How To Write A Research Paper
Research Paper Methods Section


How To Write The Methods Section of a Research Paper Step-by-Step
13 min read
Published on: Mar 6, 2024
Last updated on: Oct 28, 2024
People also read
How to Write a Research Paper Step by Step
How to Write a Proposal For a Research Paper in 10 Steps
A Comprehensive Guide to Creating a Research Paper Outline
Types of Research - Methodologies and Characteristics
350+ Interesting Research Paper Topics to Get You Started
Interesting Psychology Research Topics & Ideas
Qualitative Research - Types, Methods & Examples
Understanding Quantitative Research - Definition, Types, Examples, And More
Research Paper Example - Examples for Different Formats
How To Start A Research Paper - Steps With Examples
How To Write a Literature Review for a Research Paper | Steps & Examples
Types of Qualitative Research Methods - An Overview
Understanding Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research - A Complete Guide
How to Cite a Research Paper in Different Citation Styles
Easy Sociology Research Topics for Your Next Project
200+ Outstanding History Research Paper Topics With Expert Tips
How To Write a Hypothesis in a Research Paper | Steps & Examples
How to Write an Introduction for a Research Paper - A Step-by-Step Guide
How to Write a Good Research Paper Title
How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper in 3 Simple Steps
How to Write an Abstract For a Research Paper with Examples
How To Write a Thesis For a Research Paper Step by Step
How to Write a Discussion For a Research Paper | Objectives, Steps & Examples
How to Write the Results Section of a Research Paper - Structure and Tips
How to Write a Problem Statement for a Research Paper in 6 Steps
How to Find Sources For a Research Paper | A Guide
Share this article
The method and material section stands as the cornerstone of any research paper. Crafting this section with precision is important, especially when aiming for a target journal.
If you're navigating the intricacies of research paper writing and pondering on how to ace the methodology, fear not – we've got you covered. Our guide will walk you through the essentials, ensuring your methodology shines in the eyes of your target journal.
Let's jump into the basics of the method section!
On This Page On This Page -->
What is the Methods Section of a Research Paper?
The methods section of a research paper provides a detailed description of the procedures, techniques, and methods employed to conduct the study. It outlines the steps taken to collect, analyze, and interpret data, allowing other researchers to replicate the study and assess the validity of the results.
This section includes information on the study design, participants, materials or apparatus used, data collection procedures, and statistical analyses. Typically, the methodology section is placed after the introduction and before the results section in a research paper.

Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
Importance of Methods Section
The methods section of a research paper holds significant importance. Here is why:
- Replicability: The methods section ensures the replicability of the study by providing a clear and comprehensive account of the procedures used.
- Transparency: It enhances transparency, allowing other researchers to understand and evaluate the validity of the study's findings.
- Credibility: A well-documented methods section enhances the credibility of the research, instilling confidence in the study's design and execution.
- Guidance for Future Research: It serves as a guide for future research, offering insights into methodologies that can be applied or modified in similar studies.
- Ethical Considerations: The section highlights ethical considerations, promoting responsible and accountable research practices.
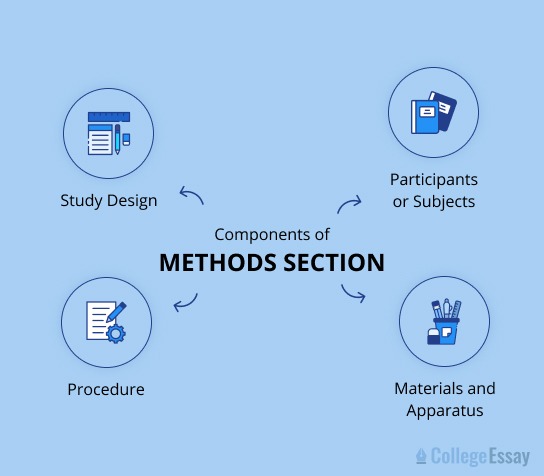
Structure of Methods Section of a Research Paper
There are some important parts of the method section of a research paper that you will need to include, whether you have done an experimental study or a descriptive study.
Provided structured approach below ensures clarity and replicability of the research methodology:
Formatting of the Methods Section
Make the main " Methods " heading centered, bold, and capitalized. For subtopics under "Methods," like participant details or data collection, use left-aligned, bold, and title cases.
Feel free to include even sub-headings for more specifics. This formatting helps readers easily follow your study steps.
Next, we will address the most common query, i.e., how to write the methodology section of a research paper. Let’s explain the steps for writing the methodology section of a research paper:
Step 1: Start with Study Design
The initial step in the method section of a research paper is to provide a clear description of the study type. This involves outlining the overall plan and structure of the research.
Different types of studies, such as cohort, case-control, and cross-sectional, may be employed based on the research objectives.
For instance:
Starting with the study design sets the stage for understanding the methodology. It provides readers with a foundation for subsequent sections in the methods portion of the research paper.
Step 2: Describe Participants
In the methods section, the second step involves providing a detailed account of the participants involved in the study. Start by describing the characteristics of both human and non-human subjects, using clear and descriptive language.
Address specific demographic characteristics relevant to your study, such as age, sex, ethnic or racial group, gender identity, education level, and socioeconomic status. Clearly outlining these essential details ensures transparency, replicability, and a comprehensive understanding of the study's sample.
Sampling Procedures:
- Clearly outline how participants were selected, specifying any inclusion and exclusion criteria applied.
- Appropriately identify the sampling procedure used, such as random sampling, convenience sampling, or stratified sampling.
- If applicable, note the percentage of invited participants who actually participated.
- Specify if participants were self-selected or chosen by their institutions (e.g., schools submitting student data).
Sample Size and Power:
- Detail the intended sample size estimation per condition and the statistical power aimed for in the study.
- Provide information on any analyses conducted to determine the sample size and power.
- Emphasize the importance of statistical power for detecting effects if present.
- State whether the final sample size differed from the originally intended sample.
- Base your interpretations of study outcomes solely on the final sample, reinforcing the importance of transparency in reporting.
Step 3: State Materials or Apparatus
In the third step, thoroughly describe the materials or apparatus used in your research. In addition, gives detailed information on the tools and techniques employed to measure relevant outcome variables.
Primary and Secondary Measures:
- Clearly define both primary and secondary outcome measures aligned with research questions.
- Specify all instruments used, citing hardware models, software versions, or references to manuals/articles.
- Report settings of specialized apparatus, such as screen resolution.
Reliability and Validity:
- For each instrument, detail measures of reliability and validity.
- Include an explanation of how consistently (reliability) and precisely (validity) the method measures the targeted variables.
- Provide examples or reference materials to illustrate the reliability and validity of tests, questionnaires, or interviews.
Covariates and Quality Assurance:
- Describe any covariates considered and their relevance to explaining or predicting outcomes.
- Review methods used to assure measurement quality, such as researcher training, multiple assessors, translation procedures, and pilot studies.
- For subjectively coded data, report interrater reliability scores to gauge consistency among raters.
Step 4 Write the Procedure
Next is the procedure section of the research paper, which thoroughly details the procedures applied for administering the study, processing data, and planning data analyses. Include qualitative , quantitative or mixed methods approaches taken to gather data.
Data Collection Methods and Research Design
- Summarize data collection methods (e.g., surveys, tests) and the overall research design.
- Provide detailed procedures for administering surveys, tests, or any other data collection instruments.
- Clarify the research design framework, specifying whether it's experimental, quasi-experimental, descriptive, correlational, and/or longitudinal.
- For multi-group studies, report assignment methods, group instructions, interventions, and session details.
Data Analysis
- Clearly state the planned data analysis methods for each research question or hypothesis.
- Specify descriptive statistics, inferential statistical tests, and any other analysis techniques.
- Include software or tools used for data analysis (e.g., SPSS, R).
- Provide a brief rationale for choosing each analysis method.
Step 5: Mention Ethical Approvals
In the fifth step of the methods section, explicitly address the ethical considerations of your research, ensuring transparency and adherence to ethical standards. Here are some key ethical considerations:
- IRB Approval:
Clearly state that the research received approval from the Institutional Review Board (IRB) or an equivalent ethical review body.
- Informed Consent:
Specify the process of obtaining informed consent, including the provision of information sheets to participants.
- Confidentiality:
Describe measures taken to maintain confidentiality, such as assigning unique identification numbers and securing data.
- Participant Rights:
Emphasize participants' right to withdraw from the study at any point without consequences.
- Debriefing:
Mention if debriefing procedures were implemented to address any participant concerns post-study.
Methods Section of Research Paper Examples
Exploring sample methodology sections is crucial when composing your first research paper, as it enhances your understanding of the structure. We provide PDF examples of methodology sections that you can review to gain inspiration for your own research paper.
Methods Section of A Qualitative Research Paper
Methods Section of Research Paper Template
Methods Section of Research Proposal Example
Methods Section of Research Paper APA
How To Write A Method For An Experiment
Journal Guidelines to Consider
When writing the methods section, be mindful of the specific guidelines set by your target journal. These guidelines can vary, impacting the structure, word limitations, and even the presentation of your methodology.
Here's a detailed explanation, along with an example:
Structure & Word Limitations
If a journal follows APA guidelines, it might allow flexibility in structuring the method section. However, some journals may impose strict limitations on the manuscript's length and the number of subsections.
For instance, a journal might specify a maximum of 3000 words for the entire paper and limit the method section to 500 words. In such cases, ensure you adhere to these constraints, potentially submitting supplemental files for additional details.
Standardized Checklists
Journals often request authors to use standardized checklists for various study types to ensure completeness.
For a randomized clinical trial, the CONSORT(Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials) checklist might be required. If your research involves observational studies, the STROBE (Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology) checklist may be applicable.
For diagnostic accuracy studies, adherence to the STARD (Standards for the Reporting of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies) checklist is common. These checklists serve as a systematic way to include essential details in your manuscript, aligning with the journal's preferred reporting standards.
Blind Review Procedures
Some journals implement single- or double-blind review procedures. If a double-blind review is in place, authors need to remove any information that might reveal their identity or institutional affiliations.
For instance, the method section cannot explicitly mention the institution's name, researchers' identities, or the institutional ethics committee. This ensures an unbiased evaluation of the research without reviewers being influenced by the authors' affiliations.
The Dos And Don’ts Of Writing The Methods Section
While it's important to be thorough, certain elements are better suited for other sections of the paper. Here are some Do’s and Don’ts of writing the methods section:
Dos of Writing the Methods Section
Here are what to include in the methods section:
- Clarity and Precision: Clearly and concisely describe the procedures used in your study. Ensure that another researcher can replicate your work based on your explanation.
- Chronological Order: Present the methods in a logical and chronological sequence. This helps readers follow the flow of your research.
- Detail and Specificity: Provide sufficient detail to allow for replication. Specify equipment, materials, and procedures used, including any modifications.
- Consistency with Study Design: Align your methods with the overall design of your study. Clearly state whether it's experimental, observational, or another design.
- Inclusion of Participants: Detail participant characteristics, including demographics and any inclusion/exclusion criteria. Clearly state the sample size.
- Operational Definitions: Define and operationalize key variables. Clearly explain how each variable was measured or manipulated.
- Transparency in Data Collection: Describe the data collection process, including the timing, location, and any relevant protocols followed during the study.
- Statistical Information: Outline the statistical methods used for analysis. Specify the software, tests employed and significance levels.
- Ethical Considerations: Discuss ethical approvals obtained, informed consent procedures, and measures taken to ensure participant confidentiality. Address any potential conflicts of interest.
Don'ts of Writing the Methods Section
- Extraneous Details: Unlike the discussion section avoid including unnecessary details or information that does not contribute directly to understanding the research methods.
- Results Discussion: Refrain from discussing or interpreting the results in the methods section. Focus solely on describing the methods employed.
- Ambiguity and Vagueness: Steer clear of vague or ambiguous language. Be precise and specific in your descriptions.
- Overemphasis on Background: While some background information is relevant, avoid turning the methods section into an extensive literature review . Keep the focus on the research methods.
- Personal Opinions: Do not include personal opinions or anecdotes. Stick to factual and objective descriptions.
- Excessive Jargon: Minimize the use of technical jargon that may be confusing to readers who are not experts in your field. If necessary, provide clear explanations.
- Inadequate Explanation of Modifications: If you deviate from standard procedures, clearly explain the modifications and justify why they were made.
- Inconsistency with Design: Ensure that your methods align with the study design. Avoid inconsistencies that could create confusion for readers.
In conclusion , learning the art of writing the methods section is pivotal for any research paper. Following a step-by-step approach, from defining the study design to detailed data collection and analysis, ensures clarity and replicability.
Remember, precision matters. If you find yourself grappling with the intricacies of your methodology, don't hesitate to reach out to CollegeEssay.org.
Our professional writing service is ready to assist you in crafting a robust and well-structured methods section.
Connect with our research paper writing service for expert guidance and conquer the challenges of research paper writing.
Nova A. (Literature, Marketing)
As a Digital Content Strategist, Nova Allison has eight years of experience in writing both technical and scientific content. With a focus on developing online content plans that engage audiences, Nova strives to write pieces that are not only informative but captivating as well.
Need Help With Your Essay?
Also get FREE title page, Turnitin report, unlimited revisions, and more!
Keep reading

50% OFF ON CUSTOM ESSAYS
Essay Services
- Argumentative Essay Service
- Descriptive Essay Service
- Persuasive Essay Service
- Narrative Essay Service
- Analytical Essay Service
- Expository Essay Service
- Comparison Essay Service
Writing Help
- Term Paper Writing Help
- Research Writing Help
- Thesis Help
- Dissertation Help
- Report Writing Help
- Speech Writing Help
- Assignment Help
Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
- Formatting Guides
- APA Methods Section: Guide on How to Write & Tips & Examples
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Other Essays
- Main Academic Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Essay Guides
- Research Paper Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides
APA Methods Section: Guide on How to Write & Tips & Examples

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
The methods section of an APA-style paper is where you describe in detail how you conducted your research. This includes details about the participants, materials, and procedures used during the study. APA style provides distinct instructions on how to format your methodology section.
In this guide, you will learn how to format an APA methods section and see the overall layout. You will also find examples of various elements within the APA methods section as well as explanations of how to structure each element.
APA Methods Section: Overview
Methods section APA also provides information on the methodology of a study. This information shows some results of participants. Along with the name of a methodology used. You should include thorough information on your sample, measurements , and techniques utilized in your paper. So that others may understand and reproduce your study.
Methods Section APA: Major Subsections
APA style methods section includes specific details of research and an approach you used. The techniques and processes employed in a research study or experiment are described in this part of your research paper. This part of an article is crucial. It lets other researchers understand exactly how you did your study. It also allows them to replicate an experiment and evaluate other techniques that could generate different findings. You may need one more blog on how to write a results section APA , you will find it on our platform.
APA Methods Section: Participants
One of the main APA paper methods sections is the participant’s section. Here, a subject, its characteristics, power, and size are described. For example, the number of female (or male) participants. The age range and average age. The percentage of participants who belong to various ethnic groups. It can be "Caucasian," "African American," "Latino/a," "East Asian," "Indian," "Native American," and "other". Ethnic group names should be capitalized because they are proper nouns. When describing a group of individuals, the correct form is to use a term that is widely accepted by that group. Just in case, remember that StudyCrumb's APA paper writer can figure out the methods section for you at any time.
APA Methodology: Apparatus and Materials
APA Methodology apparatus and materials provide the primary and secondary data or measurements. They allow organically measure the tests conducted on a study. In this part, you should provide a description of any equipment or physical settings that were important aspects of your study. If you are conducting a study that involves precise measurement, you will want to be very specific about equipment you used. For example, if you are measuring how quickly a participant responds to a stimulus on a computer screen, you need to describe some software you are using, important characteristics of a monitor (size, refresh rate, contrast, etc.), and distance of participants from this monitor. Do not bother describing the size of a room you used. Or its general layout unless these are important to your study.
APA Methods Section: Procedure
Writing a methods section APA also constitutes procedure. It includes research, design, and analysis that fully complement the study in question. A researcher offers a step-by-step account of a participants' experience. Do not include any data analysis or other research activity that does not directly involve the participants. Do not know how to format statistics? Use one more blog on our platform that will explain everything about reporting statistics in APA .
How to Format APA Methods Section
The APA methods section format constitutes intervals, deviations, and specific fonts. It allows for some deeper characterization of study. Subheadings should be used to separate method sections into subsections. Participants, materials, design, and technique are typical subsections. Each subsection has its own heading, proper formatting of which is described in the APA manual.
APA Methods Section Example
Sample methods section APA has variables and control analysis through quantitative reasoning. You should offer enough information. So that your study can be reproduced in all of its key aspects. However, you should leave out parts of your research that are unlikely to affect the conclusion. Such as exact room temperature, room color, and furniture specifics (assuming they are not independent variables). Furthermore, you should avoid repeating material that has already been provided in another part. Do not describe your questionnaire in the Procedure paragraph if you discuss it in the Materials subsection.
APA Methods Section: Bottom Line
So, methods Section APA has its goal, and rules you should stick to. Its purpose is to clearly display what approaches you used in your experiment. Also, what people participated in it, and what you did in your research overall. It doesn’t have a general format or edition. Yet formatting is done through wider understanding of how APA referencing works.
To get the perfect APA methods section done, use our writing services. And never miss a deadline on your project! Our professional writers can help you deal with your work timely.
Frequently Asked Questions About APA Methods Section
1. how long should an apa method section be.
To answer how long is methods section APA, it doesn’t have some fixed length but make sure you write in concise words.
2. What tense should I use in APA methods section?
An APA methods section should use past tense. You need to show completed actions of a methodology. Even if you haven't finished your research yet.
3. Where does the methodology section go in a research paper?
Methodology section of any research paper goes between the introduction and the conclusion. Usually, it goes normally in chapter 3 after literature review.
4. What are the differences between an APA methods section and results section?
An APA methods section describes procedure while results section describes some measurements taken.

Emma Flores knows all about formatting standards. She shares with StudyCrumb readers tips on creating academic papers that will meet high-quality standards.
You may also like

Methods Section of Research Paper: Writing Steps

The methods section of a research paper can feel a bit intimidating, but it's actually one of the most straightforward parts. Here, you're basically walking readers through the steps you took to conduct your research. Every choice, from your data collection techniques to how you analyzed the results, matters because it ensures others can follow your process or validate your findings.
When writing about materials and methods in research paper, you're not just listing steps; you're explaining your approach and reasoning behind it. Why did you choose that specific method? What made it the best fit for your study? You add clarity and depth, giving readers confidence in your work, by answering these questions
Let our expert university essay writing services break down how to write the methods section of a research paper so it's less overwhelming.
What Is the Methods Section of a Research Paper
The methods section explains how you conducted your research. It's a detailed explanation of the steps you took to gather data, what tools or techniques you used, and how you analyzed the information. The goal is to give readers enough detail so they can understand your process and, if needed, replicate the study themselves.
This section covers things like your research design (was it experimental, observational, or something else?), the participants or materials involved, the procedures you followed, and the methods used to analyze the results. It's all about transparency—making sure others know exactly what you did and why you did it. And what is the purpose of the methods section in a research paper, you may ask? Let's look into that below.
For detailed information about the research methods in psychology , check out this blog.

Wednesday Addams
Mysterious, dark, and sarcastic
You’re the master of dark humor and love standing out with your unconventional style. Your perfect costume? A modern twist on Wednesday Addams’ gothic look. You’ll own Halloween with your unapologetically eerie vibe. 🖤🕸️
Struggling with Your Research Methods?
Let us help you create an accurate methods section that meets academic standards!
Why Is the Methods Section Important
Writing the methods section of a research paper is important because it shows the foundation of your research. If the methods aren't clear or reliable, then the entire study can be questioned. This section gives readers the confidence that your findings are valid by showing that your research was conducted in a logical, well-planned way. It's also key for reproducibility—other researchers should be able to follow your steps and get similar results if they replicate the study.
For example, imagine you're reading a paper about a new way to reduce anxiety through mindfulness exercises. If the methods part of a research paper doesn't clearly explain how the exercises were conducted, how many participants were involved, or how the results were measured, it's hard to trust the conclusion. But if the steps are detailed and make sense, you can see that the research was solid and potentially use it to build further studies or apply the findings in practice.
Methods Section of Research Paper: Structure Breakdown
Your methods section should follow a chronological order, starting with the first step (such as selecting participants) and ending with the last step (like analyzing the data). These sections are often divided into labeled subsections, each covering a specific part of the research process. The methods section outline can vary based on the type of project and discipline, but the following are common elements:
- Study Design : It explains whether your study is experimental, observational, or something else. It's the framework guiding your investigation.
- Setting and Subjects : This part describes where the study took place and who or what was involved. Whether it's a group of participants, animals, or objects, this section covers all the details of your sample.
- Data Collection : When writing the methods section of a research paper, here you explain how you gathered your data—through surveys, interviews, experiments, etc. You also need to include the tools or instruments you used.
- Data Analysis : Once you collected the data, how did you make sense of it? This part explains the methods you used to analyze your results, whether through statistical software or manual coding.
- Ethical Approval : If your study involves human or animal subjects, you must explain how you obtained ethical clearance. This ensures your research was conducted responsibly and followed ethical guidelines.
These parts of a methods section are quite simple and straightforward—you can even start drafting it while your research is ongoing. Alternatively, you have the option to request - write my research paper for me cheap , and we’ll take care of it immediately.
How to Write the Methods Section of a Research Paper
Writing the methods section doesn't have to be complicated. Follow the seven key steps below to structure this section effectively:
- Start with an Overview
- Describe Your Study Design
- Explain the Setting and Subjects
- Detail Your Data Collection Methods
- Outline Your Data Analysis Approach
- Address Ethical Considerations
- Provide Enough Detail for Replication
Step 1. Start with an Overview
The first step is to give readers a general idea of how your research was conducted. This overview should be brief, but it should cover the essential aspects of your approach—like the type of study, the key methods you used, and the overall goal of the research.
For example, you might write: "This study used a mixed-methods approach to investigate the effects of virtual reality on improving memory recall in elderly participants. A combination of cognitive tests and participant feedback was used to measure the impact."
This overview gives readers the gist of your study—what you were testing, who was involved, and how you gathered data. By mentioning both cognitive tests and feedback, you're hinting at the blend of methods without giving everything away upfront. Keep it clear, straightforward, and enough to hook your readers.
Step 2. Describe Your Study Design
The study design section answers the question: How did you structure your research? Be clear about whether your study was experimental, observational, qualitative, or something else. The goal is to explain the backbone of your research, giving readers a sense of how you planned to gather and interpret your data.
For example, you could say: "This study followed an experimental design, where participants were randomly assigned to either a virtual reality group or a traditional memory exercise group. The outcomes of both groups were compared to determine the effect of the intervention."
Don't go overboard with details here, but make sure you're clear about how your study was set up. This helps readers understand the logic behind your research and how you aimed to reach your conclusions.
Step 3. Explain the Setting and Subjects
This step is all about where and with whom the research took place. You'll need to describe the setting, whether it was in a lab, a classroom, or even online. Then, introduce your subjects or participants. Were they people, animals, or objects? And how did you select them? It's important to clarify these details so readers can understand the environment and who (or what) was involved.
For instance:
"The study took place in a community center with 40 elderly participants aged 65 and older. Participants were recruited through local senior groups and were chosen based on their willingness to engage in cognitive activities."
In the methods section of research paper, the setting and subjects are clearly defined, giving readers a good sense of where the research happened and who was part of it.
Step 4. Detail Your Data Collection Methods
Now, it's time to explain how you collected your data. This section is crucial because it shows readers the tools and techniques you used to gather information. Did you conduct surveys, run experiments, or hold interviews? Make sure to mention the methods clearly, including any specific equipment or instruments you used.
For example, you might write:
"Data were collected through two methods: cognitive tests that measured short-term memory performance and structured interviews that gathered qualitative feedback on the participants' experiences with virtual reality."
Notice how the sentence flows. You're not just listing methods; you're linking them together with a clear purpose. This helps create a smooth narrative while giving enough detail for others to understand how the data was gathered.
Step 5. Outline Your Data Analysis Approach
After collecting your data, the next step is to explain how you analyzed it. This is where you describe the methods or tools you used to make sense of the results. Were statistical tests involved? Did you categorize qualitative data? It's important to explain your approach so readers understand how you interpreted the findings.
"Quantitative data from the cognitive tests were analyzed using a t-test to compare memory performance between the two groups. Qualitative data from the interviews were coded thematically to identify common patterns in participant feedback."
Here, you're showing how both numbers and words were processed—giving a full picture of your analysis techniques. Keep it simple, but don't leave out important details.
Step 6. Address Ethical Considerations
Every study involving human or animal subjects must consider ethics. In this section, mention how you ensured the safety and rights of participants. Did you get informed consent? Was there any risk involved, and how was it minimized? Ethical approval shows that your research was conducted responsibly.
"All participants provided informed consent before the study began, and the research was approved by the local ethics committee. Participants were free to withdraw at any time, and confidentiality was strictly maintained throughout the study."
This reassures readers that you followed proper procedures, ensuring that the research was ethically sound.
Step 7. Provide Enough Detail for Replication
Lastly, give enough information so that someone else could replicate your study if needed. This doesn't mean overwhelming readers with every tiny detail, but the methods should be clear and specific enough that others can follow them. The goal is transparency.
For example: "Each participant completed three 30-minute virtual reality sessions over a two-week period, with cognitive tests administered before and after each session. The same protocol was followed for the traditional memory exercise group."
This kind of detail ensures that anyone trying to replicate your research can follow the same steps, reinforcing the reliability of your study.
How to Write a Methods Section APA
When writing the APA methods section, it's important to follow a clear format. Here's a brief overview of what to include:
- Participants: In this part, describe the people who took part in your study. Start by explaining how you found them and the total number involved. For a proposal, mention how many participants you aim to include; for completed research, give the actual number. Include important details like age, gender, and other relevant characteristics. For example, you might say, "Participants (N = 150) will consist of 70 males and 80 females, aged 18-24."
- Materials: This section details the tools and instruments used in your study. Make sure to provide enough information so someone else could replicate your research. If you use existing surveys or scales, mention their names and how they will be used. For example, you could write: "The Beck Depression Inventory (Beck et al., 1961) will measure participants' depressive symptoms. It includes 21 items rated on a scale from 0 to 3, where higher scores indicate more severe depression."
- Procedure: Describe the steps that participants will follow in order. Clearly explain how they will be recruited, how you will obtain their consent, and what they will do during the study. For example: "Participants will be recruited through social media ads and will fill out an online consent form before starting the survey. They will answer demographic questions and then complete the main questionnaire on study habits."
In summary, the methods section in APA style should be organized into these subsections, each providing enough detail for others to replicate your study.
Methods Section of Research Paper Example
Below is a simplified real-life example to illustrate how the methods section is structured.
Tips and Pitfalls to Avoid
Even though writing the methods section of research paper can be straightforward, there are a few things to watch out for. Here are some tips to keep in mind—and some common pitfalls you'll want to avoid:
Be Clear, Not Vague - One common mistake is being too vague about what you did. For example, saying "participants completed a survey" doesn't give enough information. Instead, describe the survey, how it was administered, and what it measured. A better version would be: "Participants completed a 20-question survey on stress levels, administered online via Google Forms."
Avoid Overloading with Unnecessary Details - While it's essential to be detailed, don't drown your readers in irrelevant info. For example, if you're describing the software used for analysis, just mention it briefly unless it's crucial to understand your study. Instead of going into every setting you used, say: "Data was analyzed using SPSS, version 26."
Stay Consistent - One pitfall is inconsistencies between different sections of your paper. If you say you're going to measure five variables in your methods section, don't list six in your results. This creates confusion and makes your study harder to follow. Stay consistent throughout.
Don't Skip Ethical Considerations - Sometimes, writers forget to address ethics in their methods section. Make sure you include a brief mention of how you got informed consent and ensured confidentiality. For example, you could say: "All participants gave informed consent, and their data was anonymized to protect their privacy."
Proofread Carefully - Lastly, don't underestimate the power of proofreading. Small errors in your methods section can make a big difference. If a reader gets stuck on a typo or unclear phrase, they might miss your main point. So, go through your writing one more time to make sure everything flows smoothly.
What to Include in the Methods Section of a Research Paper
When writing the methods section, it's important to cover all key aspects without overwhelming your readers with unnecessary detail. Here's a checklist to guide you:
- Participants or Subjects Start by describing who or what was involved in the study. This could include participants, animals, or specific materials. Provide relevant details like age, sex, and other characteristics, but keep it brief unless the specifics are crucial to your research.
- Materials or Equipment Mention the tools, software, or equipment used in your study. Be sure to include important details like versions of software or manufacturers of equipment. But avoid unnecessary details—just the essentials.
- Procedure Lay out the steps of your research, focusing on how you collected and analyzed data. Include enough detail for someone else to replicate your study, but don't bog it down with irrelevant minutiae.
- Data Analysis Briefly explain how you analyzed your data. Mention any statistical tests or software used. If a specific method was used for data analysis, describe it concisely.
- Ethical Considerations If applicable, include a short statement on how ethical standards were met, such as obtaining informed consent or ensuring confidentiality.
The methods section of research paper is about precision and clarity. By including all the key elements—participants, materials, procedures, and data analysis—you provide readers with a clear roadmap of your research. Keep it simple, stay focused, and make sure someone could replicate your study from your description.
Stuck on the Methods Section?
EssayPro's experts can make it easy. Get our tailored guidance with a precise methods section!
What Is the Methods Section of a Research Paper?
What should be included in the methods section of a research paper, how to start the methods section of a research paper.

Annie Lambert
specializes in creating authoritative content on marketing, business, and finance, with a versatile ability to handle any essay type and dissertations. With a Master’s degree in Business Administration and a passion for social issues, her writing not only educates but also inspires action. On EssayPro blog, Annie delivers detailed guides and thought-provoking discussions on pressing economic and social topics. When not writing, she’s a guest speaker at various business seminars.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
Guidelines for Writing APA Style Method Sections . (n.d.). https://www.tamuct.edu/coe/docs/Guidelines-for-Writing-APA-Style-Method-Sections-Revised.pdf


Affiliate 💸
Get started free
Research Project Guide
How To Write The Methods Section of Research Paper In 9 Easy Steps
Master the methods section of your research paper in just 9 easy steps. Get clear guidance to enhance your writing!
Oct 29, 2024

Starting a research project can feel like wandering in a foreign city without a map. You need a plan, a clear path, and tools to guide you through the chaos. That's where the methods section of your research paper comes in. It's your blueprint, laying out the precise steps you took to test your hypothesis and collect your data. This guide will show you how to craft a clear, concise methods section to help understand how to start a research project on the right foot and finish your research quickly and efficiently.
You'll learn how to choose the correct research methods, describe them in detail, and anticipate any potential challenges you may face. By the end, you'll thoroughly understand how to write a methods section that will help you achieve your research goals and produce a well-organized and easy-to-read paper.
Table Of Contents
What Is The Methods Section of the Research
Correct Order of Methods Section
Examples of methods section of research paper, different formats of methods section, supercharge your researching ability with otio — try otio for free today, what is the methods section of the research paper.

The methods section of a research paper is indispensable. It’s where you map out exactly what you did, how, and what you used to get it done. This section is about the details—consider it your experimental playbook. After the introduction sets the stage, the methods section takes the baton and runs with it, laying down the steps before getting into results and discussion. You’ll want to state what actions you took, the techniques you used, the tools and equipment involved, and even why you chose specific protocols or software. The aim is to provide a clear, replicable path so that others can follow your footsteps or at least understand how you arrived at your conclusions.
Why is the Methods Section So Crucial?
The methods section holds the keys to understanding the reliability and validity of any study. It allows readers to judge your research's trustworthiness and, if needed, replicate your findings. This section is like a blueprint; it not only supports your study's context and authenticity but also plays a vital role in the success of your paper. If your methods section is lacking, expect early rejections or a slew of revisions during the publication process. Reviewers often scrutinize this section to assess the robustness of your research protocol and data analysis. The methods section is your opportunity to show off your research chops and field expertise.

1. Research Design: Crafting Your Strategy
Your research design is the backbone of your study, defining your overall strategy for addressing your research question. Whether you choose an experimental, observational, qualitative, or mixed-methods approach, explaining why this method is legitimate within your discipline is crucial. Explain why it's the most effective approach to your research questions or objectives. This information may sometimes appear in the opening paragraph of the Methods section rather than as a separate subsection.
2. Ethical Approval: Crossing the T’s and Dotting the I’s
Every study must adhere to ethical guidelines, and you must specify which governing board or regulatory body approved your study. If an Institutional Review Board (IRB) gives the green light, provide the approval number assigned to your project.
3. Setting: Finding the Perfect Spot
Detail how you determined your research location and why it suits your project. If you have any previous connection or institutional affiliation with this spot, mention it here.
4. Participants: Who’s in the Study?
Explain when, where, and how you recruited participants. Were they aware of the study’s true purpose? Describe your selection criteria and demographic characteristics. If applicable, discuss the representativeness of your sample, intended sample size, initial and final sample sizes, and any dropouts.
5. Instruments: Tools of the Trade
Describe the instrument in detail if you used a survey, questionnaire, or interview questions. Specify whether you created or used an existing one, and cite it if applicable. Discuss who administered it, how many questions it included, the topics covered, question types, and measured variables. Provide evidence of the instrument’s reliability and validity. If you used multiple instruments, consider separate subheadings.
6. Procedure(s)/Intervention: What Happened During the Study?
If your study involved an experiment or intervention, provide a comprehensive description. Discuss group divisions, control groups, sorting methods, the experiment’s location, duration, and session count. Explain who delivered the intervention, participant interaction, instructions, apparatuses, and clinical treatments or educational interventions.
7. Data Collection: Capturing the Details
For qualitative studies, describe your data collection protocol . Specify who collected the data, in what form, over what period, and how it was recorded and stored. Address any steps taken to ensure reflexivity consistency and limit bias.
8. Data Analysis: Making Sense of It All
All essential details are whether your data were transformed for analysis, who analyzed and interpreted it, and what software was used. Outline statistical tests, scoring methods, missing data, excluded data, and how coding categories or themes were developed. This information may appear in some fields at the beginning of the results section.
Let Otio be your AI research and writing partner . Today, knowledge workers, researchers, and students face content overload, often using fragmented, manual tools to manage their workflows. With the ability to create content at the click of a button, this problem will only grow. Otio provides an AI-native workspace for researchers , helping them collect diverse data sources, extract critical takeaways with AI-generated notes and source-grounded Q&A, and create draft outputs efficiently. Try Otio for free today !

Related Reading
• How to Find Academic Sources • How to Analyze Quantitative Data • Can Ai Write a Paper for Me • How Long Does It Take to Write a Research Paper • How to Create a Research Question • Research Methodology Types • How to Organize a Research Paper • Argumentative Essay Topics

1. Taming Information Overload with Otio
Research can be overwhelming, especially with the flood of information available. Otio offers a solution by providing an integrated workspace for researchers. It helps you gather diverse data sources like bookmarks, articles, and videos. With AI-generated notes and Q&A capabilities, Otio extracts critical insights . You can then use these to draft outputs, streamlining the journey from research to writing. Otio’s features include AI-generated notes in various formats like PDFs and videos. You can interact with individual links or whole knowledge bases, similar to a chat with ChatGPT. Try Otio as your AI research and writing ally — it's free!
2. Knowing the Guidelines Inside Out
Before writing your methods section, study the author's instructions for your target journal. Follow the guidelines meticulously. For instance, you might need to change the section heading from “Materials and Methods” to “ Patients and the Method ,” depending on the journal. Some journals may prefer not to disclose the names of institutions in open-label reports. You might also need to adhere to specific style guides, like the APA format. Using standardized checklists for different study types for biomedical research can help ensure you cover all essential details.
3. Weaving a Cohesive Narrative
The experiments in your methods section should be presented logically to help readers understand the development of your study. Organizing methods chronologically is effective. For a clinical trial, you might start with the study’s setting and timeline, then detail patient recruitment, study design, randomization, group assignments, interventions, and data collection and analysis techniques.
4. Aligning with the Results
To enhance readability, align the order of your methods with the results. This coherence will guide readers through your findings more smoothly.
5. Adding Clarity with Subheadings
Break down the methods section using subheadings for each experiment. This structure aids readers in following along. You can use the specific objective of each experiment as a subheading or the experiment's name if applicable.
6. Details, Details, Details
Include every detail you considered when designing the study or collecting data, as minor variations can impact results and interpretation. For outcome measures, provide information on validity and reliability and cite existing literature to support these measures. Describe materials, equipment, or stimuli used, and don’t forget to mention sample size estimation and potential calculation if relevant.
7. Ethical Considerations
Address ethical approval early in the methods section. Specify whether your study was approved by an ethics committee or institutional review board and whether you obtained informed consent from participants or guardians.
8. Specifying Variables Clearly
Identify control, independent, dependent, and extraneous variables that might influence your study’s results. For example, if your research involves teaching methods, prior knowledge of the topic could be an extraneous variable.
9. Detailing Statistical Analysis
Describe all statistical tests, significance levels, and software used. Consult with a biostatistician, and mention if their recommendations informed your analysis. Provide justification for the statistical methods chosen, such as why you opted for a one-tailed or two-tailed analysis.

Defining Your Participants with Precision
When detailing your Methods section , clarity is critical. Start by describing your sample like this: "We recruited 879 adults, aged 18 to 28, with 56% identifying as female. All participants had completed a minimum of 12 years of education. We obtained ethical approval from the university's board and recruited participants online through Amazon Mechanical Turk (MTurk). We targeted a geographically diverse group from the Midwest using a screening survey. Each participant received $5 upon completion."
Calculating Sample Size and Ensuring Power
Determining your sample size is crucial. Explain it clearly: "Using a sample size calculator, we determined that at least 783 participants were needed to detect a correlation coefficient of ±.1 with 80% power and a significance level of .05."
Outlining Your Materials
Describe the tools you used in your study. For example: "Our primary outcome measures were religiosity and trust in science. Religiosity refers to involvement in religious traditions, while trust in science reflects confidence in scientific research. We also examined if gender and parental education levels predicted religiosity."
Measuring Religiosity
Explain how you measured your variables: "We assessed religiosity using the Centrality of Religiosity scale (Huber, 2003), which includes 15 questions across five subscales. An example item is, 'How often do you feel that something divine intervenes in your life?' Responses range from 1 (very often) to 5 (never), with an internal consistency of .83."
Assessing Trust in Science
Describe your other measures similarly: "We measured trust in science using the General Trust in Science index (McCright et al., 2013). This consists of four items rated on a scale from 1 (completely distrust) to 5 (completely trust). An example question is, 'To what extent do you trust scientists to produce unbiased and accurate knowledge?' The index has an internal consistency of .8."
Detailing Your Procedure
Walk readers through your process: "Participants completed the survey online via Qualtrics, which included demographic questions, the Centrality of Religiosity scale , an unrelated anagram task, and the General Trust in Science index. We included the filler task to prevent priming effects, and an attention check was embedded within the religiosity scale."
Analyzing Your Data
Finally, explain your analysis methods: "We used Pearson's correlation coefficient to assess the relationship between religiosity and trust in science. A t-test evaluated the significance of the correlation. We conducted multiple linear regression for the secondary hypothesis to see if parental education and gender predicted religiosity."
• How to Write a Psychology Research Paper • Research Questions Examples • Research Paper Abstract Example • How to Write Results in a Research Paper • Title Page for Research Paper • How to Cite a Research Paper • Best AI for Data Analysis • How to Write a Discussion in a Research Paper • Best AI for Writing Research Papers • Data Collection Tools • Ai Visualization Tools

Here are various ways to structure the methods section of a research paper. Your choice will depend on your field, research design, and how you want to communicate your process.
1. IMRAD Format: The Classic Approach
Widely used in science and medical research , this format breaks down the methods into clear subsections:
Participants
Provide details about who was involved, including demographics and how they were chosen.
Materials/Measures
Describe the tools, tests, or questionnaires used.
Outline the steps taken, including any experimental changes.
Explain the methods for statistical or qualitative analysis.
2. Chronological Format: Step-by-Step Guidance
This approach works well for studies that follow a sequence, such as those in social sciences or historical research. Organize the section by the order of each method, specifying timing and duration for phases like data collection.
3. Thematic Organization: Grouping by Themes
This format is ideal for qualitative studies. It groups methods by themes, and it's advantageous in ethnographic research. You can explain data collection and analysis by theme, showing how each area was explored.
4. Comparative Approach: Juxtaposing Methods
Use this format for studies comparing two or more methods, populations, or locations. Describe each method separately, then explain the reasoning behind the comparison and how you conducted it.
5. Subsection Approach: Handling Complexity
Break the methods into subsections for complex studies like mixed methods or engineering research. Describe quantitative and qualitative methods separately and include a section on how these data types were integrated.
6. Diagrammatic Format: Visualizing the Process
Use a flowchart or diagram to summarize your process in fields like engineering or biomedical science. Follow this with detailed explanations of each step, which is helpful if your protocol is complicated.
7. Protocol-Based Format: Sticking to the Script
In clinical trials or laboratory studies, detail the specific protocols or procedures followed. Cite published protocols if applicable, and describe interventions, controls, and how blinding or randomization was handled.
8. Case Study Format: Focusing on Specifics
For case studies, begin with the selection and background of each case. List your data sources, then describe how data was collected and analyzed, often comparing across cases.
Choose the format that best suits your study and communicates your methods to readers.
Today’s researchers face a deluge of content. Managing information is a herculean task, from academic articles to endless streams of tweets. Many professionals resort to combining bookmarking and note-taking tools, which only adds to the chaos. Enter Otio, an AI-native workspace designed to streamline research workflows. It lets you collect data from diverse sources, including YouTube videos and books. With Otio , you can extract critical takeaways using AI-generated notes and source-grounded Q&A chats. You can even create drafts based directly on your collected sources. The goal is simple: get you from a reading list to your first draft as quickly as possible.
The Otio Experience: Your Personal AI Research Assistant
Consider having AI-generated notes for all your bookmarks, whether YouTube videos or PDFs. That’s what Otio offers . You can even chat with individual links or entire knowledge bases, just like ChatGPT. This isn’t just convenience; it’s about enhancing productivity. You’ll be able to focus on crafting a compelling narrative or argument for your research paper. Otio’s AI-assisted writing tools can help you make that happen faster than possible.
Your Next Step with Otio
Let Otio be your AI research and writing partner. It’s free, so you can try it today and see how it can transform your research workflow.
• Note-taking AI for Students • Milanote vs Notion • Obsidian vs Evernote • Claude AI Alternative • Milanote vs Miro • Logseq vs Obsidian • Best Chat Gpt Alternatives • Zotero vs Mendeley • Writesonic vs Jasper

Dec 21, 2024
Research Data Management
20+ Best Product Research Tools for Efficient Research

Dec 20, 2024
12 Best Workflow Automation Software for Enhanced Productivity
Join over 100,000 researchers changing the way they read & write

Chrome Extension
© 2024 Frontdoor Labs Ltd.
Terms of Service
Privacy Policy
Refund Policy
Join over 50,000 researchers changing the way they read & write
Join thousands of other scholars and researchers
Try Otio Free
© 2023 Frontdoor Labs Ltd.
Research Paper Writing Guides
Research Paper Methods Section
Last updated on: Dec 14, 2024
A Guide to Writing The Methods Section of A Research Paper
By: Donna C.
11 min read
Reviewed By: Rylee W.
Published on: Jan 5, 2024

The methods section is often called the backbone of a research paper, and for good reason. It's where you explain how you conducted your study.
It allows readers to evaluate its validity, replicate your work, and trust your findings. Think of it as a detailed roadmap guiding others through your research process, from the design and materials to the analysis techniques.
This guide will explain everything you need to know to write an effective methods section. From understanding its purpose to outlining important components, we'll provide tips, examples, and guidance to help you present your research process in the best light.
Ready to tackle your methods section? Let’s dive in!

On this Page
What is the Methods Section of A Research Paper?
When writing a research paper the methods section is where researchers detail how their study was conducted. It outlines the design, materials, procedures, and techniques used to gather and analyze data.
The methodology section comes after the Introduction and before the Results section in a research paper.
It ensures transparency, allowing readers to evaluate the research’s validity and replicate it if needed. Essentially, it answers: What steps were taken to achieve the results?
Importance of Methods Section in Research Paper
The methods section is more than just a procedural guide—it’s a critical component of your research paper that adds credibility and clarity.
Here’s why it matters:
- Promotes Transparency: Clearly explains how the study was conducted.
- Enables Replication: Allows other researchers to replicate the study for further validation.
- Establishes Credibility: Demonstrates the rigor and reliability of your research process.
- Facilitates Peer Review: Helps reviewers assess the study's methodology and accuracy.
- Addresses Ethical Considerations: Highlights how ethical guidelines were followed during the research.
- Supports Knowledge Building: Serves as a reference for future studies in the field.
5 Parts of the Method Section and their Writing Tips
The methods section of a research paper consists of several important parts. Each part is like a building block, contributing to the strength and reliability of your study.
- Participants
- Materials and Instruments
- Data Analysis
- Ethical Considerations
Let’s explain these parts and learn how to write the materials and methods section of a research paper:
Part 1: Define Your Participants
This section is all about introducing the individuals or subjects who took part in your study. Think of it as providing a snapshot of who they are and why they were chosen.
You’ll include details like their demographics, how many participants you had, and the criteria you used to select them.
How to Write the Participants' Sub-Section
Here’s how you can describe your participants in a clear and straightforward way:
- Define Your Population: Start by explaining who your study is focused on. Be clear about any inclusion or exclusion criteria you used to define your group.
- Demographic Details: Share relevant details about your participants, like their age, gender, or any other important traits that relate to your research.
- Sample Size and Selection Criteria: Mention how many participants you had and how they were chosen. Be sure to include the sample size estimation process, explaining whether you used random sampling or selected participants in a specific way.
- Relevant Characteristics: If there’s anything specific about your participants that’s crucial for your study—like their experience in a certain area—be sure to mention it.
Part 2: Describe the Materials and Instruments
In this subsection, you'll explain the tools and resources you used to gather data for your study. This could include anything from machinery to surveys or questionnaires.
It’s your chance to let readers know what helped you find sources and collect the information for your research.
How to Write the Materials and Instruments Section
Here’s a simple guide to writing this part:
- List Materials Clearly: Begin by listing everything you used in your study, like equipment or tools. Be specific—include the make, model, and any changes or updates made to them.
- Purpose and Role: Explain what each item or tool was used for. For example, if you used a survey, tell readers how it helped collect data.
- Insight into Resources: Offer a little more detail on why you chose these specific materials and how they played a key role in gathering the data needed for your study.
Part 3: Outline the Procedures
In this section, you'll describe the step-by-step process you followed during your study. It helps readers understand how your research was conducted and ensures transparency in your methods.
How to Write the Procedure Section of a Research Paper
Here’s how to break it down:
- Introduction and Familiarization: Start by explaining the first steps of your study, like any introductory sessions or getting participants familiar with the study. This helps set the stage for what’s to come.
- Sequential Outline: Lay out the procedures in a clear, step-by-step order. You want your readers to follow the flow of your study easily.
- Controlled Environments: If your study took place in a controlled environment (like a lab), explain that here. Mention anything that might have affected your results, like specific conditions or settings you used.
- Consistent Data Collection: Point out how you kept the data collection process consistent. For example, explain if sessions were scheduled regularly to reduce any outside influences that could affect the results.
Part 4: Explain Data Analysis Methods
This segment explains how you processed and analyzed the data you collected. It applies to all types of research papers and studies including cross-sectional studies, case reports, or case-control studies . This helps readers understand how the information was turned into meaningful results, offering clarity on how different study designs contributed to the analysis.
How to Write the Data Analysis Section
Here’s how to approach it:
- Data Entry and Software: Start by explaining how you entered the collected data into a system. Mention any software or tools you used for analyzing the data, like SPSS, Excel, or any other relevant program.
- Descriptive and Inferential Statistics: Make a clear distinction between descriptive statistics (like averages or percentages) and inferential statistics (methods used to make predictions or test hypotheses). Be sure to explain which methods you used and why they were appropriate for your research.
- Quantitative Variables: If your study includes numerical data, explain how you processed those numbers. For example, you might have calculated the mean (average) or standard deviation (how spread out the data is). Explain why these calculations are important for your study.
- Meta-Analysis: If the study involves a meta-analysis, PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta Analyses) will guide the statistical methods used to synthesize data from multiple studies.
Note: In the methods section, you can only outline the methods and analyses you used. The interpretation of the results from these analyses is reserved for the discussion section .
Part 5: Address Ethical Considerations
Addressing ethical considerations holds primary importance. This section explains how participant rights were protected, including the ethical approvals obtained and ensuring transparency in how the research was conducted ethically.
When addressing ethical considerations, it's important to follow established guidelines such as the CONSORT (Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials). It ensures transparency and rigor in the reporting of clinical trials, including detailed participant consent and clear methodology.
How to Write the Ethical Considerations Section
Here’s how to cover the ethical aspects of your study:
- Ethical Approval: First, make it clear whether your study received ethical approval from a review board. Mention the name of the board and any reference numbers related to the approval.
- Informed Consent: Explain how you obtained informed consent from your participants. This means they were fully briefed on what the study involved, and you ensured they understood their rights, including confidentiality and anonymity.
- Voluntary Participation: Emphasize that participation was completely voluntary. Participants should have known that they could withdraw from the study at any time without any negative consequences.
- Transparency: Be open about the steps you took to protect participants' rights and data. This could include measures to maintain confidentiality or secure data handling.
Understanding the significance of each element within the methods section is important for researchers and readers alike.
It not only enhances the credibility of the study but also validates your research.
Methods Section of a Research Paper Examples
The methods section is not just a list of steps; it's like telling a story of how a study happens.
Let’s take a look at some samples to learn how to explain the methods clearly.
Sample Methods Section Of Research Paper Template
Methods Section Of Research Paper APA
Statistical Analysis Methods Section Example
Methods Section Of A Qualitative Research Paper
Do’s and Don’ts of Writing the Methods Section
Check out these do’s and don’ts for crafting a thorough methods section of a research paper:
Wrapping up, this blog is your go-to guide for creating a standout methods section. It shows you how to explain things clearly, whether it's about people in your study, the tools you used, or the steps you followed.
However, if you still feel overwhelmed by the process of creating the method section for your research paper, you can buy research papers from the top paper writing service online!
At Sharkpapers.com, we understand your research paper struggles. That’s why we offer the best college paper writers for students.
Our expert researchers help you craft an outstanding paper that contributes to the existing study.
So, don’t waste time! Place your order to get the best service online today!
Frequently Asked Questions
How to write a method for an experiment.
To write a method for an experiment: list materials and steps clearly, specify variables and data collection, and conclude with expected results. Keep it simple and easy to read.
How to Write the Measures Section of A Research Paper?
To write the Measures section:
- Describe tools and variables
- Explain operationalization
- Scale details, reliability, validity, pilot testing, and scoring
- Ensures clarity and replicability.
What Are The 5 Elements of The Method Section of A Research Paper?
The main elements of method section of a research paper includes:
- Research Design
- Measures or Instruments

Donna writes on a broad range of topics, but she is mostly passionate about social issues, current events, and human-interest stories. She has received high praise for her writing from both colleagues and readers alike. Donna is known in her field for creating content that is not only professional but also captivating.
Was This Blog Helpful?
Keep reading.
- Learn How to Write a Research Paper: Step-by-Step Guide

- Everything You Need To Know To Conduct Effective Qualitative Research

- Types of Qualitative Research Methods with Examples

- Best 300+ Ideas For Research Paper Topics in 2024

- How to Write a Proposal for a Research Paper: Steps & Examples

- A Beginner’s Guide on How to Write an Abstract

- 13 Best Tips to Start a Research Paper

- How To Write An Introduction For A Research Paper - A Complete Guide
- Learn How To Write An Abstract For A Research Paper with Examples and Tips

- How to Write a Literature Review for a Research Paper | A Complete Guide

- How to Write a Research Paper Thesis: A Detailed Guide

- How to Write a Research Paper Title That Stands Out

- A Detailed Guide To Writing a Research Paper Conclusion

- How To Write The Results Section of A Research Paper | Steps & Tips

- How to Write a Problem Statement for a Research Paper: An Easy Guide

- How to Find Sources for a Research Paper | Books, Articles, Journals & more!

- A Detailed Guide: How to Write a Discussion for a Research Paper
)
- How To Write A Hypothesis In A Research Paper - A Guide with Examples

- Learn How To Cite A Research Paper in Basic Formats

- The Ultimate List of Ethical Research Paper Topics in 2024
- 150+ Controversial Research Paper Topics to Get You Started

- How to Edit Research Papers With Precision: A Detailed Guide

- A Comprehensive List of Argumentative Research Paper Topics
- A Detailed List of Amazing Art Research Paper Topics

- Diverse Biology Research Paper Topics for Students: A Comprehensive List

- 230 Interesting and Unique History Research Paper Topics
- 190 Best Business Research Paper Topics
- 200+ Engaging and Novel Literature Research Paper Topics
- A Guide on How to Write a Social Science Research Paper
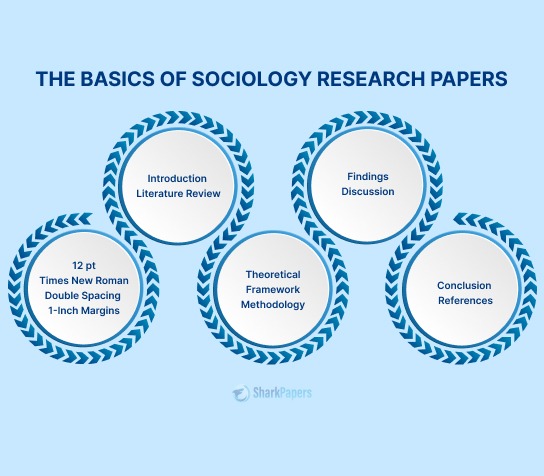
- Sociology Research Papers: Format, Outline, and Topics
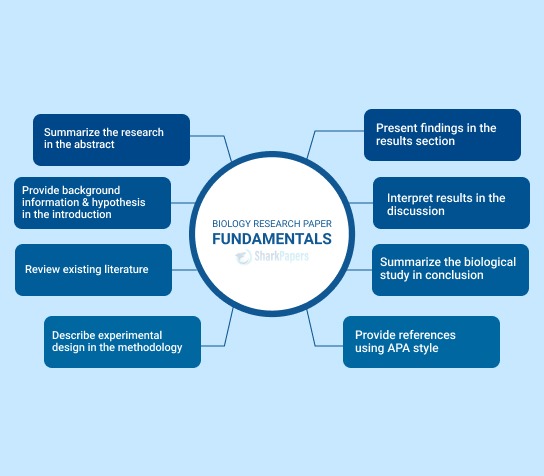
- Understanding the Basics of Biology Research Papers
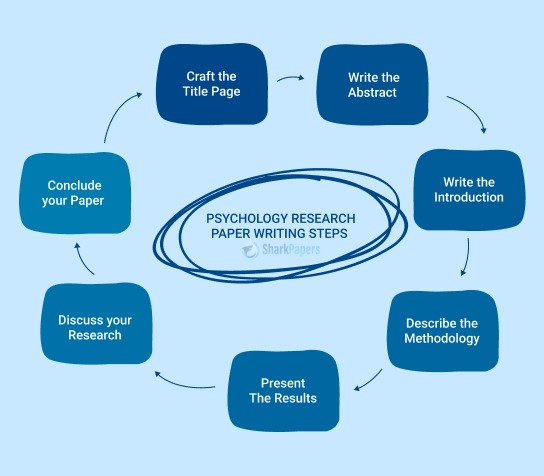
- How to Write a Psychology Research Paper: Guide with Easy Steps
- Exploring the Different Types of Research Papers: A Guide

- Scientific Research Paper: Types, Formats, Structure & Writing Process

- Argumentative Research Paper | A Step-by-Step Guide

- Analytical Research Papers: A Detailed Walkthrough

- Experimental Research Paper Explained Comprehensively

- An In-Depth Look at Psychology Research Paper Examples

- 15+ Research Paper Examples for Different Types and Formats

- Free Argumentative Research Paper Examples

- Refine Your Literary Skills with Literature Research Paper Examples

- Get Inspired by 10+ Biology Research Paper Examples

- A Comprehensive Guide to History Research Paper Examples

- An Extensive List of Business Research Paper Examples

- 10+ Best APA Research Paper Examples for Effective Writing

- 10+ Expertly Crafted MLA Research Paper Examples

- Explore 8+ Chicago Research Paper Examples for Academic Excellence

- 15+ Examples of Abstracts for Research Papers

- Exploring IEEE Research Paper Examples: A Practical Guide

- Exploring Research Paper Thesis Examples: A Beginner's Guide

- 10 Free Research Paper Proposal Examples
-12114.jpg)
- A Look at 10 Interesting Art Research Paper Examples

- Survey Research Papers: Types, Format, Writing & Examples

- A Closer Look Into Research Paper Format: APA, MLA, Chicago & IEEE

- APA Research Paper Format 7th Edition: Guide with Examples

- MLA Research Paper Format Made Easy: Step-by-Step Guide

- Formatting Research Paper Title Page in APA, MLA & Chicago

- Crafting the Perfect Research Paper Outline | Steps & Examples

- A Detailed Guide to Chicago Research Paper Format

- An Easy Guide to IEEE Research Paper Format

- 12+ Practical Research Paper Outline Examples for Structuring Your Thoughts

- Engaging Psychology Research Paper Topics for Your Next Project

Struggling With Your Paper?
Get a Custom Paper Written at
with a FREE Turnitin report, AI report, title page, unlimited revisions, and a lot more!
LIMITED TIME ONLY
People Also Read
OFFER EXPIRES SOON!
© 2024 - All rights reserved
Disclaimer: All client orders are fulfilled by our team of experienced, professional writers. The essays and papers we provide are intended to serve as educational tools and reference models only, and should not be submitted as original work.
LOGIN TO YOUR ACCOUNT
SIGN UP TO YOUR ACCOUNT
- Your phone no.
- Confirm Password
- I have read Privacy Policy and agree to the Terms and Conditions .
FORGOT PASSWORD
- SEND PASSWORD
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write a Methods Section for a Research Paper
A common piece of advice for authors preparing their first journal article for publication is to start with the methods section: just list everything that was done and go from there. While that might seem like a very practical approach to a first draft, if you do this without a clear outline and a story in mind, you can easily end up with journal manuscript sections that are not logically related to each other.
Since the methods section constitutes the core of your paper, no matter when you write it, you need to use it to guide the reader carefully through your story from beginning to end without leaving questions unanswered. Missing or confusing details in this section will likely lead to early rejection of your manuscript or unnecessary back-and-forth with the reviewers until eventual publication. Here, you will find some useful tips on how to make your methods section the logical foundation of your research paper.
Not just a list of experiments and methods
While your introduction section provides the reader with the necessary background to understand your rationale and research question (and, depending on journal format and your personal preference, might already summarize the results), the methods section explains what exactly you did and how you did it. The point of this section is not to list all the boring details just for the sake of completeness. The purpose of the methods sections is to enable the reader to replicate exactly what you did, verify or corroborate your results, or maybe find that there are factors you did not consider or that are more relevant than expected.
To make this section as easy to read as possible, you must clearly connect it to the information you provide in the introduction section before and the results section after, it needs to have a clear structure (chronologically or according to topics), and you need to present your results according to the same structure or topics later in the manuscript. There are also official guidelines and journal instructions to follow and ethical issues to avoid to ensure that your manuscript can quickly reach the publication stage.
Table of Contents:
- General Methods Structure: What is Your Story?
- What Methods Should You Report (and Leave Out)?
- Details Frequently Missing from the Methods Section
More Journal Guidelines to Consider
- Accurate and Appropriate Language in the Methods
General Methods Section Structure: What Is Your Story?
You might have conducted a number of experiments, maybe also a pilot before the main study to determine some specific factors or a follow-up experiment to clarify unclear details later in the process. Throwing all of these into your methods section, however, might not help the reader understand how everything is connected and how useful and appropriate your methodological approach is to investigate your specific research question. You therefore need to first come up with a clear outline and decide what to report and how to present that to the reader.
The first (and very important) decision to make is whether you present your experiments chronologically (e.g., Experiment 1, Experiment 2, Experiment 3… ), and guide the reader through every step of the process, or if you organize everything according to subtopics (e.g., Behavioral measures, Structural imaging markers, Functional imaging markers… ). In both cases, you need to use clear subheaders for the different subsections of your methods, and, very importantly, follow the same structure or focus on the same topics/measures in the results section so that the reader can easily follow along (see the two examples below).
If you are in doubt which way of organizing your experiments is better for your study, just ask yourself the following questions:
- Does the reader need to know the timeline of your study?
- Is it relevant that one experiment was conducted first, because the outcome of this experiment determined the stimuli or factors that went into the next?
- Did the results of your first experiment leave important questions open that you addressed in an additional experiment (that was maybe not planned initially)?
- Is the answer to all of these questions “no”? Then organizing your methods section according to topics of interest might be the more logical choice.
If you think your timeline, protocol, or setup might be confusing or difficult for the reader to grasp, consider adding a graphic, flow diagram, decision tree, or table as a visual aid.
What Methods Should You Report (and Leave Out)?
The answer to this question is quite simple–you need to report everything that another researcher needs to know to be able to replicate your study. Just imagine yourself reading your methods section in the future and trying to set up the same experiments again without prior knowledge. You would probably need to ask questions such as:
- Where did you conduct your experiments (e.g., in what kind of room, under what lighting or temperature conditions, if those are relevant)?
- What devices did you use? Are there specific settings to report?
- What specific software (and version of that software) did you use?
- How did you find and select your participants?
- How did you assign participants into groups?
- Did you exclude participants from the analysis? Why and how?
- Where did your reagents or antibodies come from? Can you provide a Research Resource Identifier (RRID) ?
- Did you make your stimuli yourself or did you get them from somewhere?
- Are the stimuli you used available for other researchers?
- What kind of questionnaires did you use? Have they been validated?
- How did you analyze your data? What level of significance did you use?
- Were there any technical issues and did you have to adjust protocols?
Note that for every experimental detail you provide, you need to tell the reader (briefly) why you used this type of stimulus/this group of participants/these specific amounts of reagents. If there is earlier published research reporting the same methods, cite those studies. If you did pilot experiments to determine those details, describe the procedures and the outcomes of these experiments. If you made assumptions about the suitability of something based on the literature and common practice at your institution, then explain that to the reader.
In a nutshell, established methods need to be cited, and new methods need to be clearly described and briefly justified. However, if the fact that you use a new approach or a method that is not traditionally used for the data or phenomenon you study is one of the main points of your study (and maybe already reflected in the title of your article), then you need to explain your rationale for doing so in the introduction already and discuss it in more detail in the discussion section .
Note that you also need to explain your statistical analyses at the end of your methods section. You present the results of these analyses later, in the results section of your paper, but you need to show the reader in the methods section already that your approach is either well-established or valid, even if it is new or unusual.
When it comes to the question of what details you should leave out, the answer is equally simple ‒ everything that you would not need to replicate your study in the future. If the educational background of your participants is listed in your institutional database but is not relevant to your study outcome, then don’t include that. Other things you should not include in the methods section:
- Background information that you already presented in the introduction section.
- In-depth comparisons of different methods ‒ these belong in the discussion section.
- Results, unless you summarize outcomes of pilot experiments that helped you determine factors for your main experiment.
Also, make sure your subheadings are as clear as possible, suit the structure you chose for your methods section, and are in line with the target journal guidelines. If you studied a disease intervention in human participants, then your methods section could look similar to this:
Since the main point of interest here are your patient-centered outcome variables, you would center your results section on these as well and choose your headers accordingly (e.g., Patient characteristics, Baseline evaluation, Outcome variable 1, Outcome variable 2, Drop-out rate ).
If, instead, you did a series of visual experiments investigating the perception of faces including a pilot experiment to create the stimuli for your actual study, you would need to structure your methods section in a very different way, maybe like this:
Since here the analysis and outcome of the pilot experiment are already described in the methods section (as the basis for the main experimental setup and procedure), you do not have to mention it again in the results section. Instead, you could choose the two main experiments to structure your results section ( Discrimination and classification, Familiarization and adaptation ), or divide the results into all your test measures and/or potential interactions you described in the methods section (e.g., Discrimination performance, Classification performance, Adaptation aftereffects, Correlation analysis ).
Details Commonly Missing from the Methods Section
Manufacturer information.
For laboratory or technical equipment, you need to provide the model, name of the manufacturer, and company’s location. The usual format for these details is the product name (company name, city, state) for US-based manufacturers and the product name (company name, city/town, country) for companies outside the US.
Sample size and power estimation
Power and sample size estimations are measures for how many patients or participants are needed in a study in order to detect statistical significance and draw meaningful conclusions from the results. Outside of the medical field, studies are sometimes still conducted with a “the more the better” approach in mind, but since many journals now ask for those details, it is better to not skip this important step.
Ethical guidelines and approval
In addition to describing what you did, you also need to assure the editor and reviewers that your methods and protocols followed all relevant ethical standards and guidelines. This includes applying for approval at your local or national ethics committee, providing the name or location of that committee as well as the approval reference number you received, and, if you studied human participants, a statement that participants were informed about all relevant experimental details in advance and signed consent forms before the start of the study. For animal studies, you usually need to provide a statement that all procedures included in your research were in line with the Declaration of Helsinki. Make sure you check the target journal guidelines carefully, as these statements sometimes need to be placed at the end of the main article text rather than in the method section.
Structure & word limitations
While many journals simply follow the usual style guidelines (e.g., APA for the social sciences and psychology, AMA for medical research) and let you choose the headers of your method section according to your preferred structure and focus, some have precise guidelines and strict limitations, for example, on manuscript length and the maximum number of subsections or header levels. Make sure you read the instructions of your target journal carefully and restructure your method section if necessary before submission. If the journal does not give you enough space to include all the details that you deem necessary, then you can usually submit additional details as “supplemental” files and refer to those in the main text where necessary.
Standardized checklists
In addition to ethical guidelines and approval, journals also often ask you to submit one of the official standardized checklists for different study types to ensure all essential details are included in your manuscript. For example, there are checklists for randomized clinical trials, CONSORT (Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials) , cohort, case-control, cross‐sectional studies, STROBE (STrengthening the Reporting of OBservational studies in Epidemiology ), diagnostic accuracy, STARD (STAndards for the Reporting of Diagnostic accuracy studies) , systematic reviews and meta‐analyses PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta‐Analyses) , and Case reports, CARE (CAse REport) .
Make sure you check if the manuscript uses a single- or double-blind review procedure , and delete all information that might allow a reviewer to guess where the authors are located from the manuscript text if necessary. This means that your method section cannot list the name and location of your institution, the names of researchers who conducted specific tests, or the name of your institutional ethics committee.

Accurate and Appropriate Language in the Methods Section
Like all sections of your research paper, your method section needs to be written in an academic tone . That means it should be formal, vague expressions and colloquial language need to be avoided, and you need to correctly cite all your sources. If you describe human participants in your method section then you should be especially careful about your choice of words. For example, “participants” sounds more respectful than “subjects,” and patient-first language, that is, “patients with cancer,” is considered more appropriate than “cancer patients” by many journals.
Passive voice is often considered the standard for research papers, but it is completely fine to mix passive and active voice, even in the method section, to make your text as clear and concise as possible. Use the simple past tense to describe what you did, and the present tense when you refer to diagrams or tables. Have a look at this article if you need more general input on which verb tenses to use in a research paper .
Lastly, make sure you label all the standard tests and questionnaires you use correctly (look up the original publication when in doubt) and spell genes and proteins according to the common databases for the species you studied, such as the HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee database for human studies .
Visit Wordvice AI’s AI Text Editor to receive a free grammar check and English editing services (including manuscript editing , paper editing , and dissertation editing ) before submitting your manuscript to journal editors.
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you’re on board with our cookie policy

- A Research Guide
- Research Paper Guide
How to Write a Methods Section for a Research Paper
- Purpose of methods section
- Key components
- How to describe
- Step-by-step guide
- Methods section formats
- Additional elements

Purpose of the Methods section
What key components must be included in the methods section.
- Research design. This is the most important section to help your audience see the methods used. Make sure to structure your research methodology correctly and follow the rules of the scientific field. Depending on your work type, the research design of a methods section should represent an outline with the basic introduction, set objectives, a lab/field environment, and other related elements.
- Participants. When dealing with a sample group or a case study, you must discuss the research participants. Always narrow things down to why a specific group of participants have been chosen and talk about how it will be helpful to stay objective and unbiased.
- Equipment. This part describes the set of tools that have been used. Writing a methods section can include software, hardware, voice recorders, chemical equipment, special labs, and more.
- Materials. Describe what materials have been used for your studies. Talk about the studies and procedures used based on the available data.
- Variables. Talk about independent and dependent variables. The independent variables are related to those elements of your research that can be changed, like the amount of water or the use of certain colors to replicate a process. As for dependent variables, these are those affected by specific changes. In other words, variables in a methods section can change during the process of studies, like the experiment outcome or exceptions in the sample group.
- Participant behavior . This is where you talk about what has been experienced by the participants (if relevant). A methods section example may include a description of actions taken, processes experienced, and the environment used to conduct the research.
How to describe your research design and procedures?
- Reflect on your hypothesis . Talk about variables or aspects you should research. This is a procedure section of a research paper where you describe the type of information you must collect as you work on your main arguments. Narrow down the scope of data that has to be evaluated.
- Define your research approach . In most cases, it can be either qualitative or quantitative. While you can choose a mixture of both for your paper, focusing on one to clarify a relevant section is recommended.
- Choose your research design type . If you are dealing with quantitative research, it’s possible to use experimental, quasi-experimental, correlational, or descriptive design methods. Suppose you are choosing a qualitative design methodology. In that case, you may approach ethnography (a method based on cultural immersion, inside research), phenomenology (research based on the perspective of an individual, an intuitive analytical variable), or a grounded method (social-based research).
- Define your research sampling method . The risk here is to generate excessive data, making it extremely challenging to see things to include and avoid. You can choose a probabilistic sampling method or a deterministic sampling approach, also known as non-random selection. Certain methods can fit better depending on the materials section of the research paper. If you still choose a non-random design, the only challenge is that the latter sampling method is more biased.
- Evaluate the best data collection method . Start your Methodology section by marking the difference between your primary (surveys, interviews) and secondary data (references that have already been published) sources.
- Choose an approach to data analysis . You can alternate between qualitative and quantitative data analysis methods section approaches.
Step-by-step guide on how to compose your Methods section
- Step 1: Focus on two main purposes of your Methods section. You should help your target audience understand your research project easier and make it possible to replicate all the vital processes.
- Step 2: Offer sufficient information to make replication unbiased and complete. While you may have your research project ready for publishing, providing overly detailed information is only sometimes necessary. Always check things twice to learn the requirements. Most importantly, keep your research transparent, provide a clear methodology, and keep every step easy to replicate.
- Step 3: To make things easier, imagine you are an individual in your target audience. Think about how you would replicate your study and what scientific paper methods you would find accessible. Ask yourself about what information you would require. Take notes and create 2-3 outlines for additional clarity.
- Step 4: Consider adding visual aid elements. It may include relevant flow charts, mind maps, checklists, or statistical data for your methodology. It will help your readers interpret the study and avoid unnecessary steps.
- Step 5: Always adhere to strict ethical standards and scientific guidelines. Even though the “Ethical Guidelines” section will be presented in another research paper part, you must show the main arguments and thesis concerning ethical rules. It will show that you are using strict standards and following the rules related to your discipline.
Methods section checklist
- Is your logic consistent in every section?
- Does your introduction provide sufficient background information?
- Does your methodology structure sound clear and follows a chronology of the research?
- Do you provide the results of your research in the same format?
- Can you replicate your study based on a given methodology?
- Do your readers have all the necessary objectives mentioned?
- Are the tools used mentioned?

Methods section formats and features
Additional elements to consider.
- Location specifics. This is where the location and research environment can make a major difference for replication purposes.
- Limitations of the research. Talk about the limitations and specifics of the tools and methods being used.
- Writing style and tone. Remember to write in the past tense and keep the same tone throughout your research paper.
- Ethical considerations. Clarify and specify all the ethical guidelines for your institution, a scientific journal methodology, and a field of science.
- Data analysis methodology.
- Participants and subjects.
- Data collection methodology.
- Things required to replicate the research.
- Addressing the research objectives.
- Basic research question.

- Writing a Research Paper
- Research Paper Title
- Research Paper Sources
- Research Paper Problem Statement
- Research Paper Thesis Statement
- Hypothesis for a Research Paper
- Research Question
- Research Paper Outline
- Research Paper Summary
- Research Paper Prospectus
- Research Paper Proposal
- Research Paper Format
- Research Paper Styles
- AMA Style Research Paper
- MLA Style Research Paper
- Chicago Style Research Paper
- APA Style Research Paper
- Research Paper Structure
- Research Paper Cover Page
- Research Paper Abstract
- Research Paper Introduction
- Research Paper Body Paragraph
- Research Paper Literature Review
- Research Paper Background
- Research Paper Methods Section
- Research Paper Results Section
- Research Paper Discussion Section
- Research Paper Conclusion
- Research Paper Appendix
- Research Paper Bibliography
- APA Reference Page
- Annotated Bibliography
- Bibliography vs Works Cited vs References Page
- Research Paper Types
- What is Qualitative Research
Receive paper in 3 Hours!
- Choose the number of pages.
- Select your deadline.
- Complete your order.
Number of Pages
550 words (double spaced)
Deadline: 10 days left
By clicking "Log In", you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We'll occasionally send you account related and promo emails.
Sign Up for your FREE account

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Research papers in the social and natural sciences often follow APA style. This article focuses on reporting quantitative research methods. In your APA methods section, you should report enough information to understand and replicate your study, including detailed information on the sample, measures, and procedures used.
Next, we will address the most common query, i.e., how to write the methodology section of a research paper. Let's explain the steps for writing the methodology section of a research paper: Step 1: Start with Study Design. The initial step in the method section of a research paper is to provide a clear description of the study type.
The Methods section of a research article is like a roadmap leading to the core of the research, guiding the readers through the actual journey the authors took to reach their destination. In the manuscript, this section contains the essential details for other scientists to replicate the experiments of the study and help the common readers to understand the study better. This article shares ...
Methods Section APA: Major Subsections. APA style methods section includes specific details of research and an approach you used. The techniques and processes employed in a research study or experiment are described in this part of your research paper. This part of an article is crucial.
The methods section of a research paper provides the information by which a study's validity is judged. ... points to incorporate when writing the methods section. Basic Research Concepts The scientific method attempts to discover cause-and-effect relationships between objects (ie, physical matter or
Writing the methods section of a research paper is important because it shows the foundation of your research. If the methods aren't clear or reliable, then the entire study can be questioned. This section gives readers the confidence that your findings are valid by showing that your research was conducted in a logical, well-planned way.
By the end, you'll thoroughly understand how to write a methods section that will help you achieve your research goals and produce a well-organized and easy-to-read paper. Table Of Contents. What Is The Methods Section of the Research. Correct Order of Methods Section. How To Write The Methods Section of Research Paper In 9 Easy Steps
When writing a research paper the methods section is where researchers detail how their study was conducted. It outlines the design, materials, procedures, and techniques used to gather and analyze data. The methodology section comes after the Introduction and before the Results section in a research paper.
Accurate and Appropriate Language in the Methods Section. Like all sections of your research paper, your method section needs to be written in an academic tone. That means it should be formal, vague expressions and colloquial language need to be avoided, and you need to correctly cite all your sources.
Writing methods section for a research paper: how to compose, design, describe, and format ☑️ Components and additional elements ☑️ + Bonus CHECKLIST. ... The structure and formatting of the Methods section of a research paper will always depend on the type of your research. If we are dealing with a short research report, your Methods ...