories are among the many literary influences apparent in P. G. Wodehouse's Jeeves novels.” You could then back this up by quoting a passage that contains a reference to Sherlock Holmes.
- Try to show how the arguments in each paragraph link back to the main thesis of your essay.

- When creating transitions, transitional phrases can be helpful. For example, use words and phrases such as “In addition,” “Therefore,” “Similarly,” “Subsequently,” or “As a result.”
- For example, if you've just discussed the use of color to create contrast in a work of art, you might start the next paragraph with, “In addition to color, the artist also uses different line weights to distinguish between the more static and dynamic figures in the scene.”

- For example, if you're arguing that a particular kind of shrimp decorates its shell with red algae to attract a mate, you'll need to address the counterargument that the shell decoration is a warning to predators. You might do this by presenting evidence that the red shrimp are, in fact, more likely to get eaten than shrimp with undecorated shells.

- The way you cite your sources will vary depending on the citation style you're using. Typically, you'll need to include the name of the author, the title and publication date of the source, and location information such as the page number on which the information appears.
- In general, you don't need to cite common knowledge. For example, if you say, “A zebra is a type of mammal,” you probably won't need to cite a source.
- If you've cited any sources in the essay, you'll need to include a list of works cited (or a bibliography ) at the end.

- Keep your conclusion brief. While the appropriate length will vary based on the length of the essay, it should typically be no longer than 1-2 paragraphs.
- For example, if you're writing a 1,000-word essay, your conclusion should be about 4-5 sentences long. [16] X Research source
Revising the Essay

- If you don't have time to spend a couple of days away from your essay, at least take a few hours to relax or work on something else.

- Excessive wordiness
- Points that aren't explained enough
- Tangents or unnecessary information
- Unclear transitions or illogical organization
- Spelling , grammar , style, and formatting problems
- Inappropriate language or tone (e.g., slang or informal language in an academic essay)

- You might have to cut material from your essay in some places and add new material to others.
- You might also end up reordering some of the content of the essay if you think that helps it flow better.

- Read over each line slowly and carefully. It may be helpful to read each sentence out loud to yourself.
Tip: If possible, have someone else check your work. When you've been looking at your writing for too long, your brain begins to fill in what it expects to see rather than what's there, making it harder for you to spot mistakes.

Expert Q&A

Reader Videos
Share a quick video tip and help bring articles to life with your friendly advice. Your insights could make a real difference and help millions of people!
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.yourdictionary.com/articles/essay-types
- ↑ https://students.unimelb.edu.au/academic-skills/resources/essay-writing/six-top-tips-for-writing-a-great-essay
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/common_writing_assignments/research_papers/choosing_a_topic.html
- ↑ https://writingcenter.fas.harvard.edu/tips-reading-assignment-prompt
- ↑ https://library.unr.edu/help/quick-how-tos/writing/integrating-sources-into-your-paper
- ↑ https://advice.writing.utoronto.ca/researching/notes-from-research/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.fas.harvard.edu/pages/developing-thesis
- ↑ https://writingcenter.fas.harvard.edu/pages/outlining
- ↑ https://lsa.umich.edu/sweetland/undergraduates/writing-guides/how-do-i-write-an-intro--conclusion----body-paragraph.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/academic_writing/essay_writing/argumentative_essays.html
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/transitions/
- ↑ https://lsa.umich.edu/sweetland/undergraduates/writing-guides/how-do-i-incorporate-a-counter-argument.html
- ↑ https://www.plagiarism.org/article/how-do-i-cite-sources
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/conclusions/
- ↑ https://www.utsc.utoronto.ca/twc/sites/utsc.utoronto.ca.twc/files/resource-files/Intros-Conclusions.pdf
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/the_writing_process/proofreading/steps_for_revising.html
- ↑ https://open.lib.umn.edu/writingforsuccess/chapter/8-4-revising-and-editing/
- ↑ https://writing.ku.edu/writing-process
About This Article

If you need to write an essay, start by gathering information from reputable sources, like books from the library or scholarly journals online. Take detailed notes and keep track of which facts come from which sources. As you're taking notes, look for a central theme that you're interested in writing about to create your thesis statement. Then, organize your notes into an outline that supports and explains your thesis statement. Working from your outline, write an introduction and subsequent paragraphs to address each major point. Start every paragraph with a topic sentence that briefly explains the main point of that paragraph. Finally, finish your paper with a strong conclusion that sums up the most important points. For tips from our English Professor co-author on helpful revision techniques, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Muhammad Talha Javaid
Feb 7, 2019
Did this article help you?
Gabrielle Mattijetz
May 8, 2017
Shahzad Saleem
Jun 20, 2018
Barbara Gonzalez
Aug 6, 2016
Kniziel Sanders
Oct 17, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve

- Ask LitCharts AI
- Discussion Question Generator
- Essay Prompt Generator
- Quiz Question Generator

- Literature Guides
- Poetry Guides
- Shakespeare Translations
- Literary Terms
How to Write an Essay
Use the links below to jump directly to any section of this guide:
Essay Writing Fundamentals
How to prepare to write an essay, how to edit an essay, how to share and publish your essays, how to get essay writing help, how to find essay writing inspiration, resources for teaching essay writing.
Essays, short prose compositions on a particular theme or topic, are the bread and butter of academic life. You write them in class, for homework, and on standardized tests to show what you know. Unlike other kinds of academic writing (like the research paper) and creative writing (like short stories and poems), essays allow you to develop your original thoughts on a prompt or question. Essays come in many varieties: they can be expository (fleshing out an idea or claim), descriptive, (explaining a person, place, or thing), narrative (relating a personal experience), or persuasive (attempting to win over a reader). This guide is a collection of dozens of links about academic essay writing that we have researched, categorized, and annotated in order to help you improve your essay writing.
Essays are different from other forms of writing; in turn, there are different kinds of essays. This section contains general resources for getting to know the essay and its variants. These resources introduce and define the essay as a genre, and will teach you what to expect from essay-based assessments.
Purdue OWL Online Writing Lab
One of the most trusted academic writing sites, Purdue OWL provides a concise introduction to the four most common types of academic essays.
"The Essay: History and Definition" (ThoughtCo)
This snappy article from ThoughtCo talks about the origins of the essay and different kinds of essays you might be asked to write.
"What Is An Essay?" Video Lecture (Coursera)
The University of California at Irvine's free video lecture, available on Coursera, tells you everything you need to know about the essay.
Wikipedia Article on the "Essay"
Wikipedia's article on the essay is comprehensive, providing both English-language and global perspectives on the essay form. Learn about the essay's history, forms, and styles.
"Understanding College and Academic Writing" (Aims Online Writing Lab)
This list of common academic writing assignments (including types of essay prompts) will help you know what to expect from essay-based assessments.
Before you start writing your essay, you need to figure out who you're writing for (audience), what you're writing about (topic/theme), and what you're going to say (argument and thesis). This section contains links to handouts, chapters, videos and more to help you prepare to write an essay.
How to Identify Your Audience
"Audience" (Univ. of North Carolina Writing Center)
This handout provides questions you can ask yourself to determine the audience for an academic writing assignment. It also suggests strategies for fitting your paper to your intended audience.
"Purpose, Audience, Tone, and Content" (Univ. of Minnesota Libraries)
This extensive book chapter from Writing for Success , available online through Minnesota Libraries Publishing, is followed by exercises to try out your new pre-writing skills.
"Determining Audience" (Aims Online Writing Lab)
This guide from a community college's writing center shows you how to know your audience, and how to incorporate that knowledge in your thesis statement.
"Know Your Audience" ( Paper Rater Blog)
This short blog post uses examples to show how implied audiences for essays differ. It reminds you to think of your instructor as an observer, who will know only the information you pass along.
How to Choose a Theme or Topic
"Research Tutorial: Developing Your Topic" (YouTube)
Take a look at this short video tutorial from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill to understand the basics of developing a writing topic.
"How to Choose a Paper Topic" (WikiHow)
This simple, step-by-step guide (with pictures!) walks you through choosing a paper topic. It starts with a detailed description of brainstorming and ends with strategies to refine your broad topic.
"How to Read an Assignment: Moving From Assignment to Topic" (Harvard College Writing Center)
Did your teacher give you a prompt or other instructions? This guide helps you understand the relationship between an essay assignment and your essay's topic.
"Guidelines for Choosing a Topic" (CliffsNotes)
This study guide from CliffsNotes both discusses how to choose a topic and makes a useful distinction between "topic" and "thesis."
How to Come Up with an Argument
"Argument" (Univ. of North Carolina Writing Center)
Not sure what "argument" means in the context of academic writing? This page from the University of North Carolina is a good place to start.
"The Essay Guide: Finding an Argument" (Study Hub)
This handout explains why it's important to have an argument when beginning your essay, and provides tools to help you choose a viable argument.
"Writing a Thesis and Making an Argument" (University of Iowa)
This page from the University of Iowa's Writing Center contains exercises through which you can develop and refine your argument and thesis statement.
"Developing a Thesis" (Harvard College Writing Center)
This page from Harvard's Writing Center collates some helpful dos and don'ts of argumentative writing, from steps in constructing a thesis to avoiding vague and confrontational thesis statements.
"Suggestions for Developing Argumentative Essays" (Berkeley Student Learning Center)
This page offers concrete suggestions for each stage of the essay writing process, from topic selection to drafting and editing.
How to Outline your Essay
"Outlines" (Univ. of North Carolina at Chapel Hill via YouTube)
This short video tutorial from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill shows how to group your ideas into paragraphs or sections to begin the outlining process.
"Essay Outline" (Univ. of Washington Tacoma)
This two-page handout by a university professor simply defines the parts of an essay and then organizes them into an example outline.
"Types of Outlines and Samples" (Purdue OWL Online Writing Lab)
Purdue OWL gives examples of diverse outline strategies on this page, including the alphanumeric, full sentence, and decimal styles.
"Outlining" (Harvard College Writing Center)
Once you have an argument, according to this handout, there are only three steps in the outline process: generalizing, ordering, and putting it all together. Then you're ready to write!
"Writing Essays" (Plymouth Univ.)
This packet, part of Plymouth University's Learning Development series, contains descriptions and diagrams relating to the outlining process.
"How to Write A Good Argumentative Essay: Logical Structure" (Criticalthinkingtutorials.com via YouTube)
This longer video tutorial gives an overview of how to structure your essay in order to support your argument or thesis. It is part of a longer course on academic writing hosted on Udemy.
Now that you've chosen and refined your topic and created an outline, use these resources to complete the writing process. Most essays contain introductions (which articulate your thesis statement), body paragraphs, and conclusions. Transitions facilitate the flow from one paragraph to the next so that support for your thesis builds throughout the essay. Sources and citations show where you got the evidence to support your thesis, which ensures that you avoid plagiarism.
How to Write an Introduction
"Introductions" (Univ. of North Carolina Writing Center)
This page identifies the role of the introduction in any successful paper, suggests strategies for writing introductions, and warns against less effective introductions.
"How to Write A Good Introduction" (Michigan State Writing Center)
Beginning with the most common missteps in writing introductions, this guide condenses the essentials of introduction composition into seven points.
"The Introductory Paragraph" (ThoughtCo)
This blog post from academic advisor and college enrollment counselor Grace Fleming focuses on ways to grab your reader's attention at the beginning of your essay.
"Introductions and Conclusions" (Univ. of Toronto)
This guide from the University of Toronto gives advice that applies to writing both introductions and conclusions, including dos and don'ts.
"How to Write Better Essays: No One Does Introductions Properly" ( The Guardian )
This news article interviews UK professors on student essay writing; they point to introductions as the area that needs the most improvement.
How to Write a Thesis Statement
"Writing an Effective Thesis Statement" (YouTube)
This short, simple video tutorial from a college composition instructor at Tulsa Community College explains what a thesis statement is and what it does.
"Thesis Statement: Four Steps to a Great Essay" (YouTube)
This fantastic tutorial walks you through drafting a thesis, using an essay prompt on Nathaniel Hawthorne's The Scarlet Letter as an example.
"How to Write a Thesis Statement" (WikiHow)
This step-by-step guide (with pictures!) walks you through coming up with, writing, and editing a thesis statement. It invites you think of your statement as a "working thesis" that can change.
"How to Write a Thesis Statement" (Univ. of Indiana Bloomington)
Ask yourself the questions on this page, part of Indiana Bloomington's Writing Tutorial Services, when you're writing and refining your thesis statement.
"Writing Tips: Thesis Statements" (Univ. of Illinois Center for Writing Studies)
This page gives plentiful examples of good to great thesis statements, and offers questions to ask yourself when formulating a thesis statement.
How to Write Body Paragraphs
"Body Paragraph" (Brightstorm)
This module of a free online course introduces you to the components of a body paragraph. These include the topic sentence, information, evidence, and analysis.
"Strong Body Paragraphs" (Washington Univ.)
This handout from Washington's Writing and Research Center offers in-depth descriptions of the parts of a successful body paragraph.
"Guide to Paragraph Structure" (Deakin Univ.)
This handout is notable for color-coding example body paragraphs to help you identify the functions various sentences perform.
"Writing Body Paragraphs" (Univ. of Minnesota Libraries)
The exercises in this section of Writing for Success will help you practice writing good body paragraphs. It includes guidance on selecting primary support for your thesis.
"The Writing Process—Body Paragraphs" (Aims Online Writing Lab)
The information and exercises on this page will familiarize you with outlining and writing body paragraphs, and includes links to more information on topic sentences and transitions.
"The Five-Paragraph Essay" (ThoughtCo)
This blog post discusses body paragraphs in the context of one of the most common academic essay types in secondary schools.
How to Use Transitions
"Transitions" (Univ. of North Carolina Writing Center)
This page from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill explains what a transition is, and how to know if you need to improve your transitions.
"Using Transitions Effectively" (Washington Univ.)
This handout defines transitions, offers tips for using them, and contains a useful list of common transitional words and phrases grouped by function.
"Transitions" (Aims Online Writing Lab)
This page compares paragraphs without transitions to paragraphs with transitions, and in doing so shows how important these connective words and phrases are.
"Transitions in Academic Essays" (Scribbr)
This page lists four techniques that will help you make sure your reader follows your train of thought, including grouping similar information and using transition words.
"Transitions" (El Paso Community College)
This handout shows example transitions within paragraphs for context, and explains how transitions improve your essay's flow and voice.
"Make Your Paragraphs Flow to Improve Writing" (ThoughtCo)
This blog post, another from academic advisor and college enrollment counselor Grace Fleming, talks about transitions and other strategies to improve your essay's overall flow.
"Transition Words" (smartwords.org)
This handy word bank will help you find transition words when you're feeling stuck. It's grouped by the transition's function, whether that is to show agreement, opposition, condition, or consequence.
How to Write a Conclusion
"Parts of An Essay: Conclusions" (Brightstorm)
This module of a free online course explains how to conclude an academic essay. It suggests thinking about the "3Rs": return to hook, restate your thesis, and relate to the reader.
"Essay Conclusions" (Univ. of Maryland University College)
This overview of the academic essay conclusion contains helpful examples and links to further resources for writing good conclusions.
"How to End An Essay" (WikiHow)
This step-by-step guide (with pictures!) by an English Ph.D. walks you through writing a conclusion, from brainstorming to ending with a flourish.
"Ending the Essay: Conclusions" (Harvard College Writing Center)
This page collates useful strategies for writing an effective conclusion, and reminds you to "close the discussion without closing it off" to further conversation.
How to Include Sources and Citations
"Research and Citation Resources" (Purdue OWL Online Writing Lab)
Purdue OWL streamlines information about the three most common referencing styles (MLA, Chicago, and APA) and provides examples of how to cite different resources in each system.
EasyBib: Free Bibliography Generator
This online tool allows you to input information about your source and automatically generate citations in any style. Be sure to select your resource type before clicking the "cite it" button.
CitationMachine
Like EasyBib, this online tool allows you to input information about your source and automatically generate citations in any style.
Modern Language Association Handbook (MLA)
Here, you'll find the definitive and up-to-date record of MLA referencing rules. Order through the link above, or check to see if your library has a copy.
Chicago Manual of Style
Here, you'll find the definitive and up-to-date record of Chicago referencing rules. You can take a look at the table of contents, then choose to subscribe or start a free trial.
How to Avoid Plagiarism
"What is Plagiarism?" (plagiarism.org)
This nonprofit website contains numerous resources for identifying and avoiding plagiarism, and reminds you that even common activities like copying images from another website to your own site may constitute plagiarism.
"Plagiarism" (University of Oxford)
This interactive page from the University of Oxford helps you check for plagiarism in your work, making it clear how to avoid citing another person's work without full acknowledgement.
"Avoiding Plagiarism" (MIT Comparative Media Studies)
This quick guide explains what plagiarism is, what its consequences are, and how to avoid it. It starts by defining three words—quotation, paraphrase, and summary—that all constitute citation.
"Harvard Guide to Using Sources" (Harvard Extension School)
This comprehensive website from Harvard brings together articles, videos, and handouts about referencing, citation, and plagiarism.
Grammarly contains tons of helpful grammar and writing resources, including a free tool to automatically scan your essay to check for close affinities to published work.
Noplag is another popular online tool that automatically scans your essay to check for signs of plagiarism. Simply copy and paste your essay into the box and click "start checking."
Once you've written your essay, you'll want to edit (improve content), proofread (check for spelling and grammar mistakes), and finalize your work until you're ready to hand it in. This section brings together tips and resources for navigating the editing process.
"Writing a First Draft" (Academic Help)
This is an introduction to the drafting process from the site Academic Help, with tips for getting your ideas on paper before editing begins.
"Editing and Proofreading" (Univ. of North Carolina Writing Center)
This page provides general strategies for revising your writing. They've intentionally left seven errors in the handout, to give you practice in spotting them.
"How to Proofread Effectively" (ThoughtCo)
This article from ThoughtCo, along with those linked at the bottom, help describe common mistakes to check for when proofreading.
"7 Simple Edits That Make Your Writing 100% More Powerful" (SmartBlogger)
This blog post emphasizes the importance of powerful, concise language, and reminds you that even your personal writing heroes create clunky first drafts.
"Editing Tips for Effective Writing" (Univ. of Pennsylvania)
On this page from Penn's International Relations department, you'll find tips for effective prose, errors to watch out for, and reminders about formatting.
"Editing the Essay" (Harvard College Writing Center)
This article, the first of two parts, gives you applicable strategies for the editing process. It suggests reading your essay aloud, removing any jargon, and being unafraid to remove even "dazzling" sentences that don't belong.
"Guide to Editing and Proofreading" (Oxford Learning Institute)
This handout from Oxford covers the basics of editing and proofreading, and reminds you that neither task should be rushed.
In addition to plagiarism-checkers, Grammarly has a plug-in for your web browser that checks your writing for common mistakes.
After you've prepared, written, and edited your essay, you might want to share it outside the classroom. This section alerts you to print and web opportunities to share your essays with the wider world, from online writing communities and blogs to published journals geared toward young writers.
Sharing Your Essays Online
Go Teen Writers
Go Teen Writers is an online community for writers aged 13 - 19. It was founded by Stephanie Morrill, an author of contemporary young adult novels.
Tumblr is a blogging website where you can share your writing and interact with other writers online. It's easy to add photos, links, audio, and video components.
Writersky provides an online platform for publishing and reading other youth writers' work. Its current content is mostly devoted to fiction.
Publishing Your Essays Online
This teen literary journal publishes in print, on the web, and (more frequently), on a blog. It is committed to ensuring that "teens see their authentic experience reflected on its pages."
The Matador Review
This youth writing platform celebrates "alternative," unconventional writing. The link above will take you directly to the site's "submissions" page.
Teen Ink has a website, monthly newsprint magazine, and quarterly poetry magazine promoting the work of young writers.
The largest online reading platform, Wattpad enables you to publish your work and read others' work. Its inline commenting feature allows you to share thoughts as you read along.
Publishing Your Essays in Print
Canvas Teen Literary Journal
This quarterly literary magazine is published for young writers by young writers. They accept many kinds of writing, including essays.
The Claremont Review
This biannual international magazine, first published in 1992, publishes poetry, essays, and short stories from writers aged 13 - 19.
Skipping Stones
This young writers magazine, founded in 1988, celebrates themes relating to ecological and cultural diversity. It publishes poems, photos, articles, and stories.
The Telling Room
This nonprofit writing center based in Maine publishes children's work on their website and in book form. The link above directs you to the site's submissions page.
Essay Contests
Scholastic Arts and Writing Awards
This prestigious international writing contest for students in grades 7 - 12 has been committed to "supporting the future of creativity since 1923."
Society of Professional Journalists High School Essay Contest
An annual essay contest on the theme of journalism and media, the Society of Professional Journalists High School Essay Contest awards scholarships up to $1,000.
National YoungArts Foundation
Here, you'll find information on a government-sponsored writing competition for writers aged 15 - 18. The foundation welcomes submissions of creative nonfiction, novels, scripts, poetry, short story and spoken word.
Signet Classics Student Scholarship Essay Contest
With prompts on a different literary work each year, this competition from Signet Classics awards college scholarships up to $1,000.
"The Ultimate Guide to High School Essay Contests" (CollegeVine)
See this handy guide from CollegeVine for a list of more competitions you can enter with your academic essay, from the National Council of Teachers of English Achievement Awards to the National High School Essay Contest by the U.S. Institute of Peace.
Whether you're struggling to write academic essays or you think you're a pro, there are workshops and online tools that can help you become an even better writer. Even the most seasoned writers encounter writer's block, so be proactive and look through our curated list of resources to combat this common frustration.
Online Essay-writing Classes and Workshops
"Getting Started with Essay Writing" (Coursera)
Coursera offers lots of free, high-quality online classes taught by college professors. Here's one example, taught by instructors from the University of California Irvine.
"Writing and English" (Brightstorm)
Brightstorm's free video lectures are easy to navigate by topic. This unit on the parts of an essay features content on the essay hook, thesis, supporting evidence, and more.
"How to Write an Essay" (EdX)
EdX is another open online university course website with several two- to five-week courses on the essay. This one is geared toward English language learners.
Writer's Digest University
This renowned writers' website offers online workshops and interactive tutorials. The courses offered cover everything from how to get started through how to get published.
Writing.com
Signing up for this online writer's community gives you access to helpful resources as well as an international community of writers.
How to Overcome Writer's Block
"Symptoms and Cures for Writer's Block" (Purdue OWL)
Purdue OWL offers a list of signs you might have writer's block, along with ways to overcome it. Consider trying out some "invention strategies" or ways to curb writing anxiety.
"Overcoming Writer's Block: Three Tips" ( The Guardian )
These tips, geared toward academic writing specifically, are practical and effective. The authors advocate setting realistic goals, creating dedicated writing time, and participating in social writing.
"Writing Tips: Strategies for Overcoming Writer's Block" (Univ. of Illinois)
This page from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign's Center for Writing Studies acquaints you with strategies that do and do not work to overcome writer's block.
"Writer's Block" (Univ. of Toronto)
Ask yourself the questions on this page; if the answer is "yes," try out some of the article's strategies. Each question is accompanied by at least two possible solutions.
If you have essays to write but are short on ideas, this section's links to prompts, example student essays, and celebrated essays by professional writers might help. You'll find writing prompts from a variety of sources, student essays to inspire you, and a number of essay writing collections.
Essay Writing Prompts
"50 Argumentative Essay Topics" (ThoughtCo)
Take a look at this list and the others ThoughtCo has curated for different kinds of essays. As the author notes, "a number of these topics are controversial and that's the point."
"401 Prompts for Argumentative Writing" ( New York Times )
This list (and the linked lists to persuasive and narrative writing prompts), besides being impressive in length, is put together by actual high school English teachers.
"SAT Sample Essay Prompts" (College Board)
If you're a student in the U.S., your classroom essay prompts are likely modeled on the prompts in U.S. college entrance exams. Take a look at these official examples from the SAT.
"Popular College Application Essay Topics" (Princeton Review)
This page from the Princeton Review dissects recent Common Application essay topics and discusses strategies for answering them.
Example Student Essays
"501 Writing Prompts" (DePaul Univ.)
This nearly 200-page packet, compiled by the LearningExpress Skill Builder in Focus Writing Team, is stuffed with writing prompts, example essays, and commentary.
"Topics in English" (Kibin)
Kibin is a for-pay essay help website, but its example essays (organized by topic) are available for free. You'll find essays on everything from A Christmas Carol to perseverance.
"Student Writing Models" (Thoughtful Learning)
Thoughtful Learning, a website that offers a variety of teaching materials, provides sample student essays on various topics and organizes them by grade level.
"Five-Paragraph Essay" (ThoughtCo)
In this blog post by a former professor of English and rhetoric, ThoughtCo brings together examples of five-paragraph essays and commentary on the form.
The Best Essay Writing Collections
The Best American Essays of the Century by Joyce Carol Oates (Amazon)
This collection of American essays spanning the twentieth century was compiled by award winning author and Princeton professor Joyce Carol Oates.
The Best American Essays 2017 by Leslie Jamison (Amazon)
Leslie Jamison, the celebrated author of essay collection The Empathy Exams , collects recent, high-profile essays into a single volume.
The Art of the Personal Essay by Phillip Lopate (Amazon)
Documentary writer Phillip Lopate curates this historical overview of the personal essay's development, from the classical era to the present.
The White Album by Joan Didion (Amazon)
This seminal essay collection was authored by one of the most acclaimed personal essayists of all time, American journalist Joan Didion.
Consider the Lobster by David Foster Wallace (Amazon)
Read this famous essay collection by David Foster Wallace, who is known for his experimentation with the essay form. He pushed the boundaries of personal essay, reportage, and political polemic.
"50 Successful Harvard Application Essays" (Staff of the The Harvard Crimson )
If you're looking for examples of exceptional college application essays, this volume from Harvard's daily student newspaper is one of the best collections on the market.
Are you an instructor looking for the best resources for teaching essay writing? This section contains resources for developing in-class activities and student homework assignments. You'll find content from both well-known university writing centers and online writing labs.
Essay Writing Classroom Activities for Students
"In-class Writing Exercises" (Univ. of North Carolina Writing Center)
This page lists exercises related to brainstorming, organizing, drafting, and revising. It also contains suggestions for how to implement the suggested exercises.
"Teaching with Writing" (Univ. of Minnesota Center for Writing)
Instructions and encouragement for using "freewriting," one-minute papers, logbooks, and other write-to-learn activities in the classroom can be found here.
"Writing Worksheets" (Berkeley Student Learning Center)
Berkeley offers this bank of writing worksheets to use in class. They are nested under headings for "Prewriting," "Revision," "Research Papers" and more.
"Using Sources and Avoiding Plagiarism" (DePaul University)
Use these activities and worksheets from DePaul's Teaching Commons when instructing students on proper academic citation practices.
Essay Writing Homework Activities for Students
"Grammar and Punctuation Exercises" (Aims Online Writing Lab)
These five interactive online activities allow students to practice editing and proofreading. They'll hone their skills in correcting comma splices and run-ons, identifying fragments, using correct pronoun agreement, and comma usage.
"Student Interactives" (Read Write Think)
Read Write Think hosts interactive tools, games, and videos for developing writing skills. They can practice organizing and summarizing, writing poetry, and developing lines of inquiry and analysis.
This free website offers writing and grammar activities for all grade levels. The lessons are designed to be used both for large classes and smaller groups.
"Writing Activities and Lessons for Every Grade" (Education World)
Education World's page on writing activities and lessons links you to more free, online resources for learning how to "W.R.I.T.E.": write, revise, inform, think, and edit.
- PDFs for all 136 Lit Terms we cover
- Downloads of 2003 LitCharts Lit Guides
- Teacher Editions for every Lit Guide
- Explanations and citation info for 42,322 quotes across 2003 books
- Downloadable (PDF) line-by-line translations of every Shakespeare play
Need something? Request a new guide .
How can we improve? Share feedback .
LitCharts is hiring!

- Quizzes, saving guides, requests, plus so much more.
The Five Steps of Writing an Essay
Mastering these steps will make your words more compelling
- Tips For Adult Students
- Getting Your Ged
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Deb-Nov2015-5895870e3df78caebc88766f.jpg)
- B.A., English, St. Olaf College
Knowing how to write an essay is a skill that you can use throughout your life. The ability to organize ideas that you use in constructing an essay will help you write business letters, company memos, and marketing materials for your clubs and organizations.
Anything you write will benefit from learning these simple parts of an essay:
- Purpose and Thesis
Introduction
Body of information.
Here are five steps to make it happen:
Purpose/Main Idea
Echo / Cultura / Getty Images
Before you can start writing, you must have an idea to write about. If you haven't been assigned a topic, it's easier than you might think to come up with one of your own.
Your best essays will be about things that light your fire. What do you feel passionate about? What topics do you find yourself arguing for or against? Choose the side of the topic you are "for" rather than "against" and your essay will be stronger.
Do you love gardening? Sports? Photography? Volunteering? Are you an advocate for children? Domestic peace? The hungry or homeless? These are clues to your best essays.
Put your idea into a single sentence. This is your thesis statement , your main idea.
STOCK4B-RF / Getty Images
Choose a title for your essay that expresses your primary idea. The strongest titles will include a verb. Take a look at any newspaper and you'll see that every title has a verb.
Your title should make someone want to read what you have to say. Make it provocative.
Here are a few ideas:
- America Needs Better Health Care Now
- The Use of the Mentor Archetype in _____
- Who Is the She-Conomy?
- Why DJ Is the Queen of Pedicures
- Melanoma: Is It or Isn't It?
- How to Achieve Natural Balance in Your Garden
- Expect to Be Changed by Reading _____
Some people will tell you to wait until you have finished writing to choose a title. Other people find that writing a title helps them stay focused. You can always review your title when you've finished the essay to ensure that it's as effective as it can be.
Hero-Images / Getty Images
Your introduction is one short paragraph, just a sentence or two, that states your thesis (your main idea) and introduces your reader to your topic. After your title, this is your next best chance to hook your reader. Here are some examples:
- Women are the chief buyers in 80 percent of America's households. If you're not marketing to them, you should be.
- Take another look at that spot on your arm. Is the shape irregular? Is it multicolored? You could have melanoma. Know the signs.
- Those tiny wasps flying around the blossoms in your garden can't sting you. Their stingers have evolved into egg-laying devices. The wasps, busying finding a place to lay their eggs, are participating in the balance of nature.
Vincent Hazat / PhotoAlto Agency RF Collections / Getty Images
The body of your essay is where you develop your story or argument. Once you have finished your research and produced several pages of notes, go through them with a highlighter and mark the most important ideas, the key points.
Choose the top three ideas and write each one at the top of a clean page. Now go through your notes again and pull out supporting ideas for each key point. You don't need a lot, just two or three for each one.
Write a paragraph about each of these key points, using the information you've pulled from your notes. If you don't have enough for one, you might need a stronger key point. Do more research to support your point of view. It's always better to have too many sources than too few.
Anna Bryukhanova/E Plus / Getty Images
You've almost finished. The last paragraph of your essay is your conclusion. It, too, can be short, and it must tie back to your introduction.
In your introduction, you stated the reason for your paper. In your conclusion, you should summarize how your key points support your thesis. Here's an example:
- By observing the balance of nature in her gardens, listening to lectures, and reading everything she can get her hands on about insects and native plants, Lucinda has grown passionate about natural balance. "It's easy to get passionate if you just take time to look," she says.
If you're still worried about your essay after trying on your own, consider hiring an essay editing service. Reputable services will edit your work, not rewrite it. Choose carefully. One service to consider is Essay Edge .
Good luck! The next essay will be easier.
- 6 Steps to Writing the Perfect Personal Essay
- How to Write a Research Paper That Earns an A
- Reach Your Goals With a Personal Development Plan
- 10 Writing Ideas Concerning Women
- Writing SMART Goals
- Writing Practice Tests While You Study
- How to Practice Critical Thinking in 4 Steps
- 5 Time Management Tips for Busy Students
- How to Write a Learning Contract and Realize Your Goals
- The Secret Power of Your Mind to Become What You Think
- 5 Ways to Improve Adult Literacy
- A Step-By-Step Guide to Resolving Conflicts Peacefully
- How to Prepare for Online Classes
- How to Read Faster
- How to Be a Good Listener
- 5 Things That Make It Easier to Go Back to School as an Adult
Make Your Essay Structure Rock-Solid with These Tips

So you’ve been assigned an essay. Or, probably more realistically, two, three, or four essays . . . and they’re all due the same week.
We’ve all been there: overwhelmed, staring down that blank screen, and not sure which essay to start with or how to get it started.
In high school and college, it’s not enough to just write strong essays. One of the most important skills to develop is writing strong essays efficiently . And the foundation of that skill is knowing how to structure an essay. With a template for the basic essay structure in hand, you can focus on what really matters when you’re writing essays: your arguments and the evidence you’re using to support them. Take a look at the basic essay structure below and see how the parts of an essay work together to present a coherent, well-reasoned position, no matter what topic you’re writing about.
Make your essays shine. Polish your writing with Grammarly Write with Grammarly
Basic essay structure: the 3 main parts of an essay
Almost every single essay that’s ever been written follows the same basic structure:
Introduction
Body paragraphs.
This structure has stood the test of time for one simple reason: It works. It clearly presents the writer’s position, supports that position with relevant examples, and neatly ties their supporting arguments together in a way that makes their position evident.
It all starts here. This is where you introduce the topic you’re discussing in your essay and briefly summarize the points you’ll make in the paragraphs that follow.
This is also where you state your thesis. Your thesis is the most important part of your essay because it’s the point you’re making . It needs to take a clear stance and shouldn’t include hedging language that undermines that stance like “seems to” or “possibly could.”
Here are a few examples of thesis statements:
- In the final scene of The Awakening , Edna Pontellier’s decision demonstrates that it was impossible for her to have the lifestyle she truly wanted in the society in which she lived.
- Due to its volatility and lack of government regulation, Bitcoin cannot become a viable currency for everyday purchases.
- While the habitability of Mars has not yet been proven, evidence suggests that it was once possible due to bacteria samples found on the Red Planet.
An easy way to write your thesis statement is to think of it as a summary of your essay. Your thesis makes and supports your essay’s point in one concise sentence.
When you proofread your finished essay, make sure your thesis is clearly stated in your introduction paragraph. If it’s not clear, go back and write a definitive thesis statement.
>>Read More: How to Write a Persuasive Essay
Your essay’s body paragraphs are where you support your thesis statement with facts and evidence. Each body paragraph should focus on one supporting argument for your thesis by discussing related data, content, or events.
If you’re not sure whether you should include a specific point or detail in your body paragraphs, refer back to your thesis statement. If the detail supports your thesis, it should be in your essay. If it doesn’t, leave it out. Your thesis statement is the core of your basic essay structure, so everything else in the essay needs to relate to it in some way.
In your essay’s conclusion paragraph , you summarize the points you made and bring your argument to its logical conclusion. Because your reader is now familiar with your thesis, the summary in your conclusion paragraph can be more direct and conclusive than the one in your intro paragraph.
>>Read More: 7 Writing Tips from Professors to Help you Crush your First Essays
How many paragraphs are in an essay?
There’s no hard-and-fast requirement for college essays. In high school, you were probably taught to write five-paragraph essays. This is a solid essay structure to work with, but in college, you generally have more flexibility with assignment lengths and formats.
Now, consider five the minimum—not the standard—number of paragraphs you should include in your essays.
Essay structure examples
There are a few different ways to present information in an essay. Often, your assignment will tell you what kind of essay to write, such as a chronological, compare and contrast, or problems-methods-solution essay. If you’re not sure which is best for your assignment, ask your instructor.
Chronological
A chronological essay guides the reader through a series of events. This essay structure is ideal if you’re writing about:
- A current or historical event
- A book or article you read for class
- A process or procedure
With this kind of essay, you first introduce your topic and summarize the series of events in your introduction paragraph. Then, each body paragraph takes the reader through a key stage in that series, which might be a decisive battle in history, a pivotal scene in a novel, or a critical stage in a judicial process. In your conclusion, you present the end result of the series you discussed, underscoring your thesis with this result.
Compare and contrast
A compare-and-contrast essay has a structure that discusses multiple subjects, like several novels, concepts, or essays you’ve been assigned to read.
There are a few different ways to structure a compare-and-contrast essay. The most obvious is to spend one paragraph discussing the similarities between the topics you’re covering (comparing), then one paragraph detailing their differences (contrasting), followed by a paragraph that explores whether they’re more alike or more different from each other.
Another method is to only compare, where each of your body paragraphs discusses a similarity between the topics at hand. Or you can go the only-contrast route, where your body paragraphs explore the differences. Whichever you decide on, make sure each paragraph is focused on one topic sentence . Every new comparison or contrast should occupy its own paragraph.
Problems-methods-solution
As its name implies, this kind of essay structure presents the writer’s position in three segments:
- Ways to resolve the problem
- The solution achieved by using these strategies to resolve the problem
This kind of essay works great if you’re discussing methods for resolving a problem, like knowing how to distinguish between credible and non-credible sources when you’re doing research for assignments. It can also work when you’re tasked with explaining why certain solutions haven’t worked to fix the problems they were created for.
With this kind of essay, begin by introducing the problem at hand. In the subsequent body paragraphs, cover possible methods for resolving the problem, discussing how each is suited to fixing the problem, and potential challenges that can arise with each. You can certainly state which you think is the best choice—that could even be your thesis statement. In your conclusion paragraph, summarize the problem again and the desired resolution, endorsing your method of choice (if you have one).
In this kind of essay, you can also include a call to action in your final paragraph. A call to action is a direct order for the reader to take a specific action, like “call your congressperson today and tell them to vote no” or “visit grammarly.com today to add Grammarly browser extension for free.”
>>Read More: How to Write Better Essays: 5 Concepts you Must Master
With the basic essay structure down, you can get to writing
For a lot of students, getting started is the hardest part of writing an essay. Knowing how to structure an essay can get you past this seemingly insurmountable first step because it gives you a clear skeleton upon which to flesh out your thoughts. With that step conquered, you’re on your way to crushing your assignment.

How to Write an Essay: 7 Steps for Clear, Effective Writing
by Yen Cabag | 9 comments

High school students are frequently tasked with writing essays, which also play a big role in the college admissions process. But they’re not alone: professionals taking exams like the IELTS or LSATs also need to know how to write clear, concise, and persuasive essays.
Even if you don’t consider yourself a wordsmith, you don’t have to be intimidated by essays and writing assignments. When you learn the basic steps and the most common structures, you will find that it becomes easier to write down your thoughts on any given subject.
What Are the Different Types of Essays?
Essays can come in many different forms. The most common types include the following:
- Narrative Essay: The narrative essay shares information in the form of a story and from a clearly defined point of view .
- Expository Essay: This type of essay explains, illustrates, or clarifies a topic. This also includes instructional pieces with step-by-step directions.
- Descriptive Essay: Descriptive essays do exactly what their name implies: they describe an event, phenomenon, or any other subject in detail.
- Persuasive Essay: This type of essay aims to convince the audience to adapt a certain perspective or idea.
- Compare and Contrast Essay: This type of writing pinpoints how similar or different two or more things are from one another.
- Problem-Solution Essay: This essay highlights an issue, influences the reader to care about it, suggests a solution, and tackles possible objections.
How Do You Begin an Essay?
Nothing is more daunting for a writer than staring at a blank page. This is why you need to have an action plan for starting your essay.
1. Decide on your essay type and topic.
Sometimes, you will already have an assigned essay type or topic, so that will save you one step. If these were not assigned to you, you have to think of possible topics that you can write on. This will also help determine the type of essay you will be writing.
Some questions you can ask yourself to find a good topic include:
- What is something I’m passionate about?
- What is one thought or idea I want to share?
- Is there any misconception I want to correct?
- What is the best way to present this topic of information (with regard to the types of essays)?
2. Brainstorm and research the topic you’ve chosen.
Once you’ve chosen your topic, brainstorm all the different supporting ideas that you can talk about for the topic. Start with the basic facts about your idea, asking questions such as what , where , who , when , why , and how .
You can use the Mind Map method to brainstorm connecting ideas, or you can also just jot down bullet points as you encounter them in your research.
If your topic calls for it and if time allows, you may want to consider conducting quick interviews with experts on the subject. These will serve as a primary source for your essay.
3. Develop your thesis statement.
After you have brainstormed and researched, write down your thesis statement . A thesis statement consists of one or two sentences that sum up the primary subject or argument of your essay.
Generally, the thesis statement will present your main topic while also expressing what position you hold regarding the subject.
4. Write your outline.
Once you have your thesis statement, you can start to prepare your outline . Many people skip the outline process, thinking it’s a waste of time.
But really, an outline can help you organize your thoughts before you start writing and actually save you time, since you’ll avoid beating around the bush or jumping from one idea to another without a clear direction.
One common structure for an essay is the Five-Paragraph Essay, with the following parts:
- Introduction with thesis statement
- Main Point #1
- Main Point #2
- Main Point #3
- Conclusion
Although this structure is made up of five paragraphs, we can easily use the same model and make it into a Five-Part Essay Structure. This means that we will stay within the pattern, but each main point may have more than one paragraph.
When you write your outline, make sure that each paragraph has only one main point. Jumbling too many points in one paragraph tends to confuse your reader. Also, make sure that your main points are all relevant to your thesis statement.
5. Start writing.
Using your outline, you can now begin writing your essay. Some writers choose to write their paragraphs in order, beginning with the hook. The hook is the first few lines in your essay that will grab the readers’ attention.
If you can write the hook right away, well and good. If not, don’t worry, you can always come back to it after you write the body of your essay. Here are some more helpful tips for writing the body of your essay:
- Elaborate on each of your main ideas with at least one paragraph each. If your main ideas will require more than one paragraph each, feel free to write more.
- For anything point that takes up two paragraphs or more, it helps to have a brief introductory paragraph.
- Stay as concise as possible.
- Include anecdotal examples if it will help you make your point more clear.
- If you are writing a formal academic essay, avoid using first-person pronouns.
6. Pay attention to how you cite references.
In ancient Greece, using other people’s ideas was seen as the mark of a smart person. But in this day and age, plagiarism is a serious offense, so you need to be careful when citing other people’s work.
To avoid plagiarism , be sure to paraphrase any ideas you collect from your research instead of copying them word for word. If you do use them as is, put them in quotes.
Next, use the proper citations. Plagiarism does not only constitute copying the idea verbatim, but you also have to reference the source of the idea itself, if possible. Depending on your teacher’s preferences, you can use the APA in-text citation style or the MLA style .
7. Edit your work.
After you write your first draft, refine and proofread your work to make sure you fix all grammatical and spelling errors. You can use a tool like Grammarly when you do this to have fresh “eyes” looking at your work, but don’t rely solely on software—always review your work at least once yourself or have another (human) do it!
When editing, pay attention to the words you use: remove all unnecessary words and work on using strong verbs in place of weak ones.
Also, fact check all the information you have in your essay, especially when citing other sources.
Tips for Writing Essays
If you keep these tips in mind, writing an essay will soon become much easier for you and you’ll see your writing (of all kinds) start to improve.
Keep practicing and you will find that it’s much easier to get your thoughts on paper and present a coherent piece for your readers.
Did you find this post helpful? Let us know in the comments below!
If you enjoyed this post, then you might also like:
- How to Write a Thesis Statement
- How to Avoid Plagiarism: 6 Tips for Staying Out of Trouble
- How to Write a Research Paper: The Complete Guide for Students
- Grammarly Review: Is It Worth the Hype?
Yen Cabag is the Blog Writer of TCK Publishing. She is also a homeschooling mom, family coach, and speaker for the Charlotte Mason method, an educational philosophy that places great emphasis on classic literature and the masterpieces in art and music. She has also written several books, both fiction and nonfiction. Her passion is to see the next generation of children become lovers of reading and learning in the midst of short attention spans.
I found this post to be informative and very helpful
Thanks Clarise, we’re so glad you found the post helpful! :)
Thanks for the info
you’re very welcome, we hope you found it helpful! :)
It ws usefull information. Thanks a lot.
After you write your first draft, refine and proofread your work to make sure you fix all grammatical and spelling errors.
Hi Sara, yes, it’s very important to proofread and self-edit essays before submitting them :)
I really find this guidelines helpful and I appreciate it
We’re glad you found the post helpful, Fatima! :)

Learn More About
- Fiction (223)
- Nonfiction (71)
- Blogging (47)
- Book Promotion (29)
- How to Get Reviews (9)
- Audiobooks (17)
- Book Design (11)
- Ebook Publishing (13)
- Hybrid Publishing (8)
- Print Publishing (9)
- Self Publishing (70)
- Traditional Publishing (54)
- How to Find an Editor (12)
- Fitness (4)
- Mindfulness and Meditation (7)
- Miscellaneous (119)
- New Releases (17)
- Career Development (75)
- Online Courses (46)
- Productivity (47)
- Personal Finance (21)
- Podcast (179)
- Poetry Awards Contest (3)
- Publishing News (8)
- Readers Choice Awards (5)
- Reading Tips (145)
- Software (18)
- Technology (18)
- Contests (4)
- Grammar (65)
- Word Choice (68)
- Writing a Book (72)
- Writing Fiction (196)
- Writing Nonfiction (83)

How to Write a College Essay: The Ultimate Step-by-Step Guide

One way to think of your college essay is as the heart of your application—as in, it helps an admissions officer see who you are, what you value, and what you bring to their campus and community.
And before we talk you through how to write your college essay, we want to acknowledge something fairly strange about this process: namely, that this is a kind of writing that you’ve maybe never been asked to do before.
In that sense, college essays are a bizarre bait-and-switch—in high school, you’re taught a few different ways to write (e.g., maybe some historical analysis, or how to analyze literature, or creative writing), and then to apply to college, you’re asked to write something fairly different (or maybe completely different) from any of the things you’ve been asked to write in high school.
So first we’ll talk you through
the purpose of your college essay
and the degree to which it is important in your application (preview: it won’t be as important for some people as for others)
and then we’ll walk you step-by-step through how to write an essay that can help you stand out in the application process.
Let’s dive in.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Brainstorming your college essay topic, how to structure & outline a college essay, the difference between a boring and a stand-out personal statement.
- A quick word on “common” or “cliché” topics
- The “home” essay: a quick college essay case study
- Five (more) ways to find a thematic thread for your personal statement
- Montage essay structure FAQ’s
- Narrative essay structure FAQ’s
How to write a college essay: understanding what it is and how important it can be
What’s the purpose of your college essay (aka the personal statement).
This is your main essay. Your application centerpiece. The part of your application you’re likely to spend the most time on.
Assuming you’re applying via the Common App (here’s our how-to guide for that), the personal statement is likely to be 500-650 words long (so about a page) and many of the colleges you’re applying to will require it. (If you’re applying to the UCs, you’ll need to write some totally different essays .)
What’s a college essay’s purpose?
Jennifer Blask, Executive Director for International Admissions at the University of Rochester, puts it beautifully: “So much of the college application is a recounting of things past—past grades, old classes, activities the student has participated in over several years. The essay is a chance for the student to share who they are now and what they will bring to our campus communities.”
Basically, college admission officers are looking for three takeaways in your college essay:
Who is this person?
Will this person contribute something of value to our campus?
Can this person write?
If you want to dig deeper into how admissions officers are thinking during the admissions process , or into what colleges look for in students , check out those two guides.
How important is your college essay?
That really depends on a lot of factors, but two of the biggest are the schools you’re applying to, and your academic profile. Here’s one way to think of the importance of essays:
Essays are less important if
You’re applying to “selective” colleges (around a 15-50% acceptance rate) and your academic profile is stronger than other applicants’
You’re applying in-state to large colleges, and/or to less competitive programs (e.g. you live in Sacramento and are applying to UC Riverside as an English major)
Essays are more important if
You’re applying to “highly-selective” aka “highly rejective”) colleges, meaning they have a less than 15% acceptance rate
You’re applying to “selective” colleges (around a 15-50% acceptance rate) but your academic profile isn’t as strong as other applicants’
You’re applying to really competitive programs (for example, engineering and computer science at some schools have way, way more applicants than spots) and/or you’re applying out-of-state to a state school system (e.g. you live in Montana and want to go to school at the University of Washington, and/or you want to study CS at UW).
To illustrate further—CEG’s Tom Campbell, who used to be an Assistant Dean of Admissions at Pomona , puts it this way: around 80% of the applicants to Pomona in a given year when he worked there were academically admissible. Meaning at schools like Pomona (with its 7ish% acceptance rate), grades and test scores don’t really get you in—they just get your foot in the door.
And an important thing to understand on that last note: if you get rejected from the “highly rejective” schools, it will tend to have a lot more to do with things like institutional priorities —some things in this process are out of your control.
Below are the five exercises I have every student complete before I meet with them:
Essence Objects Exercise : 12 min.
Values Exercise : 4 min.
21 Details Exercise : 20 min.
Everything I Want Colleges to Know About Me Exercise : 20 min.
The Feelings and Needs Exercise : 15-20 min.
I recommend recording all the content from your exercises in one document to keep things neat. If you’ve been working as you go, you’ve already completed these, so make sure to do this step now. You can use our downloadable Google doc with these exercises if you’d like.
At the start of the essay process, I ask students two questions:
Have you faced significant challenges in your life?
Do you want to write about them?
Because here’s an important qualifier:
Even if you’ve faced challenges, you do not have to write about them in your personal statement.
I mention this now because, in my experience, many students are under the impression that they have to write about challenges—that it’s either expected, or that it’s somehow better to do so.
Neither is true. (And to be sure it’s clear: you do not have to write about trauma in your college essay to stand out .)
I’ve seen many, many incredible essays—ones that got students into every school you’re hoping to get into—that had no central challenge.
If your answer is “Maybe … ?” because you’re not sure what qualifies as a challenge, it’s useful to think of challenges as being on a spectrum.
On the weaker end of the spectrum would be things like getting a bad grade or not making X sports team. On the strong end of the spectrum would be things like escaping war. Being extremely shy but being responsible for translating for your family might be around a 3 or 4 out of 10. (Check this out if you want to read more about college essay topics to maybe avoid .)
It’s possible to use Narrative Structure to write about a challenge anywhere on the spectrum, but it’s much, much harder to write an outstanding essay about a weaker challenge.
Sometimes students pick the hardest challenge they’ve been through and try to make it sound worse than it actually was. Beware of pushing yourself to write about a challenge merely because you think these types of essays are inherently “better.” Focusing myopically on one experience can sideline other brilliant and beautiful elements of your character.
If you’re still uncertain, don’t worry. I’ll help you decide what to focus on. But, for the sake of this blog post, answer those first two questions with a gut-level response.
| 1. Challenges? | Yes/No | |
| 2. Vision for your future? | Yes/No |
In the sections that follow, I’ll introduce you to two structures: Narrative Structure, which works well for describing challenges, and Montage Structure, which works well for essays that aren’t about challenges.
Heads-up: Some students who have faced challenges find after reading that they prefer Montage Structure to Narrative Structure. Or vice versa. If you’re uncertain which approach is best for you, I generally recommend experimenting with montage first; you can always go back and play with narrative.
How to write a college essay using montage structure
A montage is, simply put, a series of moments or story events connected by a common thematic thread.
Well-known examples from movies include “training” montages, like those from Mulan , Rocky , or Footloose , or the “falling in love” montage from most romantic comedies. Or remember the opening to the Pixar movie Up ? In just a few minutes, we learn the entire history of Carl and Ellie’s relationship. One purpose is to communicate a lot of information fast. Another is to allow you to share a lot of different kinds of information, as the example essay below shows.
Narrative Structure vs. Montage Structure explained in two sentences:
In Narrative Structure, story events connect chronologically.
In Montage Structure, story events connect thematically.
Here’s a metaphor to illustrate a montage approach:
Imagine that each different part of you is a bead and that a select few will show up in your essay. They’re not the kind of beads you’d find on a store-bought bracelet; they’re more like the hand-painted beads on a bracelet your little brother made for you.
The theme of your essay is the thread that connects your beads.
You can find a thread in many, many different ways. One way we’ve seen students find great montage threads is by using the 5 Things Exercise . I’ll get detailed on this a little bit later, but essentially, are there 5 thematically connected things that thread together different experiences/moments/events in your life? For example, are there 5 T-shirts you collected, or 5 homes or identities, or 5 entries in your Happiness Spreadsheet .
And to clarify, your essay may end up using only 4 of the 5 things. Or maybe 8. But 5 is a nice number to aim for initially.
Note the huge range of possible essay threads. To illustrate, here are some different “thread” examples that have worked well:
Sports have had a powerful influence on me, from my understanding of history, to numbers, to my relationships, extracurricular activities, and even my career choice.
I lived with 5 different families as an exchange student, and each one taught me something valuable that I’ll carry with me to college.
Crassulaceae plants, which can reproduce via stem or leaf fragments, are a great analogy for not only how I make art, but how I choose to live each day.
Binary star systems are a metaphor for my relationship with my parents.
I am “trans” in so many ways … let me describe a few.
To understand who I am, you must understand how I cook.
Pranks have shaped my life in a variety of ways.
The number 12 has influenced so much in my life, from my relationship to sports, to how I write, to my self-esteem.
All of these threads stemmed from the brainstorming exercises in this post.
We’ll look at an example essay in a minute, but before we do, a word (well, a bunch of words) on how to build a stronger montage (and the basic concept here also applies to building stronger narratives).
Would you Rather watch instead?
To frame how to think about possible college essay topics ... .
Imagine you’re interviewing for a position as a fashion designer, and your interviewer asks you what qualities make you right for this position. Oh, and heads-up: That imaginary interviewer has already interviewed a hundred people today, so you’d best not roll up with, “because I’ve always loved clothes” or “because fashion helps me express my creativity.” Why shouldn’t you say those things? Because that’s what everyone says.
Many students are the same in their personal statements—they name cliché qualities/skills/values and don’t push their reflections much further.
Why is this a bad idea?
Let me frame it this way:
A boring personal statement chooses a common topic, makes common connections, and uses common language.
A stand-out personal statement chooses an un common topic, makes un common connections, and uses un common language.
Boring personal statement: I want to be a doctor (common topic) because I’m empathetic and I love helping people (common connections) and I really want to make the world a better place (common language).
Better personal statement: I want to run a tech-startup (more uncommon topic) because I value humor, “leading from the battlefield,” and stuff that makes me cry (uncommon connections for an essay on this topic), and because my journey to this place took me from being a scrawny 12-year-old kid to a scrawny 12-year-old man (uncommon language).
Important: I’m not saying you should pick a weird topic/thread just so it’ll help you stand out more on your essay. Be honest. But consider this: The more common your topic is ... the more un common your connections need to be if you want to stand out.
What do I mean?
For example, tons of students write doctor/lawyer/engineer essays; if you want to stand out, you need to say a few things that others don’t tend to say.
How do you figure out what to say? By making uncommon connections.
They’re the key to a stand-out essay.
The following two-part exercise will help you do this.
2-minute exercise: Start with the cliché version of your essay.
What would the cliché version of your essay focus on?
If you’re writing a “Why I want to be an engineer” essay, for example, what 3-5 common “engineering” values might other students have mentioned in connection with engineering? Use the Values Exercise for ideas.
Collaboration? Efficiency? Hands-on work? Probably yes to all three.
Once you’ve spent 2 minutes thinking up some common/cliché values, move onto the next step.
8-Minute Exercise: Brainstorm uncommon connections.
For example, if your thread is “food” (which can lead to great essays, but is also a really common topic), push yourself beyond the common value of “health” and strive for unexpected values. How has cooking taught you about “accountability,” for example, or “social change”? Why do this? We’ve already read the essay on how cooking helped the author become more aware of their health. An essay on how cooking allowed the author to become more accountable or socially aware would be less common.
In a minute, we’ll look at the “Laptop Stickers” essay. One thing that author discusses is activism. A typical “activist” essay might discuss public speaking or how the author learned to find their voice. A stand-out essay would go further, demonstrating, say, how a sense of humor supports activism. Perhaps it would describe a childhood community that prioritized culture-creation over culture-consumption, reflecting on how these experiences shaped the author’s political views.
And before you beg me for an “uncommon values” resource, I implore you to use your brilliant brain to dream up these connections. Plus, you aren’t looking for uncommon values in general ; you’re looking for values uncommonly associated with your topic/thread .
Don’t get me wrong ... I’m not saying you shouldn’t list any common values, since some common values may be an important part of your story! In fact, the great essay examples throughout this book sometimes make use of common connections. I’m simply encouraging you to go beyond the obvious.
Also note that a somewhat-common lesson (e.g., “I found my voice”) can still appear in a stand-out essay. But if you choose this path, you’ll likely need to use either an uncommon structure or next-level craft to create a stand-out essay.
Where can you find ideas for uncommon qualities/skills/values?
Here are four places:
1. The Values Exercise
This is basically a huge list of qualities/skills/values that could serve you in a future career.
2. O*Net Online
Go to www.onetonline.org and use the “occupation quick search” feature to search for your career. Once you do, a huge list will appear containing knowledge, skills, and abilities needed for your career. This is one of my favorite resources for this exercise.
3. School websites
Go to a college's website and click on a major or group of majors that interest you. Sometimes they’ll briefly summarize a major in terms of what skills it’ll impart or what jobs it might lead to. Students are often surprised to discover how broadly major-related skills can apply.
4. Real humans
Ask 3 people in this profession what unexpected qualities, values, or skills prepared them for their careers. Please don’t simply use their answers as your own; allow their replies to inspire your brainstorming process.
Once you’ve got a list of, say, 7-10 qualities, move on to the next step.
A quick word on “common” or “cliché” college essay topics
Common personal statement topics include extracurricular activities (sports or musical instruments), service trips to foreign countries (aka the “mission trip” essay where the author realizes their privilege), sports injuries, family illnesses, deaths, divorce, the “meta” essay (e.g., “As I sit down to write my college essays, I think about...”), or someone who inspired you (common mistake: This usually ends up being more about them than you).
While I won’t say you should never write about these topics, if you do decide to write about one of these topics, the degree of difficulty goes way up. What do I mean? Essentially, you have to be one of the best “soccer” essays or “mission trip” essays among the hundreds the admission officer has likely read (and depending on the school, maybe the hundreds they’ve read this year ). So it makes it much more difficult to stand out.
How do you stand out? A cliché is all in how you tell the story. So, if you do choose a common topic, work to make uncommon connections (i.e., offer unexpected narrative turns or connections to values), provide uncommon insights (i.e., say stuff we don’t expect you to say) or uncommon language (i.e., phrase things in a way we haven’t heard before).
Or explore a different topic. You are infinitely complex and imaginative.
Sample montage structure college essay:
My laptop stickers.
My laptop is like a passport. It is plastered with stickers all over the outside, inside, and bottom. Each sticker is a stamp, representing a place I’ve been, a passion I’ve pursued, or community I’ve belonged to. These stickers make for an untraditional first impression at a meeting or presentation, but it’s one I’m proud of. Let me take you on a quick tour: “ We <3 Design ,” bottom left corner. Art has been a constant for me for as long as I can remember. Today my primary engagement with art is through design. I’ve spent entire weekends designing websites and social media graphics for my companies. Design means more to me than just branding and marketing; it gives me the opportunity to experiment with texture, perspective, and contrast, helping me refine my professional style. “ Common Threads ,” bottom right corner. A rectangular black and red sticker displaying the theme of the 2017 TEDxYouth@Austin event. For years I’ve been interested in the street artists and musicians in downtown Austin who are so unapologetically themselves. As a result, I’ve become more open-minded and appreciative of unconventional lifestyles. TED gives me the opportunity to help other youth understand new perspectives, by exposing them to the diversity of Austin where culture is created, not just consumed. Poop emoji , middle right. My 13-year-old brother often sends his messages with the poop emoji ‘echo effect,’ so whenever I open a new message from him, hundreds of poops elegantly cascade across my screen. He brings out my goofy side, but also helps me think rationally when I am overwhelmed. We don’t have the typical “I hate you, don’t talk to me” siblinghood (although occasionally it would be nice to get away from him); we’re each other’s best friends. Or at least he’s mine. “ Lol ur not Harry Styles ,” upper left corner. Bought in seventh grade and transferred from my old laptop, this sticker is torn but persevering with layers of tape. Despite conveying my fangirl-y infatuation with Harry Styles’ boyband, One Direction, for me Styles embodies an artist-activist who uses his privilege for the betterment of society. As a $42K donor to the Time’s Up Legal Defense Fund, a hair donor to the Little Princess Trust, and promoter of LGBTQ+ equality, he has motivated me to be a more public activist instead of internalizing my beliefs. “ Catapult ,” middle right. This is the logo of a startup incubator where I launched my first company, Threading Twine. I learned that business can provide others access to fundamental human needs, such as economic empowerment of minorities and education. In my career, I hope to be a corporate advocate for the empowerment of women, creating large-scale impact and deconstructing institutional boundaries that obstruct women from working in high-level positions. Working as a women’s rights activist will allow me to engage in creating lasting movements for equality, rather than contributing to a cycle that elevates the stances of wealthy individuals. “ Thank God it’s Monday ,” sneakily nestled in the upper right corner. Although I attempt to love all my stickers equally (haha), this is one of my favorites. I always want my association with work to be positive. And there are many others, including the horizontal, yellow stripes of the Human Rights Campaign ; “ The Team ,” a sticker from the Model G20 Economics Summit where I collaborated with youth from around the globe; and stickers from “ Kode with Klossy ,” a community of girls working to promote women’s involvement in underrepresented fields. When my computer dies (hopefully not for another few years), it will be like my passport expiring. It’ll be difficult leaving these moments and memories behind, but I probably won’t want these stickers in my 20s anyways (except Harry Styles, that’s never leaving). My next set of stickers will reveal my next set of aspirations. They hold the key to future paths I will navigate, knowledge I will gain, and connections I will make.
Cool, huh? And see what I mean about how you can write a strong personal statement without focusing on challenges you’ve faced?
Going back to that “thread and beads” metaphor with the “My Laptop Sticker” essay:
The “beads” are the different experiences that link to the values of creativity, open-mindedness, humor, courage, and entrepreneurialism.
The “thread” (i.e., the theme that ties everything together) is her laptop stickers. Each one represents a quality of the author’s personality. Actually, there’s a second thematic thread: Those qualities will also serve her in her women’s rights activism. Bonus!
The outline that got her there
Here’s the outline for the “My Laptop Stickers” essay. Notice how each bullet point discusses a value or values, connected to different experiences via her thread, and sets up the insights she could explore. (Insight, though, is the toughest part of the writing process, and will probably take the most revision, so it’s fine if you don’t have great insights in an outline or first draft. But you’ll want to get to them by your final draft.)
She found this thread essentially by using The Five Things Exercise in conjunction with the other brainstorming exercises.
Thread = Laptop Stickers
We <3 Design → art, design, experimentation
Details: spent weekend designing websites, graphics for my companies
Possible insight: Developed my own style
Common Threads → authenticity, open-mindedness
Details: Street artists, musicians in Austin
Possible insight: Creating not just consuming culture
Poop emoji → family, goofy side
Details: Brother, interactions, thinking rationally
Possible insight: Connection/vulnerability
Lol ur not Harry Styles → equality, activism, confidence
Details: Various activism as motivation/reminder to act vs just internalize
Possible insight: My growth with acting/speaking up
Catapult → entrepreneurship, social justice, awareness, meaningful work
Details: Threaded Twine, women’s rights, breaking cycles
Possible insight: Discovered my career
Thank God it's Monday → enjoyable work
Possible insight: Importance of experience/framing
Possible insight: Want work to always be this way
The Team → collaboration
Details: Model G20 Econ Summit, group collaboration
Kode with Klossy → community, social justice
Details: Promoting women in underrepresented fields
Okay, so if you’re on board so far, here’s what you need:
Some stuff to write about (ideally 4-10 things) that will make up the “beads” of your essay, and
Something to connect all the different “beads” (like a connective theme or thread)
First, let’s talk about ...
How to generate lots of ‘stuff’ to write about (aka the beads for your bracelet)
Complete all the brainstorming exercises.
Already did that? Great! Move on!
Didn’t do that? Go back , complete the exercises, and then ...
Case study: How to find a theme for your personal statement (aka the thread that connects the beads of your bracelet)
Let’s look at an example of how I helped one student find her essay thread, then I’ll offer you some exercises to help you find your own.
The “Home” essay: A quick college essay case study
First, take a look at this student’s Essence Objects and 21 Details:
My Essence Objects
Bojangle’s Tailgate Special/Iced Tea
Light blue fuzzy blanket
A box containing my baby tooth
Car keys
Gold bracelet from my grandfather
Orange, worn Nike Free Run Sneakers
Duke basketball game ticket
Palestine flag rubber wristband/ISEF Lanyard
Friendship bracelet
A pair of headphones
Yin-yang symbol
Worn, green Governor’s School East lanyard
My 21 Details
I’ve been known to have terrible spatial awareness despite being a dancer. Just last week, my shoelace got caught in an escalator and I tripped about 20 people.
Zumba and kickboxing are my favorite forms of exercise and I’m hopefully going to become certified to teach Zumba soon.
I have misophonia--sometimes I even have to eat dinner in a different room from my family.
My go-to drinks are Hi-C and Sweet Tea.
I became a pescatarian this year to avoid fried chicken, and I can honestly get a life’s worth of meat out of cod, salmon, tilapia, shrimp, you name it.
I collect funky socks--at this point, I have socks with tacos, snowmen, Santa, and even animals wearing glasses.
I’ve gotten different Myers-Briggs personality types every time I took the test. The most recent ones are ENFJ and ENFP.
I have no immediate relatives in America besides my mom, dad, and sister.
I am a diehard Duke basketball fan, and I can identify all of the Duke basketball fans at my high school on one hand.
I love discussing psychology, but sometimes I psychoanalyze.
Singing while driving is honestly one of my favorite pastimes.
My alarm for school every morning is at 5:42 am.
I hope to complete a half and full marathon within the next four years, despite not having run a 5k yet.
I realized the tooth fairy wasn’t real after I lost my second tooth, but I pretended that I still believed in it until I was in 5th grade for the tooth fairy’s “gifts”.
I could eat fruits for every single meal.
I don’t do well with confrontation.
Airports are hands-down my favorite place to be, but I hate airplanes.
If I’m not busy or working, you can usually find me in my hammock in the backyard.
I find that I form the deepest connections with people after 12am.
Sometimes, I like TV spoilers.
How this author found her thematic thread
When I met with this student for the first time, I began asking questions about her objects and details: “What’s up with the Bojangle’s Iced Tea? What’s meaningful to you about the Governor’s School East lanyard? Tell me about your relationship to dance ...”
We were thread-finding ... searching for an invisible connective [something] that would allow her to talk about different parts of her life.
Heads-up: Some people are really good at this—counselors are often great at this—while some folks have a more difficult time. Good news: When you practice the skill of thread-finding, you can become better at it rather quickly.
You should also know that sometimes it takes minutes to find a thread and sometimes it can take weeks. With this student, it took less than an hour.
I noticed in our conversation that she kept coming back to things that made her feel comfortable. She also repeated the word “home” several times. When I pointed this out, she asked me, “Do you think I could use ‘home’ as a thread for my essay?”
“I think you could,” I said.
Read her essay below, then I’ll share more about how you can find your own thematic thread.
Example essay: HOME
As I enter the double doors, the smell of freshly rolled biscuits hits me almost instantly. I trace the fan blades as they swing above me, emitting a low, repetitive hum resembling a faint melody. After bringing our usual order, the “Tailgate Special,” to the table, my father begins discussing the recent performance of Apple stock with my mother, myself, and my older eleven year old sister. Bojangle’s, a Southern establishment well known for its fried chicken and reliable fast food, is my family’s Friday night restaurant, often accompanied by trips to Eva Perry, the nearby library. With one hand on my breaded chicken and the other on Nancy Drew: Mystery of Crocodile Island, I can barely sit still as the thriller unfolds. They’re imprisoned! Reptiles! Not the enemy’s boat! As I delve into the narrative with a sip of sweet tea, I feel at home. “Five, six, seven, eight!” As I shout the counts, nineteen dancers grab and begin to spin the tassels attached to their swords while walking heel-to-toe to the next formation of the classical Chinese sword dance. A glance at my notebook reveals a collection of worn pages covered with meticulously planned formations, counts, and movements. Through sharing videos of my performances with my relatives or discovering and choreographing the nuances of certain regional dances and their reflection on the region’s distinct culture, I deepen my relationship with my parents, heritage, and community. When I step on stage, the hours I’ve spent choreographing, creating poses, teaching, and polishing are all worthwhile, and the stage becomes my home. Set temperature. Calibrate. Integrate. Analyze. Set temperature. Calibrate. Integrate. Analyze. This pulse mimics the beating of my heart, a subtle rhythm that persists each day I come into the lab. Whether I am working under the fume hood with platinum nanoparticles, manipulating raw integration data, or spraying a thin platinum film over pieces of copper, it is in Lab 304 in Hudson Hall that I first feel the distinct sensation, and I’m home. After spending several weeks attempting to synthesize platinum nanoparticles with a diameter between 10 and 16 nm, I finally achieve nanoparticles with a diameter of 14.6 nm after carefully monitoring the sulfuric acid bath. That unmistakable tingling sensation dances up my arm as I scribble into my notebook: I am overcome with a feeling of unbridled joy. Styled in a t-shirt, shorts, and a worn, dark green lanyard, I sprint across the quad from the elective ‘Speaking Arabic through the Rassias Method’ to ‘Knitting Nirvana’. This afternoon is just one of many at Governor’s School East, where I have been transformed from a high school student into a philosopher, a thinker, and an avid learner. While I attend GS at Meredith College for Natural Science, the lessons learned and experiences gained extend far beyond physics concepts, serial dilutions, and toxicity. I learn to trust myself to have difficult yet necessary conversations about the political and economic climate. Governor’s School breeds a culture of inclusivity and multidimensionality, and I am transformed from “girl who is hardworking” or “science girl” to someone who indulges in the sciences, debates about psychology and the economy, and loves to swing and salsa dance. As I form a slip knot and cast on, I’m at home. My home is a dynamic and eclectic entity. Although I’ve lived in the same house in Cary, North Carolina for 10 years, I have found and carved homes and communities that are filled with and enriched by tradition, artists, researchers, and intellectuals. While I may not always live within a 5 mile radius of a Bojangle’s or in close proximity to Lab 304, learning to become a more perceptive daughter and sister, to share the beauty of my heritage, and to take risks and redefine scientific and personal expectations will continue to impact my sense of home.
Rad essay, huh?
But here’s the question I get most often about this technique: How do I find my thematic thread?
Five (more) ways to find a thematic thread for your college personal statement
1. The “Bead-Making” Exercise (5-8 min.)
In the example above, we started with the beads, and then we searched for a thread. This exercise asks you to start with the thread of something you know well and then create the beads. Here’s how it works:
Step 1: On a blank sheet of paper, make a list of five or six things you know a lot about.
For example, I know a lot about …
Words/language
Productivity
Voices/accents
Self-help books
If you can only think of 3 or 4, that’s okay.
Step 2: Pick one of the things you wrote down, flip your paper over, and write it at the top of your paper, like this:

This is your thread, or a potential thread.
Step 3: Underneath what you wrote down, name 5-6 values you could connect to this. These will serve as the beads of your essay. You can even draw a thread connecting your beads, if you want, like this:
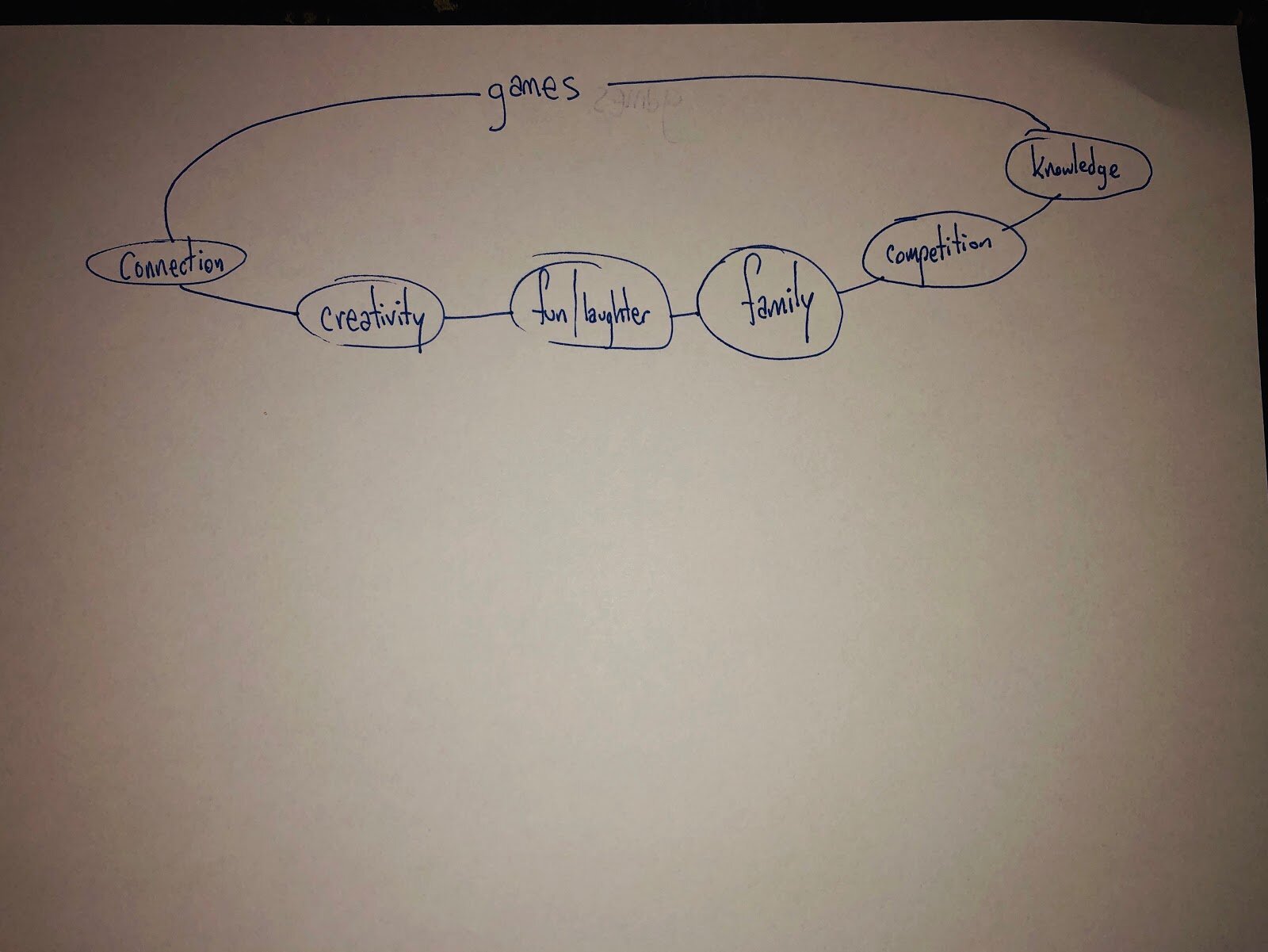
Step 4: For each value, write down a specific example, memory, image, or essence object that connects to that value. Example:
My thread: Games
My beads: Connection, creativity, fun/laughter, family, competition, knowledge
Here are my examples/memories/images/essence objects:
Connection: One memory I have is playing “I love” in a circle at camp with 20 friends and strangers. I still marvel at how quickly it helped us bond.
Creativity: After I understand how a game works, I like to try to improve it by tweaking the rules. Two examples: 1) I remember when I was young trying to find the right amount of money for the Free Parking space in Monopoly, and 2) recently, I learned the game Guesstimation is so much better if you add wagers. I see my 4-year-old daughter tweaks games too, which drives my wife crazy, as she likes to play by the rules of the game.
Fun/laughter: As I’ve aged, so much of my life has become planned/programmed, but I can still enjoy losing track of time with board games. Two weeks ago, for example, I laughed so hard I cried while playing Drawful with Lisa, Andy, and Sage.
Family: We played games like Charades and Jeopardy when I was young. (My dad was the Game Master who would come up with the categories. As I grew older, I took over the role of Game Master.)
Competition: People don’t know this about me because I seem so chill, but I am incredibly competitive. Things I rarely lose at: ping pong, Tetris, foosball, and corn hole. I’ve gotten much better over the years at hiding my competitive side, but it’s still there.
Knowledge: Can’t really think of much on this one—maybe something related to Jeopardy?
This is an actual brainstorm I did using this exercise.
And, as I write these things down, I notice a theme of youth/old age emerging. Games have changed for me as I’ve gotten older. Note that I couldn’t come up with something for the last one, “knowledge,” which is fine.
The point is this: If you know a thing well, odds are good you’ll be able to make a lot of connections to your values. And if you can find specific examples for each value, that can make for interesting paragraphs in your personal statement.
If you’re willing to spend a few more minutes, ask “so what?” of each example to see if a specific insight emerges.
And, in case you want a formula for what I’m describing, here you go:
Once you’ve written down the values and at least one example (e.g., a memory, image, essence object) for each bead, see if you have enough content for an essay.
Still haven’t found your theme? Here are ...
More ways to find a thematic thread for your personal statement
2. The “Five Things” Exercise
(Special thanks to my colleague, Dori Middlebrook, for this one.)
I mentioned this when we first started talking about Montage Structure. Similar to the “bead-making” exercise above, you identify the thread first and then develop the beads.
Step 1: Write down 5 similar things that are meaningful to you in different ways.
Examples: Five Pairs of Shoes I’ve Worn, Five Houses I’ve Lived In, Five Photographs in My Room, Five Ways Cooking Has Influenced Me, etc.
Step 2: Begin by simply naming the 5 different items.
Example: High-top tennis shoes, flip-flops, heels, cleats, bunny slippers
Step 3: Add physical details so we can visualize each one.
Step 4: Add more details. Maybe tell a story for each.
Pro tip: Try connecting each of the 5 to a different value.
Step 5: Expand on each description further and start to connect the ideas to develop them into an essay draft.
3. Thread-finding with a partner
Grab someone who knows you well (e.g., a counselor, friend, family member). Share all your brainstorming content with them and ask them to mirror back to you what they’re seeing. It can be helpful if they use reflective language and ask lots of questions. An example of a reflective observation is: “I’m hearing that ‘building’ has been pretty important in your life … is that right?” You’re hunting together for a thematic thread—something that might connect different parts of your life and self.
4. Thread-finding with photographs
Pick 10 of your favorite photos or social media posts and write a short paragraph on each one. Why’d you pick these photos? What do they say about you? Then ask yourself, “What are some things these photos have in common?” Bonus points: Can you find one thing that connects all of them?
5. Reading lots of montage example essays that work
You’ll find some here , here , and here . While you may be tempted to steal those thematic threads, don’t. Try finding your own. Have the courage to be original. You can do it.
Montage Essay Structure FAQs
Q: How do I work in extracurricular activities in a tasteful way (so it doesn’t seem like I’m bragging)?
A: Some counselors caution, with good reason, against naming extracurricular activities/experiences in your personal statement. (It can feel redundant with your Activities List.) You actually can mention them , just make sure you do so in context of your essay’s theme. Take another look at the eighth paragraph of the “My Laptop Stickers” essay above, for example:
And there are many [other stickers], including the horizontal, yellow stripes of the Human Rights Campaign; “The Team,” a sticker from the Model G20 Economics Summit where I collaborated with youth from around the globe; and stickers from “Kode with Klossy,” a community of girls working to promote women’s involvement in underrepresented fields.
A description of these extracurricular activities may have sounded like a laundry list of the author’s accomplishments. But because she’s naming other stickers (which connects them to the essay’s thematic thread), she basically gets to name-drop those activities while showing other parts of her life. Nice.
One more way to emphasize a value is to combine or disguise it with humor. Example: “Nothing teaches patience (and how to tie shoes really fast) like trying to wrangle 30 first-graders by yourself for 10 hours per week,” or “I’ve worked three jobs, but I’ve never had to take more crap from my bosses than I did this past summer while working at my local veterinarian’s office.”
In each of these examples, the little bit of humor covers the brag. Each is basically pointing out that the author had to work a lot and it wasn’t always fun. No need to push this humor thing, though. Essays don’t need to be funny to be relatable, and if the joke doesn’t come naturally, it might come across as trying too hard.
Q: How do I transition between examples so my essay “flows” well?
A: The transitions are the toughest part of this essay type. Fine-tuning them will take some time, so be patient. One exercise I love is called Revising Your Essay in 5 Steps , and it basically works like this:
Highlight the first sentence of each of your paragraphs in bold, then read each one aloud in order. Do they connect, creating a short version of your essay? If not:
Rewrite the bold sentences so that they do connect (i.e., flow) together. Once you’ve done that …
Rewrite each paragraph so it flows from those bolded sentences.
Read them aloud again. Wash, rinse, repeat until the ideas flow together.
This is a great way to figure out the “bones” (i.e., structure) of your essay.
Q: What am I looking for again?
A: You’re looking for two things:
Parts of yourself that are essential to who you are (e.g., values or “islands of your personality”), and
A theme that connects them all.
Your theme could be something mundane (like your desk) or something everyone can relate to ( like the concept of home ), but make sure that it is elastic (i.e. can connect to many different parts of you) and visual, as storytelling made richer with images.
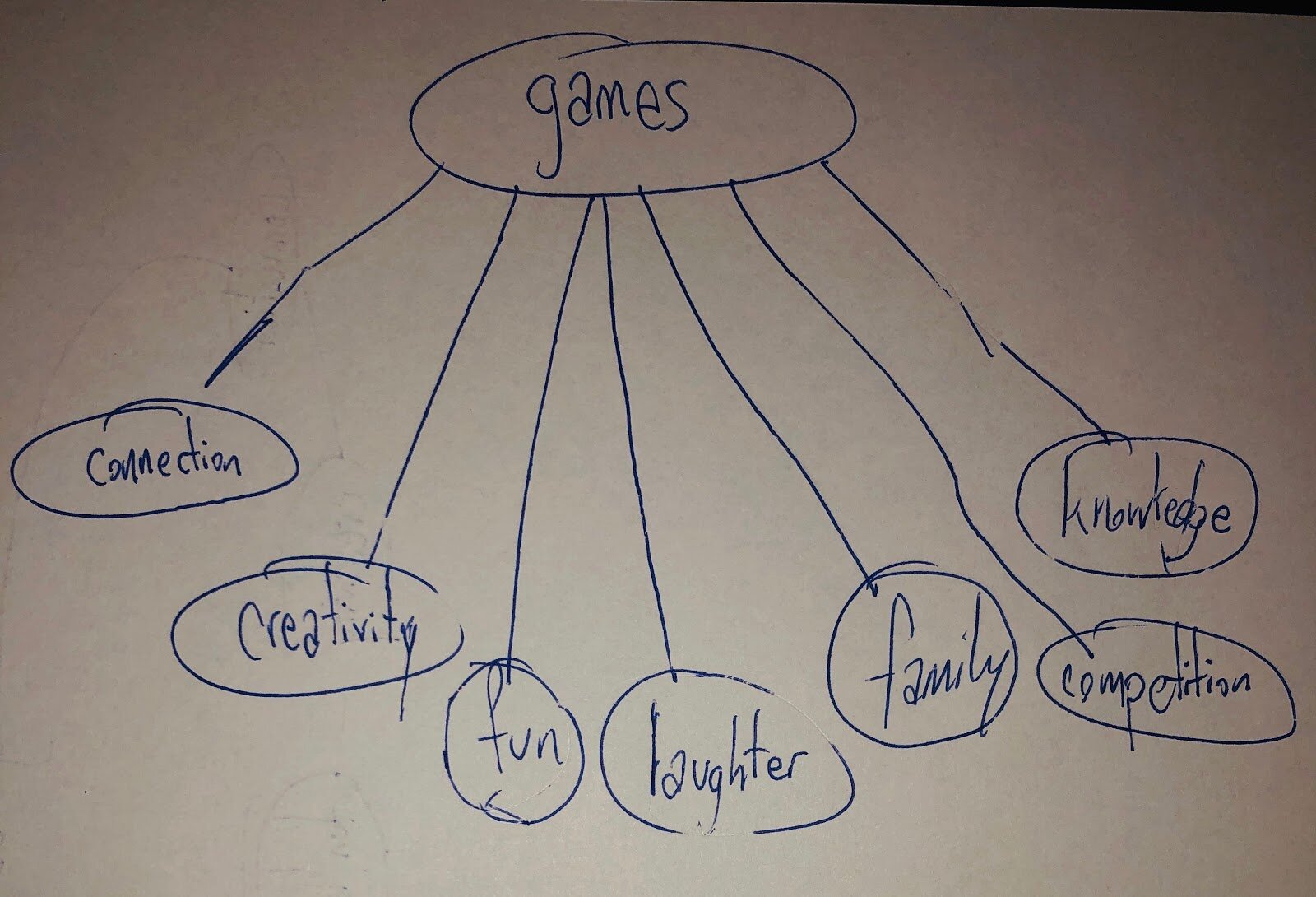
Each of the values creates an island of your personality and a paragraph for your essay.
Montage step-by-step recap:
Review your brainstorming exercises and look for threads that connect 4-7 different values through 4-7 different experiences.
Choose an order for your examples. Consider describing one example per paragraph.
Create an outline.
Write a first draft. Once you do ...
Consider using the Revising Your Essay in 5 Steps Exercise to clarify your transitions.
Q: This is hard! I’m not finding it yet and I want to give up. What should I do?
A: Don’t give up! Remember: be patient. This takes time. If you need inspiration, or assurance that you’re on the right track, check out Elizabeth Gilbert’s TED Talk , “Your Elusive Creative Genius.”
All right, moving on.
How to write a college essay using Narrative Structure
If you answered “yes” to both questions at the beginning of this guide, I recommend exploring Narrative Structure. I’ll explain this in more detail below.
My favorite content-generating exercise for Narrative Structure is the Feelings and Needs Exercise. It takes about 20 minutes (but do feel free to take longer—more time brainstorming and outlining leads to better, faster writing). Here’s how it works:
The Feelings and Needs Exercise
Time : 15-20 minutes
Instructions : You’ll find them here.
If you haven’t completed the exercise, please do it now.
(And this is a dramatic pause before I tell you the coolest thing about what you just did.)
You may notice that your completed Feelings and Needs chart maps out a potential structure for your personal statement. If you’re not seeing it, try turning your paper so that the challenges are at the top of your page and the effects are below them.
Voila. A rough outline for a narrative essay.
To clarify, this isn’t a perfect way to outline an essay. You may not want to spend an entire paragraph describing your feelings, for example, or you may choose to describe your needs in just one sentence. And now that you see how it frames the story, you may want to expand on certain columns. However, the sideways Feelings and Needs chart can help you think about how the chronology of your experiences might translate into a personal statement.
Here’s an essay that one student wrote after completing this exercise:
Example Narrative Essay: The Birth of Sher Khan The narrow alleys of Mardan, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan where I spent the first 7 years of my life were infiltrated with the stench of blood and helplessness. I grew up with Geo news channel, with graphic images of amputated limbs and the lifeless corpses of uncles, neighbors, and friends. I grew up with hurried visits to the bazaar, my grandmother in her veil and five-year-old me, outrunning spontaneous bomb blasts. On the open rooftop of our home, where the hustle and bustle of the city were loudest, I grew up listening to calls to prayer, funeral announcements, gunshots. I grew up in the aftermath of 9/11, confused. Like the faint scent of mustard oil in my hair, the war followed me to the United States. Here, I was the villain, responsible for causing pain. In the streets, in school, and in Baba’s taxi cab, my family and I were equated with the same Taliban who had pillaged our neighborhood and preyed on our loved ones. War followed me to freshman year of high school when I wanted more than anything to start new and check off to-dos in my bullet journal. Every time news of a terror attack spread, I could hear the whispers, visualize the stares. Instead of mourning victims of horrible crimes, I felt personally responsible, only capable of focusing on my guilt. The war had manifested itself in my racing thoughts and bitten nails when I decided that I couldn’t, and wouldn’t, let it win. A mission to uncover parts of me that I’d buried in the war gave birth to a persona: Sher Khan, the tiger king, my radio name. As media head at my high school, I spend most mornings mastering the art of speaking and writing lighthearted puns into serious announcements. Laughter, I’ve learned, is one of the oldest forms of healing, a survival tactic necessary in war, and peace too. During sophomore year, I found myself in International Human Rights, a summer course at Cornell University that I attended through a local scholarship. I went into class eager to learn about laws that protect freedom and came out knowledgeable about ratified conventions, The International Court of Justice, and the repercussions of the Srebrenica massacre. To apply our newfound insight, three of my classmates and I founded our own organization dedicated to youth activism and spreading awareness about human rights violations: Fight for Human Rights. Today, we have seven state chapters led by students across the U.S and a chapter in Turkey too. Although I take pride in being Editor of the Golden State’s chapter, I enjoy having written articles about topics that aren’t limited to violations within California. Addressing and acknowledging social issues everywhere is the first step to preventing war. Earlier this year, through KQED, a Bay Area broadcasting network, I was involved in a youth takeover program, and I co-hosted a Friday news segment about the Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals policy, the travel ban, and the vaping epidemic. Within a few weeks, my panel and interview were accessible worldwide, watched by my peers in school, and family thousands of miles away in Pakistan. Although the idea of being so vulnerable initially made me nervous, I soon realized that this vulnerability was essential to my growth. I never fully escaped war; it’s evident in the chills that run down my spine whenever an untimely call reaches us from family members in Pakistan and in the funerals still playing on Geo News. But I’m working towards a war-free life, internally and externally, for me and the individuals who can share in my experiences, for my family, and for the forgotten Pashtun tribes from which I hail. For now, I have everything to be grateful for. War has taught me to recognize the power of representation, to find courage in vulnerability, and best of all, to celebrate humor.
Fun fact: This essay was written by a student in one of my online courses who, as she shared this version with me, called it a “super rough draft.”
I wish my super rough drafts were this good.
I share this essay with you not only because it’s a super awesome essay that was inspired by the Feelings and Needs Exercise, but also because it offers a beautiful example of what I call the ...

Narrative Structure content sections
You can think of a narrative essay as having three basic sections: Challenges + Effects ; What I Did About It ; What I Learned . Your word count will be pretty evenly split between the three, so for a 650-word personal statement, 200ish each.
To get a little more nuanced, within those three basic sections, a narrative often has a few specific story beats. There are plenty of narratives that employ different elements (for example, collectivist societies often tell stories in which there isn’t one central main character/hero, but it seems hard to write a college personal statement that way, since you’re the focus here). You’ve seen these beats before—most Hollywood films use elements of this structure, for example.
Status Quo : The starting point of the story. This briefly describes the life or world of the main character (in your essay, that’s you).
The Inciting Incident : The event that disrupts the Status Quo. Often it’s the worst thing that could happen to the main character. It gets us to wonder: Uh-oh … what will they do next? or How will they solve this problem?
Raising the Stakes/Rising Action : Builds suspense. The situation becomes more and more tense, decisions become more important, and our main character has more and more to lose.
Moment of Truth : The climax. Often this is when our main character must make a choice.
New Status Quo : The denouement or falling action. This often tells us why the story matters or what our main character has learned. Think of these insights or lessons as the answer to the big “so what?” question.
For example, take a look at “The Birth of Sher Khan” essay above.
Notice that roughly the first third focuses on the challenges she faced and the effects of those challenges.
Roughly the next third focuses on actions she took regarding those challenges. (Though she also sprinkles in lessons and insight here.)
The final third contains lessons and insights she learned through those actions, reflecting on how her experiences have shaped her. (Again, with the caveat that What She Did and What She Learned are somewhat interwoven, and yours likely will be as well. But the middle third is more heavily focused on actions, and the final third more heavily focused on insight.)
And within those three sections, notice the beats of her story: Status Quo, The Inciting Incident, Raising the Stakes/Rising Action, Moment of Truth, New Status Quo.
How does the Feelings and Needs Exercise map onto those sections?
Pretty directly.
At the risk of stating the blatantly obvious, The Challenges and Effects columns of the Feelings and Needs Exercise … are the Challenges + Effects portion of your essay. Same with What I Did and What I Learned.
The details in your Feelings and Needs columns can be spread throughout the essay. And it’s important to note that it’s useful to discuss some of your feelings and needs directly, but some will be implied.
For example, here’s the Feelings and Needs Exercise map of the “Sher Khan” essay. And I know I just mentioned this, but I want you to notice something that’s so important, I’m writing it in bold: The author doesn’t explicitly name every single effect, feeling, or need in her essay . Why not? First, she’s working within a 650-word limit. Second, she makes room for her reader’s inferences, which can often make a story more powerful. Take a look:
Challenge 1 : She grows up surrounded by war, which is explicitly stated.
Challenge 2 : She comes to the U.S. to find safety (a need), which is implied, but instead, she is villainized, which is explicitly stated.
Effects : She is ostracized after arriving in the U.S. “Every time news of a terror attack spread,” she writes, “I could hear the whispers, visualize the stares.” Other effects are implied, and we are left to imagine—and feel for ourselves—the kind of impact this might have had on her, and on us. Vulnerability creates connection.
Feelings : Growing up in the aftermath of 9/11 leaves her feeling confused, and after she is shunned, she describes being unable to mourn the victims of horrible crimes, instead feeling “personally responsible, only capable of focusing on [her] own guilt.” She explicitly names confusion and guilt, but she doesn’t name all the things she felt, of course, as there’s no need. Here, naming 1-2 key emotions helps us understand her inner world. If you choose to do the same in your essay, it’ll help readers understand yours.
Needs : As I read this essay, I can imagine the author needed safety, order, love, respect, reassurance, connection, and many more. But these are implied by the story events and need not be explicitly stated. In fact, spelling these things out might have made the essay sound weird. Imagine if she’d said, “I needed safety and order” at the end of the first paragraph and “I needed respect, reassurance, and connection” at the end of the second paragraph. That might sound awkward or too obvious, right? While identifying your needs is a great tool for understanding your story (and self) on a deeper level, there’s no need to explicitly state them at each juncture.
What She Did About It : The author developed a radio persona called Sher Khan , attended a summer course on human rights, founded an organization dedicated to youth activism, wrote articles on restrictive blasphemy laws and the forced repatriation of refugees, and probably other things that weren’t even mentioned.
What She’s Learned/Gained : She found a sense of purpose and discovered “everything [she has] to be grateful for.” She writes: “War has taught me to never take an education or a story for granted, to find beauty in vulnerability, to remain critical of authority figures, to question what’s socially accepted, and best of all, to celebrate humor.”
Cool. Here’s another narrative example:
narrative essay: What Had to Be Done At six years old, I stood locked away in the restroom. I held tightly to a tube of toothpaste because I’d been sent to brush my teeth to distract me from the commotion. Regardless, I knew what was happening: my dad was being put under arrest for domestic abuse. He’d hurt my mom physically and mentally, and my brother Jose and I had shared the mental strain. It’s what had to be done. Living without a father meant money was tight, mom worked two jobs, and my brother and I took care of each other when she worked. For a brief period of time the quality of our lives slowly started to improve as our soon-to-be step-dad became an integral part of our family. He paid attention to the needs of my mom, my brother, and me. But our prosperity was short-lived as my step dad’s chronic alcoholism became more and more recurrent. When I was eight, my younger brother Fernando’s birth complicated things even further. As my step-dad slipped away, my mom continued working, and Fernando’s care was left to Jose and me. I cooked, Jose cleaned, I dressed Fernando, Jose put him to bed. We did what we had to do. As undocumented immigrants and with little to no family around us, we had to rely on each other. Fearing that any disclosure of our status would risk deportation, we kept to ourselves when dealing with any financial and medical issues. I avoided going on certain school trips, and at times I was discouraged to even meet new people. I felt isolated and at times disillusioned; my grades started to slip. Over time, however, I grew determined to improve the quality of life for my family and myself. Without a father figure to teach me the things a father could, I became my own teacher. I learned how to fix a bike, how to swim, and even how to talk to girls. I became resourceful, fixing shoes with strips of duct tape, and I even found a job to help pay bills. I became as independent as I could to lessen the time and money mom had to spend raising me. I also worked to apply myself constructively in other ways. I worked hard and took my grades from Bs and Cs to consecutive straight A’s. I shattered my school’s 1ooM breaststroke record, and learned how to play the clarinet, saxophone, and the oboe. Plus, I not only became the first student in my school to pass the AP Physics 1 exam, I’m currently pioneering my school’s first AP Physics 2 course ever. These changes inspired me to help others. I became president of the California Scholarship Federation, providing students with information to prepare them for college, while creating opportunities for my peers to play a bigger part in our community. I began tutoring kids, teens, and adults on a variety of subjects ranging from basic English to home improvement and even Calculus. As the captain of the water polo and swim team I’ve led practices crafted to individually push my comrades to their limits, and I’ve counseled friends through circumstances similar to mine. I’ve done tons, and I can finally say I’m proud of that. But I’m excited to say that there’s so much I have yet to do. I haven’t danced the tango, solved a Rubix Cube, explored how perpetual motion might fuel space exploration, or seen the World Trade Center. And I have yet to see the person that Fernando will become. I’ll do as much as I can from now on. Not because I have to. Because I choose to.
There’s so much to love about this essay.
Here’s a behind-the-scenes look at how the author wrote this essay so you can figure out how to write yours:
First, the author brainstormed the content of his essay using the Feelings and Needs Exercise.
Did you spot the elements of that exercise? If not, here they are:
Challenges: Domestic abuse, alcoholic step-dad, little brother Fernando’s birth, family’s undocumented status
Effects: Author and his brother shared the mental strain, father was arrested, funds were tight, mom worked two jobs, brothers took care of one another, they kept to themselves when dealing with financial and medical issues, avoided going on certain school trips, at times author was discouraged from meeting new people, grades started to slip
Feelings: Confused yet understanding, anxious, worried, relieved, alone, lost, vulnerable, lonely, disconnected, alone, heartbroken, ashamed, disillusioned
Needs: Order, autonomy, reassurance, growth, safety, understanding, empathy, hope, support, self-acceptance
What He Did About It: Took care of his youngest brother; became his own teacher; learned how to fix a bike, swim, socialize; found a job to help pay bills; improved his grades; broke a school swimming record; learned to play instruments; became the first student in his school to pass the AP Physics 1 exam; took a leadership role in clubs; and tutored and counseled friends and peers
What He Learned: He’s proud of what he’s done, but wants to do more: dance the tango, solve a Rubix Cube, explore perpetual motion, see the World Trade Center, see his little brother grow up … and do you notice the value here? Hunger . That was his number one value, by the way. And he ends by saying he’ll do these things not because he has to, but because he chooses to. This sounds like autonomy . Another one of his top values.
That’s why I love beginning with this exercise. With just 15-20 minutes of focused work, you can map out your whole story.
Next, the author used Narrative Structure to give shape to his essay.
Did you spot the Narrative Structure elements? If not, here they are:
Inciting Incident: While the author is brushing his teeth, his father is arrested for domestic abuse.
Status Quo: His father had hurt his mom physically and mentally, and the author and his brother had shared the mental strain. “It’s what had to be done,” he writes.
Raising the Stakes: The entire second and third paragraphs, which describe how living without a father meant money was tight. Things improved for a while after his mother remarried, but his stepdad’s chronic alcoholism (raise the stakes) plus a new little brother (raise the stakes again) made things even tougher. As if that weren’t enough, the author raises the stakes even further by revealing that his family was undocumented at the time.
Moment of Truth: At his lowest point, he decides to do something about it. “I grew determined to improve the quality of life for my family and myself,” he writes, then goes on to tell us all the amazing things he taught himself, the skills he learned, and interests he pursued. It’s inspiring.
New Status Quo: Remember that the initial Status Quo was the author doing “what had to be done.” Not so, by the end of the essay. In the final lines, he writes, “I’ll do as much as I can from now on. Not because I have to. Because I choose to.”
And again, notice that those fit within the framework of:
⅓: Challenges he faced and their impacts on him
⅓: What he did to work through them
⅓: What he learned through the process
Narrative essay structure FAQs
Q: Are there any situations where I may not want to write about my life struggles?
A: Yes. Sometimes it can be too difficult to discuss them. Or you may be actively dealing with a challenge. If this is the case, reach out to your counselor, a trusted mentor, or, if possible, a therapist.
If money is an issue (i.e., you feel you can’t afford a therapist) and you don’t feel comfortable sharing your struggles with your counselor, ask them if they can refer you to a therapist or counselor who works on a sliding scale. Many mental health professionals work with clients at low rates or for free.
You may also choose to write about the struggles you’ve faced without getting into all the details. Saying, for example, that you experienced verbal abuse from your father, for example, may be enough; you don’t necessarily need to share the specifics.
Q: Should I write about mental health challenges?
A: Mental health can be very difficult to write about for a few reasons:
If a student is still very much struggling through the challenges they describe, the admission reader may wonder if the student is ready for college.
In some cases, the admission officer may feel that a student is ready for college, but their institution may not be adequately equipped to help them thrive (not all colleges have the same kinds of resources, unfortunately).
Unfortunately, mental health challenges have become so common these days that many students write personal statements about them, and so it can be difficult to stand out. If you’re feeling compelled to write about a mental health challenge, consider brainstorming some uncommon connections .
Questions to ask yourself if you’re considering writing about mental health challenges:
Do I have any other topics I could write on? Are there other interesting parts of myself I’d like to share that could reveal important skills, qualities, and values? Or must I write about this? (Beware the trap discussed earlier of feeling like you must write about a challenge to write a great personal statement—it’s not true! The authors of the “ My Laptop Stickers” essay the "Home” essay were students who faced challenges but chose not to write about them.)
Have I truly worked through this? Am I able to devote the middle third of my essay to actions I’ve taken to work through the challenge and the final third to what I’ve learned? (You may not know the answers to these questions until you’ve done some writing. Maybe run your challenge through the Feelings and Needs Exercise to see what surfaces. Even if this doesn’t end up being your personal statement topic, you might learn something important about yourself.)
If I were an admission officer reading this essay, would I feel like this student has their situation handled and they are truly ready for college? (If you’re unsure, it’s a great idea to have 2-3 folks read it who have a good understanding of what colleges are looking for.)
Could the mental health challenge be a brief explanation in the Additional Info section? To see if this might work for you, see how briefly you can describe your mental health challenge using factual bullet points. Devote one bullet point to the challenge, another bullet point to what you’ve done about it, and a final bullet point describing briefly what you’ve learned.
Important: If you have a counselor, I strongly recommend consulting with them as you decide whether to discuss a mental health challenge in your personal statement. If your counselor is writing a letter on your behalf, some of the information you’d like to share may already be accounted for. Talk to them and find out.
Q: Are there any situations where I may not want to write about my career in my personal statement … even if I know what it is?
A: For sure. Say you’re interested in becoming a doctor, but you’re applying to a medical program with a supplemental prompt asking why you want to become a doctor. If you want to avoid repetition, you might not explicitly mention becoming a doctor at the end of your personal statement (you don’t have to discuss your career at all in a personal statement; many students are unsure.). Instead, you might describe how you’ve developed qualities that will equip you for a career as a doctor (e.g., creativity, for example, or the ability to lead a team).
Narrative Structure step-by-step recap :
Complete the brainstorming exercises, as these will help no matter which structure you choose. Take special care to complete the Feelings and Needs Exercise, as it will help you outline your essay.
Create an outline using the Narrative Structure described above.
Write a first draft.
Check out my blog for more Narrative Structure examples.

Here’s how you can nail your college essay in 5 steps

What is university experience without tackling the mammoth of words and hours upon hours of writing? Essays are inevitable if you’re pursuing an academic life, and you’ll encounter them soon enough just weeks into the start of your freshman year. If you’re looking for a guide on how to write an essay , here’s where we bring you the nitty-gritty stuff to ace your next paper.
How to write an essay: A step-by-step guide for college students
Step 1: understand the assignment .
Don’t assume, and don’t underestimate how easily you can misinterpret instructions. A misunderstanding is costly; you can’t get good grades if you’re not responding to the correct questions in the first place. When you’re tasked with a writing assignment , take a few minutes to read through and digest what your professor is looking for.
Read the instruction thoroughly, and highlight keywords that indicate the true purpose of the assignment. Are you writing a discursive essay, a précis, or a book review? Your writing style, tone, and formatting will need to conform to what’s required in the paper. If you’re still unclear about what you need to do, always ask your professor for clarification before proceeding.

Students can avoid over-researching by listing specific questions that will help narrow down certain viewpoints in a research topic. Source: Philippe Lopez/AFP
Step 2: Research the topic
Now that you’ve cleared the confusion, it’s time to dive into the actual pre-writing work. Researching allows you to go in-depth into a subject beyond what is studied in class, hence why it’s usually the most fun part of the entire writing process. There’s such a thing as over-researching though, and you don’t want to be overwhelmed with more information than necessary.
The key to avoiding falling into the rabbit hole of endless research is by starting smart. Put yourself in the reader’s shoes: what would you like to know most about your subject matter? Begin with a list of inquiries that are specific to your topic, eliminating anything that is too generalised.
As you research, it’s crucial to keep track of your sources and compile a reference list so you can have your facts at hand when you start writing them in your essay. You can use citation tools from websites like Mendeley or Zotero to instantly generate citations in the correct format. Your writing process will be more streamlined if you start organising your sources early on.
Step 3: Construct your thesis statement
An essay is as good as its thesis statement. Think of your paper as building a case in a defence trial. What’s the central argument or purpose of your paper? Does it invite the reader to hear your side of the story?
The thesis statement has to be something that is debatable, but not too broad. It isn’t a fact, nor an opinion, but rather a claim that can be expanded on both sides of the fence. A well-crafted thesis is a prelude to how your argument will develop, and gives readers a glimpse into where you’re going with your evidence.
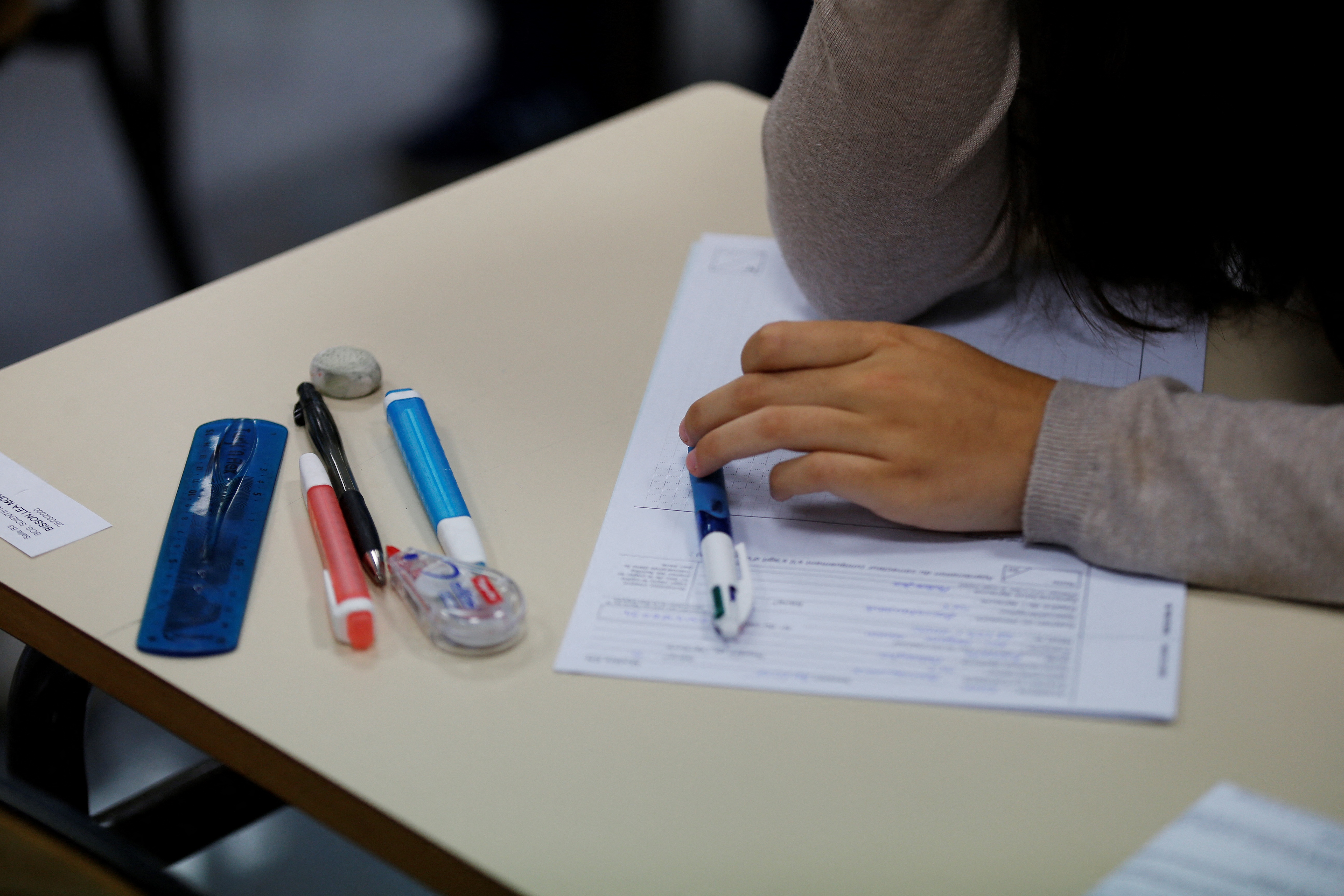

Proofreading your writing draft is a crucial step to polishing your essay before submitting it for grading. Source: Charly Triballeau/AFP
Step 4: Outlining, structuring, and concluding
You’ve got your thesis statements and painstaking research to back it up — the next step is putting them all together. A convincing essay is one that can deliver coherence and consistency throughout the pages. You want your arguments to read like they develop organically, so think about ways you can order them. If there is a timeline involved, structuring your points by chronology will make your points easier to follow.
Sectioning your paragraphs with topic sentences is another way to signal transition between ideas before introducing new supporting evidence in your writing. End each idea with real-life examples obtained from your research, and anticipate counterarguments to your claims by addressing them as much as you can in your essay.
When writing your conclusion, don’t regurgitate your previous ideas. Use the space to make a lasting impression on your readers by summarising your arguments and providing a good closure by offering a unique perspective on the larger scholarship of your subject.
Step 5: Proofread your draft
While it’s tempting to submit your essay and not look back, taking time to proofread and edit your writing is a critical step in your overall writing procedure. Try to not edit immediately after finishing your draft — let it sit for a day or two if you have the time. You’ll notice more subtle mistakes with a fresh set of eyes, and won’t lose marks in stylistic errors.
Some professors are more than happy to give feedback and suggestions to improve your draft, so make use of that if you have time to spare before the deadline. Getting professional input could be the game-changer between a lower and a higher grade for your essay.
Once you’re happy with your final draft and have cited all your sources accordingly, you’re all good to go! Remember, learning how to write an essay gets better with practice if you plan accordingly from the beginning.
Popular stories
A day in the life of a fitness coach for singapore’s national football team.

Forget London — these are the 10 best towns to visit in the UK

The fan who landed an internship at Europe’s number-one podcast

Musicians are smarter than non-musicians — especially those who play the hardest instruments to learn.

5 tips to successfully tackle your first academic essay

How to write better university assignments

Free online citation tools university students shouldn't live without
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write an Academic Essay in 7 Simple Steps
What is an academic essay?
Academic essays are a common form of writing in higher education and play a crucial role in shaping a student’s future academic success. An academic essay is a piece of writing that presents an argument based on evidence and provides the reader with a clear and well-structured understanding of a particular subject. Writing an academic essay is not just about putting together a few words and sentences. It requires careful planning, research, and critical thinking skills to produce a well-written piece that meets the expectations of the reader.
In this article, we will explore the steps involved in writing an academic essay and provide you with tips and examples to help you create a top-quality piece of writing.
Step 1: Choose an Essay Topic
The first step in writing an academic essay is to choose a topic. A topic is the main idea or subject you will write about in your essay. Choose a topic that you are interested in and have a good understanding of. It should also be relevant to the course you are studying and the assignment you are working on.
While choosing the topic for your essay, be sure to follow the formatting requirements and other guidelines of your essay prompt. Read your assignment or prompt thorough and assess what is needed. For instance, if the guidelines call for your essay to follow a certain academic formatting style (such as MLA style , APA style , Chicago style , Vancouver style , etc.), this should be applied and reviewed during the editing process. As with any academic document, be sure to apply academic writing principles to your essay.
Some additional questions to ask before you begin drafting your essay:
- What is the specific question or questions that your essay needs to answer?
- Does your academic essay need to present a critical or rhetorical analysis of a source?
- Do you need to use primary and secondary sources ?
- Is the goal of the essay to present an original argument based on original research, or is it a review of the literature ?
- Do you need to compare two or more works for your analysis?
Step 2: Conduct Research
Once you have chosen a topic, it is time to conduct research. Research is essential for an academic essay as it provides you with the information you need to support your arguments. Use a variety of sources, including books, academic journals, online databases, and other reliable sources, to gather information about your topic.
There are several different types of research that you can use to gather information for your essay, including primary research, secondary research, and tertiary research.
Primary research involves collecting original data through surveys, interviews, or experiments. This type of research is often used to gather firsthand information about a specific topic and is particularly useful when secondary sources do not exist or are limited.
Secondary research involves using existing data and information that has been collected by someone else. This includes sources such as academic journals, books, and online databases. Secondary research is often the starting point for most essay research and provides a good foundation for your own original research.
Tertiary research involves using summary or overview sources, such as textbooks, encyclopedias, and reference books, to gather information about a topic. This type of research is often used to gain a general understanding of a subject or to find specific information quickly.
When conducting research, it is important to use a variety of sources to gather information and to critically evaluate the information you find. Make sure that your sources are credible and relevant to your topic and avoid using unreliable sources, such as personal blogs or opinion pieces. Take notes as you research and keep track of your sources, including the author, publication date, and page numbers, so that you can easily reference them later in your essay.
Step 3: Create an Essay Outline
An outline is a roadmap that guides you through the writing process and helps you stay organized. A good outline should include an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Each body paragraph should include a topic sentence, supporting evidence, and a transition sentence that connects to the next paragraph. Just as an outline for a research paper presents the structure and a summary of each section of your study.
Essay outline template
This outline provides a basic structure for an essay and can be adjusted to fit the specific needs of your topic and assignment. The introduction sets the stage by providing a brief overview of the topic and a thesis statement that outlines the main argument of the essay.
The body of the essay includes three main points, each of which is supported by evidence and explained through analysis. The conclusion restates the thesis, summarizes the main points, and offers final thoughts and implications. This outline can be used as a starting point for organizing your ideas and ensuring that your essay is well-structured and well-supported.
Step 4: Write the Introduction
The introduction is the first part of your essay that the reader will read, so it is important to make a good impression. An essay introduction should provide background information on the topic, hook the reader’s attention, and present a thesis statement .
Here is an example of an introductory paragraph:
“The American Dream, once a symbol of hope and opportunity, has become increasingly elusive in recent years. Despite its origins as a means for individuals to pursue their own happiness and success, the American Dream has come to represent a set of unattainable goals that are beyond the reach of the average person. This essay will explore the ways in which the American Dream has become an unattainable goal for many Americans, including the reasons for its decline and the impact this has on society as a whole.”
This introduction provides context, raises a question, and presents a thesis statement all in under 200 words.
Step 5: Write the Body Paragraphs
The body paragraphs are where you develop your arguments and support them with evidence. Each paragraph should focus on one main idea and should include a topic sentence that introduces the idea, supporting evidence, and a transition sentence that connects to the next paragraph. Use transition words to connect paragraphs and provide a clearer structure to your arguments and overall essay.
Step 6: Write the Essay Conclusion
The essay conclusion is the final part of your essay and provides a summary of your main arguments. It should also restate your thesis statement and provide a final thought or call to action. The conclusion should leave a lasting impression on the reader and provide closure to your essay.
Here is an example of a conclusion paragraph for an academic essay about “The American Dream”:
“ In conclusion , the American Dream has undergone significant changes since its inception. Despite its original intention as a means for individuals to pursue their own happiness and success, the American Dream has come to represent an unattainable goal for many Americans. The factors contributing to this decline include economic inequality, declining social mobility, and a lack of access to education and job opportunities. This shift in the meaning of the American Dream has significant implications for society as a whole, including increased poverty and social unrest. In order to restore the American Dream to its original purpose, policymakers must address these systemic issues and work to create a more equitable society where all individuals have the opportunity to achieve their goals.”
Note the terms and phrases in bold that identify the conclusion paragraph and point to the main topics that are summarized.
Step 7: Revise and Edit Your Essay
Once you have completed the first draft of your essay, it is time to revise and edit. Review your essay for any mistakes, including grammatical errors , punctuation errors , spelling mistakes, and awkward sentence structure . Make sure that your essay is well-structured and that your arguments are well-supported with language that follows the conventions of academic writing and is appropriate for the essay assignment. To ensure your work is polished for style and free of errors, get essay editing from a professional proofreading company like Wordvice.
In conclusion, writing an academic essay is a process that requires careful planning, research, and critical thinking skills. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can write a top-quality essay that meets the expectations of the reader and earns you the grades you deserve. Remember to choose a topic that you are interested in and have a good understanding of, conduct research, create an outline, write a clear and concise introduction, develop well-supported body paragraphs, write a strong conclusion, and revise and edit your essay before submitting it.
Essay Papers Writing Online
Tips and tricks for crafting engaging and effective essays.

Writing essays can be a challenging task, but with the right approach and strategies, you can create compelling and impactful pieces that captivate your audience. Whether you’re a student working on an academic paper or a professional honing your writing skills, these tips will help you craft essays that stand out.
Effective essays are not just about conveying information; they are about persuading, engaging, and inspiring readers. To achieve this, it’s essential to pay attention to various elements of the essay-writing process, from brainstorming ideas to polishing your final draft. By following these tips, you can elevate your writing and produce essays that leave a lasting impression.
Understanding the Essay Prompt
Before you start writing your essay, it is crucial to thoroughly understand the essay prompt or question provided by your instructor. The essay prompt serves as a roadmap for your essay and outlines the specific requirements or expectations.
Here are a few key things to consider when analyzing the essay prompt:
- Read the prompt carefully and identify the main topic or question being asked.
- Pay attention to any specific instructions or guidelines provided, such as word count, formatting requirements, or sources to be used.
- Identify key terms or phrases in the prompt that can help you determine the focus of your essay.
By understanding the essay prompt thoroughly, you can ensure that your essay addresses the topic effectively and meets the requirements set forth by your instructor.
Researching Your Topic Thoroughly

One of the key elements of writing an effective essay is conducting thorough research on your chosen topic. Research helps you gather the necessary information, facts, and examples to support your arguments and make your essay more convincing.
Here are some tips for researching your topic thoroughly:
| Don’t rely on a single source for your research. Use a variety of sources such as books, academic journals, reliable websites, and primary sources to gather different perspectives and valuable information. | |
| While conducting research, make sure to take detailed notes of important information, quotes, and references. This will help you keep track of your sources and easily refer back to them when writing your essay. | |
| Before using any information in your essay, evaluate the credibility of the sources. Make sure they are reliable, up-to-date, and authoritative to strengthen the validity of your arguments. | |
| Organize your research materials in a systematic way to make it easier to access and refer to them while writing. Create an outline or a research plan to structure your essay effectively. |
By following these tips and conducting thorough research on your topic, you will be able to write a well-informed and persuasive essay that effectively communicates your ideas and arguments.
Creating a Strong Thesis Statement
A thesis statement is a crucial element of any well-crafted essay. It serves as the main point or idea that you will be discussing and supporting throughout your paper. A strong thesis statement should be clear, specific, and arguable.
To create a strong thesis statement, follow these tips:
- Be specific: Your thesis statement should clearly state the main idea of your essay. Avoid vague or general statements.
- Be concise: Keep your thesis statement concise and to the point. Avoid unnecessary details or lengthy explanations.
- Be argumentative: Your thesis statement should present an argument or perspective that can be debated or discussed in your essay.
- Be relevant: Make sure your thesis statement is relevant to the topic of your essay and reflects the main point you want to make.
- Revise as needed: Don’t be afraid to revise your thesis statement as you work on your essay. It may change as you develop your ideas.
Remember, a strong thesis statement sets the tone for your entire essay and provides a roadmap for your readers to follow. Put time and effort into crafting a clear and compelling thesis statement to ensure your essay is effective and persuasive.
Developing a Clear Essay Structure
One of the key elements of writing an effective essay is developing a clear and logical structure. A well-structured essay helps the reader follow your argument and enhances the overall readability of your work. Here are some tips to help you develop a clear essay structure:
1. Start with a strong introduction: Begin your essay with an engaging introduction that introduces the topic and clearly states your thesis or main argument.
2. Organize your ideas: Before you start writing, outline the main points you want to cover in your essay. This will help you organize your thoughts and ensure a logical flow of ideas.
3. Use topic sentences: Begin each paragraph with a topic sentence that introduces the main idea of the paragraph. This helps the reader understand the purpose of each paragraph.
4. Provide evidence and analysis: Support your arguments with evidence and analysis to back up your main points. Make sure your evidence is relevant and directly supports your thesis.
5. Transition between paragraphs: Use transitional words and phrases to create flow between paragraphs and help the reader move smoothly from one idea to the next.
6. Conclude effectively: End your essay with a strong conclusion that summarizes your main points and reinforces your thesis. Avoid introducing new ideas in the conclusion.
By following these tips, you can develop a clear essay structure that will help you effectively communicate your ideas and engage your reader from start to finish.
Using Relevant Examples and Evidence
When writing an essay, it’s crucial to support your arguments and assertions with relevant examples and evidence. This not only adds credibility to your writing but also helps your readers better understand your points. Here are some tips on how to effectively use examples and evidence in your essays:
- Choose examples that are specific and relevant to the topic you’re discussing. Avoid using generic examples that may not directly support your argument.
- Provide concrete evidence to back up your claims. This could include statistics, research findings, or quotes from reliable sources.
- Interpret the examples and evidence you provide, explaining how they support your thesis or main argument. Don’t assume that the connection is obvious to your readers.
- Use a variety of examples to make your points more persuasive. Mixing personal anecdotes with scholarly evidence can make your essay more engaging and convincing.
- Cite your sources properly to give credit to the original authors and avoid plagiarism. Follow the citation style required by your instructor or the publication you’re submitting to.
By integrating relevant examples and evidence into your essays, you can craft a more convincing and well-rounded piece of writing that resonates with your audience.
Editing and Proofreading Your Essay Carefully
Once you have finished writing your essay, the next crucial step is to edit and proofread it carefully. Editing and proofreading are essential parts of the writing process that help ensure your essay is polished and error-free. Here are some tips to help you effectively edit and proofread your essay:
1. Take a Break: Before you start editing, take a short break from your essay. This will help you approach the editing process with a fresh perspective.
2. Read Aloud: Reading your essay aloud can help you catch any awkward phrasing or grammatical errors that you may have missed while writing. It also helps you check the flow of your essay.
3. Check for Consistency: Make sure that your essay has a consistent style, tone, and voice throughout. Check for inconsistencies in formatting, punctuation, and language usage.
4. Remove Unnecessary Words: Look for any unnecessary words or phrases in your essay and remove them to make your writing more concise and clear.
5. Proofread for Errors: Carefully proofread your essay for spelling, grammar, and punctuation errors. Pay attention to commonly misused words and homophones.
6. Get Feedback: It’s always a good idea to get feedback from someone else. Ask a friend, classmate, or teacher to review your essay and provide constructive feedback.
By following these tips and taking the time to edit and proofread your essay carefully, you can improve the overall quality of your writing and make sure your ideas are effectively communicated to your readers.
Related Post
How to master the art of writing expository essays and captivate your audience, convenient and reliable source to purchase college essays online, step-by-step guide to crafting a powerful literary analysis essay, unlock success with a comprehensive business research paper example guide, unlock your writing potential with writers college – transform your passion into profession, “unlocking the secrets of academic success – navigating the world of research papers in college”, master the art of sociological expression – elevate your writing skills in sociology.

- 630 730 8825
How to Edit a College Essay: A Guide in 10 Steps
Sana rahman.
- Last Updated on September 23, 2024
Table of Contents

Once you complete the first draft of your Common App personal statement , you should give yourself a big round of applause. It’s no easy task to get it all down on paper, so congratulations on getting to this part of the process! Unfortunately, no one’s first draft is perfect, so I’m here to guide you through the next step and explain how to edit a college essay.
How to Edit a College Essay
There are lots of individualized tips that I could give you to explain how to edit a college essay, but I want to make sure you hit on every one to ensure that your essay is in the best shape possible. To make sure we’re on this journey together, I want you to imagine this process like you’re preparing for a road trip. Remember, this stuff takes time, so feel free (and a little obligated) to take a break as you’re learning how to edit a college essay.
Stage One: Mapping it Out
Before we go anywhere, we need to know where we want to go. Is our map pointing us in the right direction?
Step 1: Read Your Draft
Acting as an objective reader, give your first draft a read. When writing your college essay, one of your main goals is to make your admissions reader root for you. So when you read this, are you rooting for you? Are you convinced of what you’re arguing? Are you staying on topic with the prompt you chose in the first place? If not, you’ll be able to tell where your essay is falling flat through this initial read. Note the places where you find yourself losing attention—those will be places to check back on when you edit your essay on the paragraph and sentence level.
Step 2: Re-Outline the Essay
Here is where we’ll map out our route and detect with certainty any bumps along the way with an outline. Identify and isolate your thesis statement and the intros and conclusions of each paragraph, then list them in the form of a skeletal outline. Does it makes sense to you? Is the essay following chronologically? Thematically? If it is, the essay’s in a good place to move on to stage two. If not, this is the time to see where things went wrong. Use this outline as a skeleton to rewrite the parts that don’t work so that they better connect to the overall story.
Step 3: Re-Evaluate Your Outline
Now that you have your outline (or your map) in front of you—do you like what your thesis says about you? Is it arguing for the traits that you hope to demonstrate to college admissions? Is it representative of who you are? If it’s not, that’s okay! This is the time to catch the big issues. If you don’t like where you’re going, it’s okay to scrap the map and start again.
Stage 2: Prepping the Car
For our car (essay) to get us across the country (into your Common App portal), it has to be in running condition. Do we have enough gas to get there? Has the oil been checked?
Step 4: Asses Your “Hook”
The first thing you want to check is your introductory hook. This is the one sentence of your essay that’s going to do the most heavy lifting. The hook of your essay should draw the reader in, and there are a few very effective ways to do it. I recommend using lots of sensory language and present tense, but a grabbing rhetorical question may work just as well. This is a great part of your essay to workshop with others to make sure it’s reading effectively from someone else’s perspective. For more creative ideas on how to write an attention-grabbing opening, check out our blog post on writing a great essay hook .
Step 5: Examine Your Paragraphs
Your essay should be divided into paragraphs, and while there’s no rule about having exactly three body paragraphs sandwiched between an introduction and conclusion, there should be a purpose to each paragraph. In each section, you should introduce a new event or defend the themes in your introduction. It’s very easy to just list what you want to say per paragraph, but there’s an extra step you need to take to defend your statements in each paragraph. Just saying that you developed a great work ethic during your track season freshman year is much different than explaining how.
Step 6: Check for Authenticity
Once your hook and paragraphs are in good working order, it’s time to do yet another read through and make sure that your essay sounds like you! College admissions readers are expecting to hear from smart, well-rounded, passionate students. Emphasizing that last part, they’re expecting to hear from students. Using vocabulary outside of your usual domain will be awkwardly noticeable to an admissions reader, and it won’t help your application in the slightest. If it feels like you’re reading a thesaurus more than you’re reading yourself, make the appropriate changes.

Stage Three: Packing the Bags
Before we can race off into the sunset, we have to make sure that we have everything in the car for the long journey ahead. Snacks? Luggage? Immaculate grammar?
Step 7: Vary Sentence Structure
As you start to think about how to edit a college essay at the sentence level, the first thing you’ll want to check on is variation in your sentence structure. This is basically to say, you don’t want your sentences to be of the same length throughout. Though correct usage of colons, em dashes, and commas can be impressive in a long, drawn-out sentence, you’ll end up losing your reader’s attention if every sentence looks the same. You need to change it up. Every once in a while, see if you can put in a short sentence to break the monotony and make sure the reader is still with you.
Step 8: Check the Word Count
Your college essay prompt is, more often than not, going to supply you with a very strict word count. This is not a suggestion, and if you go over the word count, it is very possible that your admissions reader will simply stop reading. So much for your beautiful conclusion! This isn’t a comprehensive list, but to slim your essay down, try these tricks:
Being able to do something and doing something usually mean the same thing:
- Long: I was able to bring my grades up.
- Short: I brought my grades up.
Contractions are always your friend, make use of them:
- Long: I would go to the computer lab after school.
- Short: I’d go to the computer lab after school .
Time frames will become contextually evident, you don’t have to spell it out:
- Long: During my high school career… // As a child growing up…
- Short: In high school… // Growing up…
If a clause is using too much word count, turn it into an adjective:
- Long: At the dance at the end of the school year last year…
- Short: At last year’s dance…
Confident writing is good writing, cut ‘I believe’ or ‘I think’ wherever you can:
- Long: I believe participating in clubs will help me build a community.
- Short: Participating in clubs will help me build a community .
If you find yourself in the rare position of being under word count, try to get within 150 words of the maximum amount.
Step 9: Perfect Your Grammar
The last thing to do on the sentence level is to ensure that your grammar is spotless. This is a short checklist of things I’d like you to look out for:
- Subject-verb agreement. As you’re reading, you may find that there are three or four verbs in a sentence, but you only want your reader to focus on one important one. Make sure this appears as early in the sentence as possible so your reader is clued into what’s going on, and create a new sentence for the other verbs if you have to. This may even help vary your sentence structure.
- Colons and semicolons. These are perfectly fair game to use, but it’s imperative that they’re used correctly. As a general rule of thumb: colons are used to introduce something, like a list, a quotation, or a related sentence. A semicolon is used to separate two clauses; it usually takes the place of a conjunction.
- Typos. Most software will not always catch your typos if nothing is misspelled. If you meant to write ‘is’ but wrote ‘it’ instead, Google Docs will not let you know! Make sure you do an honest read-through to ensure these glaring errors are gone.
- Tense issues. When you’re writing in the present tense for one paragraph, it’s difficult to get back into the past tense with complete seamlessness. Make sure your verb tenses agree all the way through each sentence.

Stage 4: Rest Stop
On your way to your destination, you’re going to want to take a few breaks. When you stop, consider making conversations with fellow drivers.
Step 10: Seek Feedback
The last step in the editing process is to get feedback. Though you can definitely do this throughout the editing process, you may feel more comfortable giving your essay to others once you’re proud of the finished product. Getting feedback is a vital part of the editing process and is made to ensure that your essay is reading the way you want to others.
While it’s very important to get a second opinion, be cautious of seeking too many. When there’s an influx of opinions, you may forget the message you wanted to convey in the first place. Do your best to limit your number of readers to about five people. And for more focused feedback and editing suggestions, consider the help of a professional College Essay Coach .
While this advice is specifically for the Common App personal statement, these steps are applicable to all of your college essay. I will say though, supplemental essays are usually meant for you to answer straightforward questions.
Regardless of the type of essay, the key is to be intentional in your writing and editing. Editing is not just about correcting grammar or polishing sentences; it’s about refining your voice and ensuring that your narrative aligns with your goals.

How to Write the Northwestern Supplemental Essays
Though short in length, the Northwestern supplemental essays are not necessarily easier to write than the longer Common

How to End a College Essay: Six Strategies
Congratulations! You’ve reached the end of your Common App personal statement…or you’re thinking about the end of your

How to Write the UPenn Supplemental Essays
If you aim to join the ranks of UPenn’s elite students, you’ll need more than good grades and
Upcoming College Admissions workshops:

Become a National Merit Scholar by Acing the PSAT
Accolades and scholarships await! Get ready to add National Merit Scholar to your college applications, take advantage of National Merit Scholarships, and prepare for the upcoming SAT by mastering the PSAT/NMSAT.

20 Tips For College Admissions: Apply, Afford & Succeed
Unlock the secrets to apply, afford, and succeed in college admissions with our workshop. We guide both students and parents through crucial strategies, navigating deadlines, maximizing acceptance opportunities, and demystifying the financial aid landscape—essential for anyone embarking on the college journey, regardless of graduation year.

Juniors: Start Right Here, Right Now!
We guide you through the necessary steps to successfully plan for college during your junior year of high school. By having a plan, you'll reduce stress and make sure you're on the right track moving into senior year.
We are dedicated to helping students and parents successfully navigate the college admissions process, providing a personalized experience based on your unique needs and goals.
Remote Locations
- 1415 W 22nd St Tower Floor, Oak Brook, IL
- 5570 FM 423 Suite 250-2119 Frisco, TX
- 2590 Welton St Ste. 200 #1031 Denver, CO
- 12800 Whitewater Drive Suite 100-2033 Minnetonka, MN
Quick Links
- Kevin Krebs, Founder
- 630-730-8825
- Employee Login
- Students & Parents Login
- News and Press
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
© HelloCollege 2024. All Rights Reserved.

Your College Admissions Journey, Mapped Out!
Introducing our college planning timeline with a handy checklist of essential tasks, a step-by-step guide for every grade level, from freshman to senior year, AND financial aid, college applications, extracurricular activities, and more.
Articles Blog
The guide to writing an essay for beginners.
Writing an essay may be intimidating, especially for beginners. The process becomes easier if you understand the fundamental structure and strategy. Essays effectively convey ideas, argue, and critique issues. This guide will help you write an essay from structure to final draft revision. Even beginners will find the procedure easy with clear instructions and examples. Anyone can learn to write a convincing essay with the appropriate instruction. Essays allow complicated ideas to be expressed clearly with structure. Mastering essay writing will help you in many sectors, whether you’re writing for school, college, or personal projects.
Understanding Essay Structure
Essays have a simple framework that organizes thoughts and ideas. This framework underpins your writing, making it clear and easy to understand. An introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion are standard in all essays. The beginning introduces your thesis and establishes the tone for the essay. Support your argument with evidence, analysis, and examples throughout the essay. Each body paragraph should address one thesis-related concept. The conclusion concludes your argument, summarizes your essential arguments, and supports your thesis. Writing a well-organized and successful essay starts with understanding this basic framework.
Introduction: Capturing Attention
The start is crucial to your essay. Your reader will notice it first, setting the tone for the rest. A good introduction does more than present the topic—it captivates the reader. You may start with a fun fact, a challenging question, or a pertinent quotation. This hook should include background information that contextualizes your issue and makes it worth researching. Your introduction should conclude with a concise thesis statement that states your essay’s central idea. Your thesis guides your readers through the paper.
Body Paragraphs: Building Your Argument
Your essay’s body develops your thesis and provides proof. Each paragraph’s topic or opening sentence should state its central theme. The rest of the paragraph should support the topic phrase using facts, quotations, or examples. After providing the facts, explain how they help your premise and enhance your case. A coherent narrative requires each paragraph to flow logically into the next. Paragraph transitions assist the reader in going from thought to idea. After reading the body, your reader should grasp your argument and how each piece of evidence fits together.
Conclusion: Wrapping Things Up
The conclusion of your essay is your last chance to strengthen your case and wow the reader. Restate your argument based on the evidence you’ve offered throughout the essay. Avoid word-for-wording your thesis. Instead, rewrite it to reflect your newfound understanding and ideas from writing the essay. You should also briefly outline your main points and explain how they support your thesis. Firm conclusions don’t merely regurgitate facts; they bring closure. You may close with a thought-provoking comment, a reflection on your argument’s more enormous ramifications, or an action request. Your conclusion should keep readers thinking about your essay long after they finish.
Using Services for Writing
If you can’t compose an essay or don’t have time, try employing a professional writing service. Using these services, you may hire qualified writers to write a high-quality essay that matches your needs. Before using a writing service, you should review the service you want to use. Some services may not be high-quality or timely. Read customer reviews to make the proper pick. For example, services like ScamFighter can share their experiences to help you make decisions. Read reviews to avoid unreliable services and locate a writing platform that matches your demands.
Revising and Editing Your Essay
The writing process must include revising and editing. Break from your initial draft and return to it with new eyes. When reworking, focus on essay structure and flow. Does every paragraph support your thesis? Is your argument clear and logical? After fixing these significant flaws, you may edit more closely. Check for repetitious or unneeded material and simplify sentences. Finalize your essay by checking grammar, spelling, and punctuation. Grammarly and Hemingway can help you find errors and enhance your writing.
Common Types of Essays
Each type of essay has its own purpose and style. Knowing the varieties of essays will help you write effectively. For instance, narrative essays convey stories. They make sharing a personal tale or experience innovative and intriguing. On the other hand, descriptive essays describe a person, location, or object in great detail. These pieces use sensory details and sophisticated language to create vivid descriptions. Expository essays clarify an idea or provide information. They demand clear, logical thinking and breaking down complicated ideas into simpler bits. Persuasion is the focus of argumentative writing. In an argumentative essay, you take a stand on a subject and give evidence to persuade the reader.
Essay writing might be difficult, but with the appropriate attitude and mindset, it’s easier. By knowing the essay format, outlining your thoughts, and reviewing your work, you may write a convincing essay. Professional services can help you write a good essay if you find it too difficult. Read reviews before picking a service to be sure you’re choosing wisely. This guide shows novices how to create an intriguing essay for academic, career, or personal improvement.
Related Posts
6 ways to reduce stress and burnout.
Stress and burnout have become prevalent issues that negatively impact both personal well-being and professional performance in today’s fast-paced society. Balancing multiple responsibilities, meeting tight deadlines, and…
Habits to Help You Learn Better
Learning is central to growth at every level – academic, professional, or personal. While some individuals appear to learn easily, others may struggle with the retention of…
The Power of a Personal Statement Generator: Crafting Your Story with Ease
Writing a personal statement is usually the most difficult chore for professionals trying to land their ideal job or students hoping to get into demanding academic programs….
Egypt Private Tours: A Personalized Adventure Through the Land of Legends
Egypt, often referred to as the cradle of civilization, is home to some of the world’s most awe-inspiring wonders. From the towering Pyramids of Giza and the…
Designing Senior-Friendly Spaces: Our Role in Shaping the Future of Assisted Living Architecture
As the population ages, the need for thoughtfully designed, senior-friendly spaces has become a top priority for assisted living in Cincinnati. The University of Cincinnati, with its…
UpStudy Camera Math Solver: Revolutionizing Derivative and Integral Problem-Solving
Mathematics is a subject that often challenges students across the globe. Among its many branches, calculus, especially derivatives and integrals, tends to be particularly daunting for learners….
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Learning Objectives
- Determine the purpose and structure of the process analysis essay
- Understand how to write a process analysis essay
The Purpose of Process Analysis in Writing
The purpose of a process analysis essay is to explain how to do something or how something works. In either case, the formula for a process analysis essay is the same. The process is articulated into clear, definitive steps.
Almost everything we do involves following a step-by-step process. From riding a bike as children to learning various jobs as adults, we initially need instructions to effectively execute the task. Likewise, we have likely had to instruct others, so we know how important good directions are—and how frustrating it is when they are poorly put together.
Writing at Work
The next time you have to explain a process to someone at work, be mindful of how clearly you articulate each step. Strong communication skills are critical for workplace satisfaction and advancement. Effective process analysis plays a critical role in developing that skill set.
The Structure of a Process Analysis Essay
The process analysis essay opens with a discussion of the process and a thesis statement that states the goal of the process. The organization of a process analysis essay is typically chronological. That is, the steps of the process are conveyed in the order in which they usually occur. Body paragraphs will be constructed based on these steps. If a particular step is complicated and needs a lot of explaining, then it will likely take up a paragraph on its own. But if a series of simple steps is easier to understand, then the steps can be grouped into a single paragraph.
The time transitional phrases provided earlier are also helpful in organizing process analysis essays (see in 4.2 Narration, Transitional Words and Phrases for Expressing Time and in 4.3 Illustration, Phrases of Illustration ). Words such as first , second , third , next , and finally are helpful cues to orient reader and organize the content of essay.
Self-Practice Exercise 4.5
H5P: Process Analysis Practice
Exercise Preamble
Choose a process to write about. Remember that you will need to clearly articulate all the necessary steps, so it should be a process you know really well. If you’re feeling stuck, here are some ideas:
- Tying a shoelace
- Parallel parking
- Planning a successful first date
- Being an effective communicator
Begin by listing all the steps you need to undertake to achieve this process. Be as detailed as possible and include everything at this stage. Point form is fine. Just get everything out — you can edit and revise at the next step.
Now, revise your list to put the points you have already articulate above in the order that makes the most sense for your process analysis
Thesis Statement
- What will the thesis statement of your process analysis be? Remember that it should articulate the goal of the process.
- Decide how many paragraphs you will need. Remember that the steps should be articulated in order, and that you can combine smaller steps, but more complex ones may need their own paragraphs. Make a note of what will be covered in each paragraph.
- What transition words will you use to show the connections between your ideas?
Writing a Process Analysis Essay
Choose a topic that is interesting, is relatively complex, and can be explained in a series of steps. As with other rhetorical writing modes, you should choose something you know well so that you can more easily describe the finer details about each step in the process. Your thesis statement should come at the end of your introduction, and it should state the final outcome of the process you are describing.
Body paragraphs are composed of the steps in the process. Each step should be expressed using strong details and clear examples. Use time transitional phrases to help organize steps in the process and to orient readers. The conclusion should thoroughly describe the result of the process described in the body paragraphs. See Appendix 1: Readings: Examples of Essays to read an example of a process analysis essay.
Key Takeaways
- A process analysis essay explains how to do something, how something works, or both.
- The process analysis essay opens with a discussion of the process and a thesis statement that states the outcome of the process.
- The organization of a process analysis essay typically follows a chronological sequence.
- Time transitional phrases are particularly helpful in process analysis essays to organize steps and orient reader.
ENGL Resources Copyright © by Tara Horkoff. All Rights Reserved.
Share This Book
Verify originality of an essay
Get ideas for your paper
Cite sources with ease
From Start to Finish: Writing a Compelling Essay Conclusion
Updated 23 Sep 2024

Any college student tasked with writing an essay knows that a strong conclusion is just as crucial as choosing the right topic or crafting a compelling thesis statement. This guide will walk you through the do's and don'ts of writing an effective essay conclusion, along with practical examples. Often, students wonder, “Which writing service can help me write my essay online?” With our tips, you'll feel more confident in completing your assignment, even when only the final part is finished!
What is an Essay Conclusion?
An essay conclusion is the final paragraph that wraps up your argument, reflecting the main points discussed in your essay. It’s more than just a summary; it’s an opportunity to leave a lasting impression on your reader. What makes an essay conclusion unique is its ability to synthesize the key points, reinforce your thesis, and provide a sense of closure to the topic.
Writing a strong conclusion can be challenging because it requires balancing between reiterating your main ideas without simply repeating what has already been said. It should connect the arguments presented while demonstrating the broader significance of your discussion.
Special features of a well-crafted conclusion include a restatement of the thesis in light of the evidence provided, a concise summary of the main points, and a closing statement that offers insight or a call to action. The language should be clear and impactful, leaving readers with a thought-provoking final message.
Common difficulties in writing conclusions include avoiding redundancy, knowing how to articulate the significance of your findings, and ensuring that your conclusion is neither too brief nor overly extended. It’s essential to tie all elements of your essay together and avoid introducing new information.
A good conclusion gives readers a clear understanding of your argument’s importance and encourages them to think further about the subject matter. By mastering this final part of your essay, you strengthen the overall effectiveness of your writing.
How to Write an Essay Conclusion: A Step-by-Step Guide
To create an effective essay conclusion, it's essential to start by restating your thesis in a new way, reinforcing the main argument without merely repeating it. Summarizing key points helps remind readers of the evidence supporting your thesis, ensuring that the conclusion is cohesive and impactful. Additionally, connecting your argument to a broader context can highlight its significance and encourage readers to think further about the topic.
When writing a conclusion, it’s crucial to avoid common pitfalls. Do not introduce new information or arguments, as this can confuse the reader and disrupt the flow of your essay. Instead, focus on tying together the points discussed, creating a clear and logical end to your paper. Ensure your tone is consistent with the rest of your essay, whether it’s formal, persuasive, or reflective.
A strong conclusion also includes a closing statement that leaves a lasting impression . This can be a thought-provoking question, a call to action, or a final insight that resonates with your readers. For example, you could ask, “As technology evolves, how can we balance its benefits with the potential for distraction in education?”
Finally, remember that a well-crafted conclusion is concise and impactful, typically comprising about 10% of your essay’s total length. It should provide closure without feeling rushed or overly lengthy. By mastering these techniques, you can enhance the overall effectiveness of your writing, ensuring that your conclusion resonates with your audience.
Do’s and Don’ts for Writing an Essay Conclusion
Do’s.
Original Thesis: Technology can both enhance and hinder education. Restated: While technology offers valuable tools for learning, its misuse can detract from educational goals.
- Summarize Key Points: Briefly highlight the main arguments of your essay. This reinforces your points and ties everything together.
- End with a Strong Closing Statement: Use a thought-provoking question, a call to action, or a powerful statement that leaves a lasting impression.
- Connect to the Bigger Picture: Show the broader implications of your essay's findings to demonstrate its significance.
- Maintain a Consistent Tone: Ensure the conclusion matches the tone of the entire essay, whether it's formal, persuasive, or reflective.
Don’ts
- Don’t Introduce New Information: Avoid introducing new arguments or evidence in your conclusion, as this can confuse readers.
- Don’t Repeat the Introduction: Don’t simply copy your introduction or main points. Instead, synthesize them in a fresh way.
- Don’t Use Clichés: Phrases like "In conclusion" or "To sum up" are unnecessary and detract from the impact of your writing.
- Don’t Undermine Your Argument: Avoid statements like “This is just my opinion” or “I could be wrong.” Be confident in your conclusions.
- Don’t Make the Conclusion Too Long: Keep it concise and focused. The conclusion should be about 10% of your essay’s total length.
How to Conclude Different Types of Essays
Argumentative essay.
When concluding an argumentative essay, start by restating your position to reinforce your stance. Summarize the key arguments you presented, emphasizing why they support your thesis. Then, address the broader implications of your viewpoint. For example, if your essay argues for renewable energy adoption, discuss how this shift could impact future generations and suggest actions society can take to support this transition.
Compare & Contrast Essay
In a compare and contrast essay, your conclusion should highlight the main similarities and differences discussed in your body essay paragraphs. Reflect on what these comparisons reveal about the subjects. For instance, if comparing two educational systems, you might conclude with an insight into how they shape student success differently and why understanding these differences is crucial for policy-making.
Descriptive Essay
A descriptive essay’s conclusion should evoke the essence of your subject, leaving readers with a vivid image or emotion. Reiterate the main sensory details and reinforce your crafted atmosphere or mood. For example, if describing a serene beach, end with a reflection on the tranquility it offers and why such moments of peace are essential in our hectic lives.
Narrative Essay
To conclude a narrative essay, reflect on the lessons learned or the significance of your story. Tie your ending back to the beginning to create a sense of closure. If your narrative began with a difficult personal challenge, end by discussing how overcoming it changed your perspective or influenced your life path.
Analytical Essay
In an analytical essay conclusion, summarize your main findings and link them back to your thesis. Discuss the broader implications of your analysis and suggest areas for further research. For example, if analyzing a literary work, you might explore how your interpretation contributes to a deeper understanding of the author’s message.
Expository Essay
Conclude an expository essay by summarizing the key points discussed and explaining their significance. Reinforce how the information helps the reader understand the topic better. For example, if explaining a scientific concept, emphasize why it’s essential for future innovations or everyday life.
Cause and Effect Essay
The conclusion of a cause-and-effect essay should recap the leading causes and effects explored in the essay. Highlight the importance of understanding these relationships and suggest possible solutions or future implications. For example, if discussing climate change, suggest actions to mitigate its effects.
Persuasive Essay
In a persuasive essay conclusion, reinforce your position and urge the reader to take action or reconsider their viewpoint. Use compelling language to leave a strong impact. For example, if advocating for animal rights, end with a powerful call to support humane practices and animal welfare.
Reflective Essay
A reflective essay conclusion should summarize the insights gained from your experiences. Discuss how the topic influenced your thoughts and behavior, and suggest what others might learn from your reflections. For example, if reflecting on a volunteering experience, highlight how it reshaped your understanding of community service.
Process Essay
Conclude a process essay by restating the main steps involved and emphasizing the outcome. Explain why understanding this process is valuable and offer additional tips or resources. For example, if writing about baking a cake, discuss how mastering this process can boost confidence in cooking and provide a basis for more complex recipes.
How to Conclude an Essay: Paragraph Outline Structure
- Restate the Thesis: Begin your conclusion by rephrasing your thesis statement to remind readers of your main argument without simply repeating it.
- Summarize Key Points: Highlight the main points discussed in your essay. This should be a brief recap, not an exhaustive review of each argument.
- Connect to the Broader Context: Explain the significance of your argument in a broader context, such as its impact on society, future research, or practical applications.
- Provide a Final Insight or Call to Action: End with a thought-provoking question, a call to action, or a concluding thought that reinforces your essay’s overall message. This leaves the reader with something to ponder.
- Ensure Cohesion and Flow: Make sure each part of your conclusion flows logically from one point to the next, providing a clear and cohesive summary of your essay.
Conclusion: Wrapping Up Your Essay Effectively
In conclusion, crafting a strong essay ending is essential to leave a lasting impression on your reader. Your conclusion should not only restate the thesis and summarize key points but also connect your arguments to a broader context, emphasizing the significance of your work. By doing so, you provide clarity and closure, reinforcing the value of your discussion.
Ready to take your essay writing to the next level? Whether you need help refining your conclusion or polishing the entire piece, our expert services are here to assist. Contact us today to achieve your academic goals!
Was this helpful?
Thanks for your feedback.

Written by Jamie Wallace
Jamie Wallace, editor and freelance writer, specializes in Philosophy, Literature, and Art. His interdisciplinary background and passion for critical analysis enable him to assist students in crafting compelling and well-researched papers.
Related Blog Posts
How to make a cover page essay in various formatting styles: mla, apa, asa, chicago.
Cover sheets often make your first impression of your work, and each style has a specific layout, font, and structure guidelines. This article will...
150+ Personal Essay Topics to Spark Your Creativity
What Is a Personal Essay and Why Is It Important? A personal essay is a form of writing that allows the author to express personal experiences, ...
100+ Engaging Evaluation Essay Topics: From Internet Trends to Cultural Identity
Evaluation essays involve making value judgments about various subjects. To craft an effective evaluation essay, you must first identify a clear ar...
Join our 150K of happy users
- Get original papers written according to your instructions
- Save time for what matters most
Your subscription is almost coming to an end. Don’t miss out on the great content on Nation.Africa
Ready to continue your informative journey with us?
Your premium access has ended, but the best of Nation.Africa is still within reach. Renew now to unlock exclusive stories and in-depth features.
Reclaim your full access. Click below to renew.
Subscribe for a month to get full access

NMG’s climate change desk is a step in the right direction
Francis Kizito
By Guest Columnists
What you need to know:
…a dedicated team solely focusing on in-depth coverage and the impact on the socio-economic environment will be a cornerstone for this desk
On September 17, Nation Media Group Uganda announced the launch of a special desk on climate change to raise awareness and educate its readers on the issue. To understand the urgency of addressing climate change, Uganda ranks as the 13th-most-vulnerable country in the world and 160th out of 192 nations in readiness to confront the threat, according to the Notre Dame Global Adaptation Initiative (2021).
Globally, the latest data suggests that 2024 could outrank 2023 as the hottest year due to human-caused climate change pushing temperatures to record highs. A survey done by the Afrobarometer found that Ugandans who are aware of climate change are solidly behind government action to address the crisis, even at significant economic cost.
They see it as a collective responsibility and want greater engagement on the issue by the government, businesses, developed nations, and ordinary citizens. NMG’s commitment to set up a special desk for climate change coverage is a visionary step in the right direction in giving climate change stories the much-deserved attention and ensuring they are prioritised through the news cycle just like entertainment and politics. Firsthand storytelling from the most vulnerable members of society, including farmers, women, and refugees who are often ignored, and a dedicated team solely focusing on in-depth coverage and the impact on the socio-economic environment will be a cornerstone for this desk.
This desk presents an opportunity to act as a springboard onto which climate change research done by academia and development partners is broken down into the day-to-day context for an average Ugandan to understand fostering collaboration between journalists and experts from different fields for comprehensive and nuanced newsroom reporting.
Despite the intense, frequent, and extreme heat waves, droughts, and unprecedented floods, there has been a lacklustre response from the government on how to build resilient and adaptive mechanisms to combat future calamities. Having committed to reducing its net greenhouse gas emissions by 24.7 percent below business-as-usual levels by 2030, the desk will cast these events into the public discourse and create an important avenue to demand accountability from the government and other actors.
According to a handbook for journalists by Unseco, contrary to popular belief, climate is an issue full of knock-on concerns that can sell and attract new audiences online for the media; hence, an opportunity for other media houses to learn and replicate the idea of climate change desks to create national discourse and highlight sustainable development issues. This innovative approach to climate change storytelling, coupled with intriguing ideas like the first-ever Ugandan podcast on climate change titled ‘Climate Talk Uganda’ are vital steps in enhancing public discourse on climate change. I urge all Ugandans to embrace these initiatives.
Mr Francis Kizito is a Communications Officer with the Climate Smart Jobs Programme.

NMG introduces special desk for climate change
In Africa, weather pattern disruptions have caused irregular rainfall, floods, and prolonged droughts, deeply impacting agriculture, the continent’s primary livelihood

PRIME Villains and saints in Uganda garbage story
But how do you get them to take interest in garbage or floods stories and be part of the solution, not the problem? Link it to their everyday life, to their lifestyle, and to how they can be part...

PRIME Use press freedom to save the environment
Citizen journalists – and all citizens – must therefore rise to the occasion and riding on this year’s theme make their voices heard
PRIME Newsrooms need climate literacy to tell stories well
While the media has consistently published environment and climate change stories for years, there have been a lot of perceived limitations in telling the stories well

PRIME Climate change: Journalists urged to combat misinformation
Broadly, journalists were on Wednesday tasked to tell stories that influence policymakers to take action against climate change
Register to continue reading this premium article
It's free!
Register to begin your journey to our premium content Subscribe for full access to premium content
Access the best of Monitor's Independent Journalism
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write an argumentative essay | Examples & tips
How to Write an Argumentative Essay | Examples & Tips
Published on July 24, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
An argumentative essay expresses an extended argument for a particular thesis statement . The author takes a clearly defined stance on their subject and builds up an evidence-based case for it.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
When do you write an argumentative essay, approaches to argumentative essays, introducing your argument, the body: developing your argument, concluding your argument, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about argumentative essays.
You might be assigned an argumentative essay as a writing exercise in high school or in a composition class. The prompt will often ask you to argue for one of two positions, and may include terms like “argue” or “argument.” It will frequently take the form of a question.
The prompt may also be more open-ended in terms of the possible arguments you could make.
Argumentative writing at college level
At university, the vast majority of essays or papers you write will involve some form of argumentation. For example, both rhetorical analysis and literary analysis essays involve making arguments about texts.
In this context, you won’t necessarily be told to write an argumentative essay—but making an evidence-based argument is an essential goal of most academic writing, and this should be your default approach unless you’re told otherwise.
Examples of argumentative essay prompts
At a university level, all the prompts below imply an argumentative essay as the appropriate response.
Your research should lead you to develop a specific position on the topic. The essay then argues for that position and aims to convince the reader by presenting your evidence, evaluation and analysis.
- Don’t just list all the effects you can think of.
- Do develop a focused argument about the overall effect and why it matters, backed up by evidence from sources.
- Don’t just provide a selection of data on the measures’ effectiveness.
- Do build up your own argument about which kinds of measures have been most or least effective, and why.
- Don’t just analyze a random selection of doppelgänger characters.
- Do form an argument about specific texts, comparing and contrasting how they express their thematic concerns through doppelgänger characters.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

An argumentative essay should be objective in its approach; your arguments should rely on logic and evidence, not on exaggeration or appeals to emotion.
There are many possible approaches to argumentative essays, but there are two common models that can help you start outlining your arguments: The Toulmin model and the Rogerian model.
Toulmin arguments
The Toulmin model consists of four steps, which may be repeated as many times as necessary for the argument:
- Make a claim
- Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim
- Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim)
- Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives
The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays. You don’t have to use these specific terms (grounds, warrants, rebuttals), but establishing a clear connection between your claims and the evidence supporting them is crucial in an argumentative essay.
Say you’re making an argument about the effectiveness of workplace anti-discrimination measures. You might:
- Claim that unconscious bias training does not have the desired results, and resources would be better spent on other approaches
- Cite data to support your claim
- Explain how the data indicates that the method is ineffective
- Anticipate objections to your claim based on other data, indicating whether these objections are valid, and if not, why not.
Rogerian arguments
The Rogerian model also consists of four steps you might repeat throughout your essay:
- Discuss what the opposing position gets right and why people might hold this position
- Highlight the problems with this position
- Present your own position , showing how it addresses these problems
- Suggest a possible compromise —what elements of your position would proponents of the opposing position benefit from adopting?
This model builds up a clear picture of both sides of an argument and seeks a compromise. It is particularly useful when people tend to disagree strongly on the issue discussed, allowing you to approach opposing arguments in good faith.
Say you want to argue that the internet has had a positive impact on education. You might:
- Acknowledge that students rely too much on websites like Wikipedia
- Argue that teachers view Wikipedia as more unreliable than it really is
- Suggest that Wikipedia’s system of citations can actually teach students about referencing
- Suggest critical engagement with Wikipedia as a possible assignment for teachers who are skeptical of its usefulness.
You don’t necessarily have to pick one of these models—you may even use elements of both in different parts of your essay—but it’s worth considering them if you struggle to structure your arguments.
Regardless of which approach you take, your essay should always be structured using an introduction , a body , and a conclusion .
Like other academic essays, an argumentative essay begins with an introduction . The introduction serves to capture the reader’s interest, provide background information, present your thesis statement , and (in longer essays) to summarize the structure of the body.
Hover over different parts of the example below to see how a typical introduction works.
The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education. The use of the internet in academic contexts is on the rise, and its role in learning is hotly debated. For many teachers who did not grow up with this technology, its effects seem alarming and potentially harmful. This concern, while understandable, is misguided. The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its critical benefits for students and educators—as a uniquely comprehensive and accessible information source; a means of exposure to and engagement with different perspectives; and a highly flexible learning environment.
The body of an argumentative essay is where you develop your arguments in detail. Here you’ll present evidence, analysis, and reasoning to convince the reader that your thesis statement is true.
In the standard five-paragraph format for short essays, the body takes up three of your five paragraphs. In longer essays, it will be more paragraphs, and might be divided into sections with headings.
Each paragraph covers its own topic, introduced with a topic sentence . Each of these topics must contribute to your overall argument; don’t include irrelevant information.
This example paragraph takes a Rogerian approach: It first acknowledges the merits of the opposing position and then highlights problems with that position.
Hover over different parts of the example to see how a body paragraph is constructed.
A common frustration for teachers is students’ use of Wikipedia as a source in their writing. Its prevalence among students is not exaggerated; a survey found that the vast majority of the students surveyed used Wikipedia (Head & Eisenberg, 2010). An article in The Guardian stresses a common objection to its use: “a reliance on Wikipedia can discourage students from engaging with genuine academic writing” (Coomer, 2013). Teachers are clearly not mistaken in viewing Wikipedia usage as ubiquitous among their students; but the claim that it discourages engagement with academic sources requires further investigation. This point is treated as self-evident by many teachers, but Wikipedia itself explicitly encourages students to look into other sources. Its articles often provide references to academic publications and include warning notes where citations are missing; the site’s own guidelines for research make clear that it should be used as a starting point, emphasizing that users should always “read the references and check whether they really do support what the article says” (“Wikipedia:Researching with Wikipedia,” 2020). Indeed, for many students, Wikipedia is their first encounter with the concepts of citation and referencing. The use of Wikipedia therefore has a positive side that merits deeper consideration than it often receives.
An argumentative essay ends with a conclusion that summarizes and reflects on the arguments made in the body.
No new arguments or evidence appear here, but in longer essays you may discuss the strengths and weaknesses of your argument and suggest topics for future research. In all conclusions, you should stress the relevance and importance of your argument.
Hover over the following example to see the typical elements of a conclusion.
The internet has had a major positive impact on the world of education; occasional pitfalls aside, its value is evident in numerous applications. The future of teaching lies in the possibilities the internet opens up for communication, research, and interactivity. As the popularity of distance learning shows, students value the flexibility and accessibility offered by digital education, and educators should fully embrace these advantages. The internet’s dangers, real and imaginary, have been documented exhaustively by skeptics, but the internet is here to stay; it is time to focus seriously on its potential for good.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
An argumentative essay tends to be a longer essay involving independent research, and aims to make an original argument about a topic. Its thesis statement makes a contentious claim that must be supported in an objective, evidence-based way.
An expository essay also aims to be objective, but it doesn’t have to make an original argument. Rather, it aims to explain something (e.g., a process or idea) in a clear, concise way. Expository essays are often shorter assignments and rely less on research.
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays , research papers , and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises).
Add a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
The exact format of your citations depends on which citation style you are instructed to use. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago .
The majority of the essays written at university are some sort of argumentative essay . Unless otherwise specified, you can assume that the goal of any essay you’re asked to write is argumentative: To convince the reader of your position using evidence and reasoning.
In composition classes you might be given assignments that specifically test your ability to write an argumentative essay. Look out for prompts including instructions like “argue,” “assess,” or “discuss” to see if this is the goal.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). How to Write an Argumentative Essay | Examples & Tips. Scribbr. Retrieved September 23, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/argumentative-essay/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write a thesis statement | 4 steps & examples, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, how to write an expository essay, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here are some tips to help you select the perfect topic for your essay: 1. Consider Your Interests. Choose a topic that you are passionate about or interested in. Writing about something you enjoy will make the process more enjoyable and your enthusiasm will come through in your writing. 2.
The essay writing process consists of three main stages: Preparation: Decide on your topic, do your research, and create an essay outline. Writing: Set out your argument in the introduction, develop it with evidence in the main body, and wrap it up with a conclusion. Revision: Check your essay on the content, organization, grammar, spelling ...
7 steps to writing a good essay. No essay is the same but your approach to writing them can be. As well as some best practice tips, we have gathered our favourite advice from expert essay-writers and compiled the following 7-step guide to writing a good essay every time. 👍. #1 Make sure you understand the question. #2 Complete background ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Prewriting. Step 2: Planning and outlining. Step 3: Writing a first draft. Step 4: Redrafting and revising. Step 5: Editing and proofreading. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the writing process.
There are three main stages to writing an essay: preparation, writing and revision. In just 4 minutes, this video will walk you through each stage of an acad...
Here are the eight steps to write an essay: Stage 1: Planning. 1. Pick an appropriate research topic. In certain cases, your teacher or professor may assign you a topic. However, in many cases, students have the freedom to select a topic of their choice.
When you receive a paper assignment, your first step should be to read the assignment prompt carefully to make sure you understand what you are being asked to do. Sometimes your assignment will be open-ended ("write a paper about anything in the course that interests you"). But more often, the instructor will be asking you to do
5. Write an outline to help organize your main points. After you've created a clear thesis, briefly list the major points you will be making in your essay. You don't need to include a lot of detail—just write 1-2 sentences, or even a few words, outlining what each point or argument will be.
The basic steps for how to write an essay are: Generate ideas and pick a type of essay to write. Outline your essay paragraph by paragraph. Write a rough first draft without worrying about details like word choice or grammar. Edit your rough draft, and revise and fix the details. Review your essay for typos, mistakes, and any other problems.
This overview of the academic essay conclusion contains helpful examples and links to further resources for writing good conclusions. "How to End An Essay" (WikiHow) This step-by-step guide (with pictures!) by an English Ph.D. walks you through writing a conclusion, from brainstorming to ending with a flourish.
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body. This article provides useful templates and tips to help you outline your essay, make decisions about your structure, and ...
Anything you write will benefit from learning these simple parts of an essay: Here are five steps to make it happen: ThoughtCo is part of the Dotdash Meredith publishing family. Every essay--regardless of its topic--should include a title, purpose/thesis, introduction, body, and conclusion.
Basic essay structure: the 3 main parts of an essay. Almost every single essay that's ever been written follows the same basic structure: Introduction. Body paragraphs. Conclusion. This structure has stood the test of time for one simple reason: It works. It clearly presents the writer's position, supports that position with relevant ...
Stay as concise as possible. Include anecdotal examples if it will help you make your point more clear. If you are writing a formal academic essay, avoid using first-person pronouns. 6. Pay attention to how you cite references. In ancient Greece, using other people's ideas was seen as the mark of a smart person.
Step 2: Pick one of the things you wrote down, flip your paper over, and write it at the top of your paper, like this: This is your thread, or a potential thread. Step 3: Underneath what you wrote down, name 5-6 values you could connect to this. These will serve as the beads of your essay.
Step 5: Proofread your draft. While it's tempting to submit your essay and not look back, taking time to proofread and edit your writing is a critical step in your overall writing procedure. Try to not edit immediately after finishing your draft — let it sit for a day or two if you have the time. You'll notice more subtle mistakes with a ...
Step 1: Choose an Essay Topic. The first step in writing an academic essay is to choose a topic. A topic is the main idea or subject you will write about in your essay. Choose a topic that you are interested in and have a good understanding of. It should also be relevant to the course you are studying and the assignment you are working on.
Tips for Crafting an A+ Essay. 1. Understand the Assignment: Before you start writing, make sure you fully understand the assignment guidelines and requirements. If you have any doubts, clarify them with your instructor. 2. Conduct Thorough Research: Gather relevant sources and information to support your arguments.
This essay begins by discussing the situation of blind people in nineteenth-century Europe. It then describes the invention of Braille and the gradual process of its acceptance within blind education. Subsequently, it explores the wide-ranging effects of this invention on blind people's social and cultural lives.
2. Organize your ideas: Before you start writing, outline the main points you want to cover in your essay. This will help you organize your thoughts and ensure a logical flow of ideas. 3. Use topic sentences: Begin each paragraph with a topic sentence that introduces the main idea of the paragraph.
For more creative ideas on how to write an attention-grabbing opening, check out our blog post on writing a great essay hook. Step 5: Examine Your Paragraphs. Your essay should be divided into paragraphs, and while there's no rule about having exactly three body paragraphs sandwiched between an introduction and conclusion, there should be a ...
In an argumentative essay, you take a stand on a subject and give evidence to persuade the reader. Conclusion. Essay writing might be difficult, but with the appropriate attitude and mindset, it's easier. By knowing the essay format, outlining your thoughts, and reviewing your work, you may write a convincing essay.
The process analysis essay opens with a discussion of the process and a thesis statement that states the goal of the process. The organization of a process analysis essay is typically chronological. That is, the steps of the process are conveyed in the order in which they usually occur. Body paragraphs will be constructed based on these steps.
Table of contents. Step 1: Hook your reader. Step 2: Give background information. Step 3: Present your thesis statement. Step 4: Map your essay's structure. Step 5: Check and revise. More examples of essay introductions. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
Conclude a process essay by restating the main steps involved and emphasizing the outcome. Explain why understanding this process is valuable and offer additional tips or resources. For example, if writing about baking a cake, discuss how mastering this process can boost confidence in cooking and provide a basis for more complex recipes. ...
NMG's commitment to set up a special desk for climate change coverage is a visionary step in the right direction in giving climate change stories the much-deserved attention and ensuring they are...
Make a claim. Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim. Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim) Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives. The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays.