
Java Tutorial
- What is Java
- History of Java
- Features of Java
- C++ vs Java
- Hello Java Program
- Program Internal
- How to set path?
- JDK, JRE and JVM
- JVM: Java Virtual Machine
- Java Variables
- Java Data Types
- Unicode System
Control Statements
- Java Control Statements
- Java If-else
- Java Switch
- Java For Loop
- Java While Loop
- Java Do While Loop
- Java Continue
- Java Comments
Java Programs
Java object class.
- Java OOPs Concepts
- Naming Convention
- Object and Class
- Constructor
- static keyword
- this keyword
Java Inheritance
- Inheritance(IS-A)
- Aggregation(HAS-A)
Java Polymorphism
- Method Overloading
- Method Overriding
- Covariant Return Type
- super keyword
- Instance Initializer block
- final keyword
- Runtime Polymorphism
- Dynamic Binding
- instanceof operator
Java Abstraction
- Abstract class
- Abstract vs Interface
Java Encapsulation
- Access Modifiers
- Encapsulation
Java OOPs Misc
- Object class
- Object Cloning
- Wrapper Class
- Java Recursion
- Call By Value
- strictfp keyword
- javadoc tool
- Command Line Arg
- Object vs Class
- Overloading vs Overriding
Java String
- What is String
- Immutable String
- String Comparison
- String Concatenation
- Methods of String class
- StringBuffer class
- StringBuilder class
- String vs StringBuffer
- StringBuffer vs Builder
- Creating Immutable class
- toString method
- StringTokenizer class
- Java String FAQs
Java String Methods
- String charAt()
- String compareTo()
- String concat()
- String contains()
- String endsWith()
- String equals()
- equalsIgnoreCase()
- String format()
- String getBytes()
- String getChars()
- String indexOf()
- String intern()
- String isEmpty()
- String join()
- String lastIndexOf()
- String length()
- String replace()
- String replaceAll()
- String split()
- String startsWith()
- String substring()
- String toCharArray()
- String toLowerCase()
- String toUpperCase()
- String trim()
Exception Handling
- Java Exceptions
- Java Try-catch block
- Java Multiple Catch Block
- Java Nested try
- Java Finally Block
- Java Throw Keyword
- Java Exception Propagation
- Java Throws Keyword
- Java Throw vs Throws
- Final vs Finally vs Finalize
- Exception Handling with Method Overriding
- Java Custom Exceptions
Java Inner Class
- What is inner class
- Member Inner class
- Anonymous Inner class
- Local Inner class
- static nested class
- Nested Interface
Java Multithreading
- What is Multithreading
- Life Cycle of a Thread
- How to Create Thread
- Thread Scheduler
- Sleeping a thread
- Start a thread twice
- Calling run() method
- Joining a thread
- Naming a thread
- Thread Priority
- Daemon Thread
- Thread Pool
- Thread Group
- ShutdownHook
- Performing multiple task
- Garbage Collection
- Runtime class
Java Synchronization
- Synchronization in java
- synchronized block
- static synchronization
- Deadlock in Java
- Inter-thread Comm
- Interrupting Thread
- Reentrant Monitor
Java Networking
- Networking Concepts
- Socket Programming
- URLConnection class
- HttpURLConnection
- InetAddress class
Java Applet
- Applet Basics
- Graphics in Applet
- Displaying image in Applet
- Animation in Applet
- EventHandling in Applet
- JApplet class
- Painting in Applet
- Digital Clock in Applet
- Analog Clock in Applet
- Parameter in Applet
- Applet Communication
Java Reflection
- Reflection API
- newInstance() method
- creating javap tool
- creating appletviewer
- Call private method
Java Conversion
- Java String to int
- Java int to String
- Java String to long
- Java long to String
- Java String to float
- Java float to String
- Java String to double
- Java double to String
- Java String to Date
- Java Date to String
- Java String to char
- Java char to String
- Java String to Object
- Java Object to String
- Java int to long
- Java long to int
- Java int to double
- Java double to int
- Java char to int
- Java int to char
- Java String to boolean
- Java boolean to String
- Date to Timestamp
- Timestamp to Date
- Binary to Decimal
- Decimal to Binary
- Hex to Decimal
- Decimal to Hex
- Octal to Decimal
- Decimal to Octal
- JDBC Introduction
- JDBC Driver
- DB Connectivity Steps
- Connectivity with Oracle
- Connectivity with MySQL
- Access without DSN
- DriverManager
- PreparedStatement
- ResultSetMetaData
- DatabaseMetaData
- Store image
- Retrieve image
- Retrieve file
- CallableStatement
- Transaction Management
- Batch Processing
- RowSet Interface
- Internationalization
- ResourceBundle class
- I18N with Date
- I18N with Time
- I18N with Number
- I18N with Currency
- Java Array Class
- getBoolean()
- getDouble()
- getLength()
- newInstance()
- setBoolean()
- setDouble()
- Java AtomicInteger Class
- addAndGet(int delta)
- compareAndSet(int expect, int update)
- decrementAndGet()
- doubleValue()
- floatValue()
- getAndAdd()
- getAndDecrement()
- getAndSet()
- incrementAndGet()
- getAndIncrement()
- lazySet(int newValue)
- longValue()
- set(int newValue)
- weakCompareAndSet(int expect,int newValue)
- Java AtomicLong Methods
- addAndGet()
- compareAndSet()
- weakCompareAndSet()
- Java Authenticator
- getPasswordAuthentication()
- getRequestingHost()
- getRequestingPort()
- getRequestingPrompt()
- getRequestingProtocol()
- getRequestingScheme()
- getRequestingSite()
- getRequestingURL()
- getRequestorType()
- setDefault()
- Java BigDecimal class
- intValueExact()
- movePointLeft()
- movePointRight()
- Big Integer Class
- bitLength()
- compareTo()
- divideAndRemainder()
- getLowestSetBit()
- isProbablePrime()
- modInverse()
- nextProbablePrime()
- probablePrime()
- shiftLeft()
- shiftRight()
- toByteArray()
- Java Boolean class
- booleanValue()
- logicalAnd()
- logicalOr()
- logicalXor()
- parseBoolean()
Java Byte Class
- byteValue()
- compareUnsigned()
- parseByte()
- shortValue()
- toUnsignedInt()
- toUnsignedLong()
- asSubclass()
- desiredAssertionStatus()
- getAnnotatedInterfaces()
- getAnnotatedSuperclass()
- getAnnotation()
- getAnnotationsByType()
- getAnnotations()
- getCanonicalName()
- getClasses()
- getClassLoader()
- getComponentType
- getConstructor()
- getConstructors()
- getDeclaredAnnotation()
- getDeclaredAnnotationsByType()
- getDeclaredAnnotations()
- getDeclaredConstructor()
- getDeclaredConstructors()
- getDeclaredField()
- getDeclaredFields()
- getDeclaredMethod()
- getDeclaredMethods()
- getDeclaringClass()
- getFields()
- getGenericInterfaces()
- getGenericSuperClass()
- getInterfaces()
- getMethod()
- getMethods()
- getModifiers()
- getPackage()
- getPackageName()
- getProtectionDomain()
- getResource()
- getSigners()
- getSimpleName()
- getSuperClass()
- isAnnotation()
- isAnnotationPresent()
- isAnonymousClass()
- isInstance()
- isInterface()
- isPrimitive()
- isSynthetic()
- Java Collections class
- asLifoQueue()
- binarySearch()
- checkedCollection()
- checkedList()
- checkedMap()
- checkedNavigableMap()
- checkedNavigableSet()
- checkedQueue()
- checkedSet()
- checkedSortedMap()
- checkedSortedSet()
- emptyEnumeration()
- emptyIterator()
- emptyList()
- emptyListIterator()
- emptyNavigableMap()
- emptyNavigableSet()
- emptySortedMap()
- emptySortedSet()
- enumeration()
- frequency()
- indexOfSubList()
- lastIndexOfSubList()
- newSetFromMap()
- replaceAll()
- reverseOrder()
- singleton()
- singletonList()
- singletonMap()
- synchronizedCollection()
- synchronizedList()
- synchronizedMap()
- synchronizedNavigableMap()
- synchronizedNavigableSet()
- synchronizedSet()
- synchronizedSortedMap()
- synchronizedSortedSet()
- unmodifiableCollection()
- unmodifiableList()
- unmodifiableMap()
- unmodifiableNavigableMap()
- unmodifiableNavigableSet()
- unmodifiableSet()
- unmodifiableSortedMap()
- unmodifiableSortedSet()
Java Compiler Class
- Java Compiler
- compileClass()
- compileClasses()
CopyOnWriteArrayList
- Java CopyOnWriteArrayList
- lastIndexOf()
Java Math Methods
- Math.round()
- Math.sqrt()
- Math.cbrt()
- Math.signum()
- Math.ceil()
- Math.copySign()
- Math.nextAfter()
- Math.nextUp()
- Math.nextDown()
- Math.floor()
- Math.floorDiv()
- Math.random()
- Math.rint()
- Math.hypot()
- Math.getExponent()
- Math.IEEEremainder()
- Math.addExact()
- Math.subtractExact()
- Math.multiplyExact()
- Math.incrementExact()
- Math.decrementExact()
- Math.negateExact()
- Math.toIntExact()
- Math.log10()
- Math.log1p()
- Math.expm1()
- Math.asin()
- Math.acos()
- Math.atan()
- Math.sinh()
- Math.cosh()
- Math.tanh()
- Math.toDegrees
- Math.toRadians
LinkedBlockingDeque
- Java LinkedBlockingDeque
- descendingIterator()
- offerFirst()
- offerLast()
- peekFirst()
- pollFirst()
- Java Long class
LinkedTransferQueue
- Java LinkedTransferQueue
- spliterator()
- Difference between Array and ArrayList
- When to use ArrayList and LinkedList in Java
- Difference between ArrayList and Vector
- How to Compare Two ArrayList in Java
- How to reverse ArrayList in Java
- How to make ArrayList Read Only
- Difference between length of array and size() of ArrayList in Java
- How to Synchronize ArrayList in Java
- How to convert ArrayList to Array and Array to ArrayList in java
- Array vs ArrayList in Java
- How to Sort Java ArrayList in Descending Order
- How to remove duplicates from ArrayList in Java
- Java MulticastSocket
- getInterface()
- getLoopbackMode()
- getNetworkInterface()
- getTimeToLive()
- joinGroup()
- leaveGroup()
- setInterface()
- setLoopbackMode()
- setNetworkInterface()
- setTimeToLive()
- Java Number Class
Java Phaser Class
- Java Phaser
- arriveAndAwaitAdvance()
- arriveAndDeregister()
- getParent()
- awaitAdvanceInterruptibly()
- awaitAdvance()
- bulkRegister()
- forceTermination()
- getArrivedParties()
- getRegisteredParties()
- getUnarrivedParties()
- isTerminated()
ArrayList Methods
- listIterator()
- removeRange
Java Thread Methods
- currentThread()
- getPriority()
- setPriority()
- setDaemon()
- interrupt()
- isinterrupted()
- interrupted()
- activeCount()
- checkAccess()
- dumpStack()
- getStackTrace()
- enumerate()
- getThreadGroup()
- notifyAll()
- setContextClassLoader()
- getContextClassLoader()
- getDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler()
- setDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler()
Java Projects
- Free Java Projects
- Payment Bill(JSP)
- Transport (JSP)
- Connect Globe (JSP)
- Online Banking (JSP)
- Online Quiz (JSP)
- Classified (JSP)
- Mailcasting (JSP)
- Online Library (JSP)
- Pharmacy (JSP)
- Mailer (Servlet)
- Baby Care (Servlet)
- Chat Server (Core)
- Library (Core)
- Exam System (Core)
- Java Apps (Core)
- Fee Report (Core)
- Fee (Servlet)
- eLibrary (Servlet)
- Fire Detection
- Attendance System
- Fibonacci Series in Java
- Prime Number Program in Java
- Palindrome Program in Java
- Factorial Program in Java
- Armstrong Number in Java
- How to Generate Random Number in Java
- How to Print Pattern in Java
- How to Compare Two Objects in Java
- How to Create Object in Java
- How to Print ASCII Value in Java
- How to Reverse a Number in Java
- Java Program to convert Number to Word
- Automorphic Number Program in Java
- Peterson Number in Java
- Sunny Number in Java
- Tech Number in Java
- Fascinating Number in Java
- Keith Number in Java
- Neon Number in Java
- Spy Number in Java
- ATM program Java
- Autobiographical Number in Java
- Emirp Number in Java
- Sphenic Number in Java
- Buzz Number Java
- Duck Number Java
- Evil Number Java
- ISBN Number Java
- Krishnamurthy Number Java
- Bouncy Number in Java
- Mystery Number in Java
- Smith Number in Java
- Strontio Number in Java
- Xylem and Phloem Number in Java
- nth Prime Number Java
- Java Program to Display Alternate Prime Numbers
- Java Program to Find Square Root of a Number Without sqrt Method
- Java Program to Swap Two Numbers Using Bitwise Operator
- Java Program to Find GCD of Two Numbers
- Java Program to Find Largest of Three Numbers
- Java Program to Find Smallest of Three Numbers Using Ternary Operator
- Java Program to Check if a Number is Positive or Negative
- Java Program to Check if a Given Number is Perfect Square
- Java Program to Display Even Numbers From 1 to 100
- Java Program to Display Odd Numbers From 1 to 100
- Java Program to Find Sum of Natural Numbers
- Java Program to copy all elements of one array into another array
- Java Program to find the frequency of each element in the array
- Java Program to left rotate the elements of an array
- Java Program to print the duplicate elements of an array
- Java Program to print the elements of an array
- Java Program to print the elements of an array in reverse order
- Java Program to print the elements of an array present on even position
- Java Program to print the elements of an array present on odd position
- Java Program to print the largest element in an array
- Java Program to print the smallest element in an array
- Java Program to print the number of elements present in an array
- Java Program to print the sum of all the items of the array
- Java Program to right rotate the elements of an array
- Java Program to sort the elements of an array in ascending order
- Java Program to sort the elements of an array in descending order
- Java Program to Find 3rd Largest Number in an array
- Java Program to Find 2nd Largest Number in an array
- Java Program to Find Largest Number in an array
- Java to Program Find 2nd Smallest Number in an array
- Java Program to Find Smallest Number in an array
- Java Program to Remove Duplicate Element in an array
- Java Program to Print Odd and Even Numbers from an array
- How to Sort an Array in Java
- Java Matrix Programs
- Java Program to Add Two Matrices
- Java Program to Multiply Two Matrices
- Java Program to subtract the two matrices
- Java Program to determine whether two matrices are equal
- Java Program to display the lower triangular matrix
- Java Program to display the upper triangular matrix
- Java Program to find the frequency of odd & even numbers in the given matrix
- Java Program to find the product of two matrices
- Java Program to find the sum of each row and each column of a matrix
- Java Program to find the transpose of a given matrix
- Java Program to determine whether a given matrix is an identity matrix
- Java Program to determine whether a given matrix is a sparse matrix
- Java Program to Transpose matrix
- Java Program to count the total number of characters in a string
- Java Program to count the total number of characters in a string 2
- Java Program to count the total number of punctuation characters exists in a String
- Java Program to count the total number of vowels and consonants in a string
- Java Program to determine whether two strings are the anagram
- Java Program to divide a string in 'N' equal parts.
- Java Program to find all subsets of a string
- Java Program to find the longest repeating sequence in a string
- Java Program to find all the permutations of a string
- Java Program to remove all the white spaces from a string
- Java Program to replace lower-case characters with upper-case and vice-versa
- Java Program to replace the spaces of a string with a specific character
- Java Program to determine whether a given string is palindrome
- Java Program to determine whether one string is a rotation of another
- Java Program to find maximum and minimum occurring character in a string
- Java Program to find Reverse of the string
- Java program to find the duplicate characters in a string
- Java program to find the duplicate words in a string
- Java Program to find the frequency of characters
- Java Program to find the largest and smallest word in a string
- Java Program to find the most repeated word in a text file
- Java Program to find the number of the words in the given text file
- Java Program to separate the Individual Characters from a String
- Java Program to swap two string variables without using third or temp variable.
- Java Program to print smallest and biggest possible palindrome word in a given string
- Reverse String in Java Word by Word
- Reserve String without reverse() function
- Linear Search in Java
- Binary Search in Java
- Bubble Sort in Java
- Selection Sort in Java
- Insertion Sort in Java
- How to convert String to int in Java
- How to convert int to String in Java
- How to convert String to long in Java
- How to convert long to String in Java
- How to convert String to float in Java
- How to convert float to String in Java
- How to convert String to double in Java
- How to convert double to String in Java
- How to convert String to Date in Java
- How to convert Date to String in Java
- How to convert String to char in Java
- How to convert char to String in Java
- How to convert String to Object in Java
- How to convert Object to String in Java
- How to convert int to long in Java
- How to convert long to int in Java
- How to convert int to double in Java
- How to convert double to int in Java
- How to convert char to int in Java
- How to convert int to char in Java
- How to convert String to boolean in Java
- How to convert boolean to String in Java
- How to convert Date to Timestamp in Java
- How to convert Timestamp to Date in Java
- How to convert Binary to Decimal in Java
- How to convert Decimal to Binary in Java
- How to convert Hex to Decimal in Java
- How to convert Decimal to Hex in Java
- How to convert Octal to Decimal in Java
- How to convert Decimal to Octal in Java
- Java program to print the following spiral pattern on the console
- Java program to print the following pattern
- Java program to print the following pattern 2
- Java program to print the following pattern 3
- Java program to print the following pattern 4
- Java program to print the following pattern 5
- Java program to print the following pattern on the console
- Java program to print the following pattern on the console 2
- Java program to print the following pattern on the console 3
- Java program to print the following pattern on the console 4
- Java program to print the following pattern on the console 5
- Java program to print the following pattern on the console 6
- Java program to print the following pattern on the console 7
- Java program to print the following pattern on the console 8
- Java program to print the following pattern on the console 9
- Java program to print the following pattern on the console 10
- Java program to print the following pattern on the console 11
- Java program to print the following pattern on the console 12
- Singly linked list Examples in Java
- Java Program to create and display a singly linked list
- Java program to create a singly linked list of n nodes and count the number of nodes
- Java program to create a singly linked list of n nodes and display it in reverse order
- Java program to delete a node from the beginning of the singly linked list
- Java program to delete a node from the middle of the singly linked list
- Java program to delete a node from the end of the singly linked list
- Java program to determine whether a singly linked list is the palindrome
- Java program to find the maximum and minimum value node from a linked list
- Java Program to insert a new node at the middle of the singly linked list
- Java program to insert a new node at the beginning of the singly linked list
- Java program to insert a new node at the end of the singly linked list
- Java program to remove duplicate elements from a singly linked list
- Java Program to search an element in a singly linked list
- Java program to create and display a Circular Linked List
- Java program to create a Circular Linked List of N nodes and count the number of nodes
- Java program to create a Circular Linked List of n nodes and display it in reverse order
- Java program to delete a node from the beginning of the Circular Linked List
- Java program to delete a node from the end of the Circular Linked List
- Java program to delete a node from the middle of the Circular Linked List
- Java program to find the maximum and minimum value node from a circular linked list
- Java program to insert a new node at the beginning of the Circular Linked List
- Java program to insert a new node at the end of the Circular Linked List
- Java program to insert a new node at the middle of the Circular Linked List
- Java program to remove duplicate elements from a Circular Linked List
- Java program to search an element in a Circular Linked List
- Java program to sort the elements of the Circular Linked List
- Java program to convert a given binary tree to doubly linked list
- Java program to create a doubly linked list from a ternary tree
- Java program to create a doubly linked list of n nodes and count the number of nodes
- Java program to create a doubly linked list of n nodes and display it in reverse order
- Java program to create and display a doubly linked list
- Java program to delete a new node from the beginning of the doubly linked list
- Java program to delete a new node from the end of the doubly linked list
- Java program to delete a new node from the middle of the doubly linked list
- Java program to find the maximum and minimum value node from a doubly linked list
- Java program to insert a new node at the beginning of the Doubly Linked list
- Java program to insert a new node at the end of the Doubly Linked List
- Java program to insert a new node at the middle of the Doubly Linked List
- Java program to remove duplicate elements from a Doubly Linked List
- Java program to rotate doubly linked list by N nodes
- Java program to search an element in a doubly linked list
- Java program to sort the elements of the doubly linked list
- Java Program to calculate the Difference between the Sum of the Odd Level and the Even Level Nodes of a Binary Tree
- Java program to construct a Binary Search Tree and perform deletion and In-order traversal
- Java program to convert Binary Tree to Binary Search Tree
- Java program to determine whether all leaves are at same level
- Java program to determine whether two trees are identical
- Java program to find maximum width of a binary tree
- Java program to find the largest element in a Binary Tree
- Java program to find the maximum depth or height of a tree
- Java program to find the nodes which are at the maximum distance in a Binary Tree
- Java program to find the smallest element in a tree
- Java program to find the sum of all the nodes of a binary tree
- Java program to find the total number of possible Binary Search Trees with N keys
- Java program to implement Binary Tree using the Linked List
- Java program to search a node in a Binary Tree
- Java Main Method
- System.out.println()
- Java Memory Management
- Java ClassLoader
- Java Decompiler
- Java vs. JavaScript
- Java vs. Kotlin
- Java vs. Python
- Java Absolute Value
- How to Create File
- Delete a File in Java
- Open a File in Java
- Sort a List in Java
- Convert byte Array to String
- Java Basics
- How to Compile & Run Java Program
- How to Run Java Program in Eclipse
- How to Verify Java Version
- Ways to Create an Object in Java
- How to Run a Java program in Windows 10
- Runnable Interface in Java
- Java Keystore
- Get input from user in Java
- Read file line by line in Java
- Take String input in Java
- How to Read Excel File in Java
- Read XML File in Java
- CompletableFuture in Java
- Java ExecutorService
- How to iterate Map in Java
- How to Return an Array in Java
- How to Sort HashMap by Value
- How to Sort HashMap in Java
- Load Factor in HashMap
- Array vs ArrayList
- HashMap vs TreeMap
- HashSet vs HashMap class
- Compare Two ArrayList in Java
- Merge Two Arrays in Java
- Print Array in Java
- Read CSV File in Java
- Remove Special Characters from String
- ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
- ConcurrentModificationException
- NoSuchElementException
- NumberFormatException
- How to Sort ArrayList in Java
- How to Download Java
- How to Call a Method in Java
- How to Create Singleton Class in Java
- How to Find Array Length in Java
- How to Read Character in Java
- Can We Overload main() Method in Java
- How to Convert Char Array to String in Java
- How to Run Java Program in CMD Using Notepad
- How to Sort String Array in Java
- How to Compare Dates in Java
- How to Take Multiple String Input in Java Using Scanner
- How to Remove Last Character from String in Java
- How TreeMap Works Internally in Java
- Java Program to Break Integer into Digits
- Java Program to Calculate Area and Circumference of Circle
- What is Diamond Problem in Java
- Java Program to Read Number from Standard Input
- How to Download Minecraft Java Edition
- Can We Override Static Method in Java
- How to Avoid Deadlock in Java
- How to Achieve Abstraction in Java
- How Garbage Collection Works in Java
- How to Take Array Input in Java
- How to Create Array of Objects in Java
- How to Create Package in Java
- How to Print in Java
- What is Framework in Java
- Why Java is Secure
- How to Iterate List in Java
- How to Use Eclipse for Java
- Which Package is Imported by Default in Java
- Could Not Find or Load Main Class in Java
- How to Compare Two Arrays in Java
- How to Convert String to JSON Object in Java
- Which is Better Java or Python
- How to Update Java
- How to Get Value from JSON Object in Java Example
- How to Split a String in Java with Delimiter
- Structure of Java Program
- Why We Use Constructor in Java
- Java Create Excel File
- Java Interpreter
- javac is not Recognized
- Dynamic Array in Java
- Shunting yard algorithm
- Java Destructor
- Custom ArrayList in Java
- ArrayList vs HashMap
- Java Constant
- Java Tokens
- How to Enable Java in Chrome
- Java Semaphore
- Array to List in Java
- JIT in Java
- How to Clear Screen in Java
- Java Logger
- Reverse a String Using Recursion in Java
- Java Path Vs File
- Float Vs Double Java
- Stack vs Heap Java
- Abstraction vs Encapsulation
- Top 10 Java Books
- Public vs Private
- What is Java Used For
- Bitwise Operator in Java
- SOLID Principles Java
- Type Casting in Java
- Conditional Operator in Java
- Ternary Operator Java
- Java Architecture
- REPL in Java
- Types of Exception in Java
- Why String is Immutable or Final in Java
- Java vs Kotlin
- Set in Java
- Why non-static variable cannot be referenced from a static context in Java
- Java Developer Roles and Responsibilities
- Types of Classes in Java
- Marker Interface in Java
- Static Function in Java
- Unary Operators in Java
- What is Advance Java
- ArrayList Implementation
- Convert ArrayList to String Array
- Hashmap vs ConcurrentHashMap
- List vs ArrayList
- Map vs HashMap
- HashSet vs LinkedHashSet
- How TreeSet Works Internally
- LinkedHashMap vs HashMap
- Java Program to Solve Quadratic Equation
- Scope Resolution Operator in Java
- Composition in Java
- File Operations in Java
- NoClassDefFoundError in Java
- Thread Concept in Java
- Upcasting and Downcasting in Java
- Dynamic Polymorphism in Java
- String Pool in Java
- What is constructor chaining in Java
- Add elements to Array in Java
- Advantages and disadvantages of Java
- Advantages of JavaBeans
- AWS SDK for Java with Apache Maven
- AWT and Swing in Java
- AWT Program in Java
- Boolean values in Java
- ByteStream Classes in Java
- CharacterStream Classes in Java
- Class and Interface in Java
- ClassCast Exception in Java
- Cloneable in Java
- Constructor overloading in Java
- Control Flow in Java
- Convert Java Object to Json using GSON
- Convert XML to JSON in Java
- How to avoid null pointer exception in Java
- Java constructor returns a value, but what
- Singleton Class in Java
- Doubly Linked List Program in Java
- Association in Java
- Big data Java vs Python
- Branching Statements in Java
- Collections Sort in Java 8
- List vs Set in Java
- How many days required to learn Java
- Implicitly Typecasting in Java
- Legacy Class in Java
- Character Array in Java
- Equals() and Hashcode() in Java
- Externalization in Java
- Identifiers in Java
- InvocationTargetException
- Java Pass by Value
- Mutable and Immutable in Java
- Power Function in Java
- Primitive Data Types in Java
- String Array in Java
- Virtual Function in Java
- C vs C++ vs Java
- Java String Max Size
- Convert Java object to JSON
- How to Calculate Date Difference in Java
- How to Improve Coding Skills in Java
- Java Email Validation
- Java Testing Tools
- Permutation and Combination in Java
- Unique Number in Java Program
- Java Code for DES
- Pig Latin Program in Java
- Array Rotation in Java
- Equilibrium Index of an Array in Java
- Different Ways to Print Exception Message in Java
- Java Copy Constructor Example
- Why We Use Static Class in Java
- What is Core Java
- Set vs Map in Java
- How to Create a New Folder in Java
- Remove an Element from ArrayList in Java
- How to Create Test Cases for Exceptions in Java
- How to Convert JSON Array to ArrayList in Java
- How to Create a Class File in Java
- Java Spring Pros & Cons
- Java Stack Trace
- Array Slicing in Java
- Flutter vs Java
- Permutation of Numbers in Java
- Magic Number in Java
- Reference Data Types in Java
- Counter variable in Java
- How to take Character Input in Java using BufferedReader Class
- Java employee details program
- Java is case sensitive explain
- Ramanujan Number or Taxicab Number in Java
- Advanced Java Books in 2021
- Fail Fast and Fail Safe Iterator in Java
- How to build a Web Application Using Java
- Is Java Interpreted or Compiled
- Java Big Data Frameworks
- Java Get Data From URL
- No Main Manifest Attribute
- Java missing return statement
- Java program to remove duplicate characters from a string
- JUnit test case example in Java
- List of logical programs in Java
- PermGen space Java
- Unsigned Right Shift Operator in Java
- Infix to Postfix Java
- Memory Leak in Java
- How To Write Test Cases In Java
- Java 32-Bit Download For Windows 10
- FizzBuzz Program in Java
- A Java Runtime Environment JRE Or JDK Must Be Available
- Java Does Not Open
- No Java Virtual Machine was Found
- Java Program Number to Word
- Types of Garbage Collector in Java
- No Suitable Driver Found For JDBC
- AVL Tree program in Java
- Fail-fast and Fail-safe in Java
- Find unique elements in array Java
- Highest precedence in Java
- Java Closure
- Java String Encoding
- Prim's algorithm Java
- Quartz scheduler java
- Red Black Tree Java
- GC Overhead Limit Exceeded
- Generating QR Code in Java
- Delegation Event Model in Java
- Java Profilers
- Java Flight Recorder
- Bucket Sort in Java
- Java Atomic
- Wait vs Sleep in Java
- Executor Framework Java
- Gregorian calendar Java
- int vs Integer Java
- What is truncation in Java
- Java HTTP Proxy Server
- Java Static Constructor
- How to prepare for Java Interview
- Java callback function
- Java 8 vs Java 11
- Login Form Java
- Vaadin Framework Java
- EJB vs. Spring
- Types of Applets in Java
- Visitor Design Pattern Java
- Advantages of Python over Java
- Design Principles in Java
- JSON Validator Java
- Pseudocode Java
- Windows Programming Using Java
- Vert.x Java
- Complex Java Programs
- ORE Number Java
- PalPrime Number Java
- Twin Prime Numbers
- Twisted Prime Number Java
- Ugly number Java
- Achilles Number in Java
- Amicable Pair Number in Java
- Playfair Cipher Program in Java
- Java.lang.outofmemoryerror: java heap space
- Banker's Algorithm Java
- Kruskal Algorithm Java
- Longest Common Subsequence
- Travelling Salesman Problem
- & vs && in Java
- Jumping Number in Java
- Lead Number in Java
- Lucky Number in Java
- Middle Digit Number in Java
- Special Number in Java
- Passing Array to Function In Java
- Lexicographical Order Java
- Adam Number in Java
- Bell Number in Java
- Reduce Java
- LRU Cache Implementation
- Goldbach Number in Java
- How to Find Number of Objects Created in Java
- Multiply Two Numbers Without Using Arithmetic Operator in Java
- Sum of Digits of a Number in Java
- Sum of Numbers in Java
- Power of a Number in Java
- Sum of Prime Numbers in Java
- Cullen Number in Java
- Mobile Number Validation in Java
- Fermat Number in Java
- Instantiation in Java
- Exception Vs Error in Java
- flatMap() Method in Java 8
- How to Print Table in Java
- Java Create PDF
- Mersenne Number in Java
- Pandigital Number in Java
- Pell Number in Java
- Java Get Post
- Fork Join in Java
- Java Callable Example
- Blockchain Java
- Design of JDBC
- Java Anon Proxy
- Knapsack Problem Java
- Session Tracking in Java
- What is Object-Oriented Programming
- Literals in Java
- Square Free Number in Java
- What is an anagram in Java
- What is programming
- Iterate JSON Array Java
- Java Date Add Days
- Javac Command Not Found
- Factorial Program in Java Using while Loop
- Frugal Number in Java
- Java Digital Signature
- Catalan Number in Java
- Partition Number in Java
- Powerful Number in Java
- Practical Number in Java
- Chromatic Number in Java
- Sublime Number in Java
- Advanced Java Viva Questions
- Getter and Setter Method in Java Example
- How to convert String to String array in Java
- How to Encrypt Password in Java
- Instance Variable in Java
- Java File Extension
- Types of Inheritance in Java
- Untouchable Number in Java
- AES 256 Encryption in Java
- Applications of Array in Java
- Example of Static Import in Java
- Hill Cipher Program in Java
- Lazy Loading in Java
- Rectangular Number in Java
- How to Print Table in Java Using Formatter
- IdentityHashMap Class in Java
- Undulating Number in Java
- Java Obfuscator
- Java Switch String
- Applet Life Cycle in Java
- Banking Application in Java
- Duodecimal in Java
- Economical Number in Java
- Figurate Number in Java
- How to resolve IllegalStateException in Java
- Java Coding Software
- Java Create Jar Files
- Java Framework List
- Java Initialize array
- java lang exception no runnable methods
- Nonagonal Number in Java
- SexagesimalFormatter in Java
- Sierpinski Number in Java
- Vigesimal in Java
- Java Color Codes
- JDoodle Java
- Online Java Compiler
- Pyramidal Number in Java
- Relatively Prime in Java
- Java Modulo
- Repdigit Numbers in Java
- Abstract Method in Java
- Convert Text-to-Speech in Java
- Java Editors
- MVC Architecture in Java
- Narcissistic Number in Java
- Hashing Algorithm in Java
- Java Escape Characters
- Java Operator Precedence
- Private Constructor in Java
- Scope of Variables in Java
- Groovy vs Java
- Java File Upload to a Folder
- Java Full Stack
- Java Developer
- Thread States in Java
- Java EE vs Node.js
- Loose Coupling in Java
- Java Top 10 Libraries
- Method Hiding in Java
- Dijkstra Algorithm Java
- Extravagant Number in Java
- Java Unicode
- New Line in Java
- Return Statement in Java
- Order of Execution of Constructors in Java Inheritance
- Cardinal Number in Java
- Hyperfactorial in Java
- Identifier Expected Error in Java
- Java Generate UUID
- Labeled Loop in Java
- Lombok Java
- Ordinal Number in Java
- Tetrahedral Number in Java
- Cosmic Superclass in Java
- Shallow Copy Java
- BiFunction Java 8
- Equidigital Number in Java
- Fall Through in Java
- Java Reserved Keywords
- Parking Lot Design Java
- Boyer Moore Java
- Java Security Framework
- Tetranacci Number in Java
- BFS Algorithm in Java
- CountDownLatch in Java
- Counting sort in Java
- CRC Program in Java
- FileNotFoundException in Java
- InputMismatchException in Java
- Java ASCII Table
- Lock in Java
- Segment Tree in Java
- Why main() method is always static in Java
- Bellman-Ford Algorithm Java
- BigDecimal toString() in Java
- .NET vs Java
- Java ZipFile
- Lazy Propagation in Segment Tree in Java
- Magnanimous Number in Java
- Binary Tree Java
- How to Create Zip File in Java
- Java Dot Operator
- Associativity of Operators in Java
- Fenwick Tree in Java
- How annotation works in Java
- How to Find Length of Integer in Java
- Java 8 filters
- List All Files in a Directory in Java
- How to Get Day Name from Date in Java
- Zigzag Array in Java
- Class Definition in Java
- Find Saddle Point of a Matrix in Java
- Non-primitive data types in Java
- Pancake Number in Java
- Pancake Sorting in Java
- Print Matrix Diagonally in Java
- Sort Dates in Java
- Carmichael Numbers in Java
- Contextual Keywords in Java
- How to Open Java Control Panel
- How to Reverse Linked List in Java
- Interchange Diagonal Elements Java Program
- Java Set to List
- Level Order Traversal of a Binary Tree in Java
- Bully algorithm in Java
- Convert JSON File to String in Java
- Convert Milliseconds to Date in Java
- Copy Content/ Data From One File to Another in Java
- Constructor vs Method in Java
- Access Specifiers vs Modifiers
- Java vs PHP
- replace() vs replaceAll() in Java
- this vs super in Java
- Heap implementation in Java
- How to Check null in Java
- Java Arrays Fill
- Rotate Matrix by 90 Degrees in Java
- Exception Class in Java
- Transient variable in Java
- Web crawler Java
- Zigzag Traversal of a Binary Tree in Java
- Java Get File Size
- Internal Working of ArrayList in Java
- Java Program to Print Matrix in Z Form
- Vertical Order Traversal of a Binary Tree in Java
- Group By in Java 8
- Hashing Techniques in Java
- Implement Queue Using Array in Java
- Java 13 Features
- Package Program in Java
- Canonical Name Java
- Method Chaining in Java
- Orphaned Case Java
- Bottom View of a Binary Tree in Java
- Coercion in Java
- Dictionary Class in Java
- Left View of a Binary Tree in Java
- Pangram Program in Java
- Top View of a Binary Tree in Java
- Tribonacci Series in Java
- Hollow Diamond Pattern in Java
- Normal and Trace of a Matrix in Java
- Right View of a Binary Tree in Java
- Dining Philosophers Problem and Solution in Java
- Shallow Copy vs Deep Copy in Java
- Java Password Generator
- Java Program for Shopping Bill
- Lock Interface in Java
- Convert JSON to Map in Java
- Convert JSON to XML in Java
- Middle Node of a Linked List in Java
- Pernicious Number in Java
- Cohesion in Java
- How to get UTC time in Java
- Jacobsthal Number in Java
- Java Calculate Age
- Tribonacci Number Java
- Bernoulli number in Java
- Cake Number in Java
- Compare time in Java
- Compare Two Sets in Java
- Crown Pattern in Java
- Convert List to Array in Java
- Aggregation vs Composition
- Morris Traversal for Inorder in Java
- Morris Traversal for Preorder in Java
- Package Naming Conversion in Java
- India Map Pattern in Java
- Ladder Pattern in Java
- ORM Tools in Java
- Odious Number in Java
- Rat in a Maze Problem in Java
- Sudoku in Java
- Christmas Tree Pattern in Java
- Double Hashing in Java
- Magic Square in Java
- Possible Paths from Top Left to Bottom Right of a Matrix in Java
- Palindrome Partitioning Problem in Java
- Rehashing in Java
- Round Robin Scheduling Program in Java
- Types of Statements in Java
- Compound Assignment Operator in Java
- Prime Points in Java
- Butterfly Pattern in Java
- Fish Pattern in Java
- Flag Pattern in Java
- Kite pattern in Java
- Swastika Pattern in Java
- Tug of War in Java
- Clone HashMap in Java
- Fibodiv Number in Java
- Heart Pattern in Java
- How to check data type in Java
- Java Array Clone
- Use of final Keyword in Java
- Factorial of a Large Number in Java
- Race Condition in Java
- Static Array in Java
- Water Jug Problem in Java
- Electricity Bill Program in Java
- Facts about null in Java
- Maximizing Profit in Stock Buy Sell in Java
- Permutation Coefficient in Java
- Convert List to String in Java
- List of Constants in Java
- MOOD Factors to Assess a Java Program
- Computing Digit Sum of All Numbers From 1 to n in Java
- Read PDF File in Java
- Finding Odd Occurrence of a Number in Java
- Java Indentation
- Zig Zag Star and Number Pattern in Java
- Check Whether a Number is a Power of 4 or not in Java
- Kth Smallest in an Unsorted Array in Java
- BlockingQueue in Java
- Next Greater Element in Java
- Star Numbers in Java
- 3N+1 Problem in Java
- Java Program to Find Local Minima in An Array
- Processing Speech in Java
- Java Output Formatting
- House Numbers in Java
- Java Program to Generate Binary Numbers
- Longest Odd-Even Subsequence in Java
- Java Subtract Days from Current Date
- Java Future Example
- Minimum Cost Path Problem in Java
- Diffie-Hellman Algorithm in Java
- Ganesha's Pattern in Java
- Hamming Code in Java
- Map of Map in Java
- Print Pencil Shape Pattern in Java
- Zebra Puzzle in Java
- Display Unique Rows in a Binary Matrix in Java
- Rotate A Matrix By 180 Degree in Java
- Dangling Else Problem in Java
- Java Application vs Java Applet
- Dutch National Flag Problem in Java
- Java Calculate Average of List
- compareToIgnoreCase Java
- Trimorphic Numbers in Java
- Arithmetic Exception in Java
- Java instanceof operator
- Java Localization
- Minimum XOR Value Pair in Java
- Iccanobif Numbers in Java
- Java Program to Count the Occurrences of Each Character
- Java Technologies List
- Java Program to Find the Minimum Number of Platforms Required for a Railway Station
- Shift Operators in Java
- Final Object in Java
- Object Definition in Java
- Shadowing in Java
- Zipping and Unzipping Files in Java
- Display the Odd Levels Nodes of a Binary Tree in Java
- Java Variable Declaration
- Nude Numbers in Java
- Java Programming Challenges
- Java URL Encoder
- anyMatch() in Java 8
- Sealed Class in Java
- Camel case in Java
- Career Options for Java Developers to Aim in 2022
- Java Progress Bar
- Maximum Rectangular Area in a Histogram in Java
- Polygonal Number in Java
- Two Sorted LinkedList Intersection in Java
- Set Matrix Zeros in Java
- Find Number of Island in Java
- Balanced Prime Number in Java
- Minecraft Bedrock vs Java Minecraft
- arr.length vs arr[0].length vs arr[1].length in Java
- Future in Java 8
- How to Set Timer in Java
- Construct the Largest Number from the Given Array in Java
- Minimum Coins for Making a Given Value in Java
- Eclipse Shortcuts Java
- Empty Statement in Java
- Java Program to Implement Two Stacks in an Array
- Java Snippet
- Longest Arithmetic Progression Sequence in Java
- Types of Sockets in Java
- Java Program to Add Digits Until the Number Becomes a Single Digit Number
- Next Greater Number with Same Set of Digits in Java
- Split the Number String into Primes in Java
- Java Cron Expression
- Huffman Coding Java
- Java Snippet Class
- Why Java is So Popular
- Java Project idea
- Java Web Development
- Brilliant Numbers in Java
- Sort Elements by Frequency in Java
- Beautiful Array in Java
- Moran Numbers in Java
- Intersection Point of Two Linked List in Java
- Sparse Number in Java
- How to Check JRE Version
- Java Programming Certification
- Two Decimal Places Java
- Eclipse Change Theme
- Java how to Convert Bytes to Hex
- Decagonal Numbers in Java
- Java Binary to Hexadecimal Conversion
- Java Hexadecimal to Binary Conversion
- How to Capitalize the First Letter of a String in Java
- Java &0XFF Example
- Stream findFirst() Method in Java
- Balanced Parentheses in Java
- Caesar Cipher Program in Java
- next() vs nextLine()
- Java Split String by Comma
- Spliterator in java 8
- Tree Model Nodes in Jackson
- Types of events in Java
- Callable and Future in Java
- How to Check Current JDK Version installed in Your System Using CMD
- How to Round Double and Float up to Two Decimal Places in Java
- Java 8 Multimap
- Parallel Stream in Java
- Java Convert Bytes to Unsigned Bytes
- Display List of TimeZone with GMT and UTC in Java
- Binary Strings Without Consecutive Ones in Java
- Convert IP to Binary in Java
- Returning Multiple Values in Java
- Centered Square Numbers in Java
- ProcessBuilder in Java
- How to Clear Java Cache
- IntSummaryStatistics Class in Java
- Java ProcessBuilder Example
- Java Program to Delete a Directory
- Java Program to Print Even Odd Using Two Threads
- Java Variant
- MessageDigest in Java
- Alphabet Pattern in Java
- Java Linter
- Java Mod Example
- Stone Game in Java
- TypeErasure in Java
- How to Remove substring from String in Java
- Program to print a string in vertical in Java
- How to Split a String between Numbers and Letters
- String Handling in Java
- Isomorphic String in Java
- Java ImageIO Class
- Minimum Difference Subarrays in Java
- Plus One to Array Problem in Java
- Unequal Adjacent Elements in Java
- Java Parallel Stream Example
- SHA Hashing in Java
- How to make Java projects
- Java Fibers
- Java MD5 Hashing Example
- Hogben Numbers in Java
- Self-Descriptive Numbers in Java
- Hybrid Inheritance in Java
- Java IP Address (IPv4) Regex Examples
- Converting Long to Date in JAVA
- Java 17 new features
- GCD of Different SubSequences in Java
- Sylvester Sequence in Java
- Console in Java
- Asynchronous Call in Java
- Minimum Window Substring in Java
- Nth Term of Geometric Progression in Java
- Coding Guidelines in Java
- Couple Holding Hands Problem in Java
- Count Ones in a Sorted binary array in Java
- Ordered Pair in Java
- Tetris Game in Java
- Factorial Trailing Zeroes in Java
- Java Assert Examples
- Minimum Insertion To Form A Palindrome in Java
- Wiggle Sort in Java
- Java Exit Code 13
- Java JFileChooser
- What is LINQ
- NZEC in Java
- Box Stacking Problem
- K Most Frequent Elements in Java
- Parallel Programming in Java
- How to Generate JVM Heap Memory Dump
- Java Program to use Finally Block for Catching Exceptions
- Count Login Attempts Java
- Largest Independent Set in Java
- Longest Subarray With All Even or Odd Elements in Java
- Open and Closed Hashing in Java
- DAO Class in Java
- Kynea Numbers in Java
- UTF in Java
- Zygodromes in Java
- ElasticSearch Java API
- Form Feed in Java
- Java Clone Examples
- Payment Gateway Integration in Java
- What is PMD
- RegionMatches() Method in Java
- Repaint() Method in Java
- Serial Communication in Java
- Count Double Increasing Series in A Range in Java
- Longest Consecutive Subsequence in Java
- Smallest Subarray With K Distinct Numbers in Java
- String Sort Custom in Java
- Count Number of Distinct Substrings in a String in Java
- Display All Subsets of An Integer Array in Java
- Digit Count in a Factorial Of a Number in Java
- Valid Parentheses Problem in Java
- Median Of Stream Of Running Integers in Java
- Arrow Operator in Java
- Java Learning app
- Create Preorder Using Postorder and Leaf Nodes Array
- Display Leaf nodes from Preorder of a BST in Java
- Unicodes for Operators in Java
- XOR and XNOR operators in Java
- AWS Lambda in Java
- AWS Polly in Java
- SAML in Java
- SonarQube in Java
- UniRest in Java
- Override equals method in Java
- Undo and Redo Operations in Java
- Size of longest Divisible Subset in an Array in Java
- Sort An Array According To The Set Bits Count in Java
- Two constructors in one class in Java
- Union in Java
- What is New in Java 15
- ART in Java
- Definite Assignment in Java
- Cast Operator in Java
- Diamond operator in Java
- Java Singleton Enum
- Three-way operator | Ternary operator in Java
- GoF Design Pattern Java
- Shorthand Operator in Java
- What is new in Java 17
- How to Find the Java Version in Linux
- What is New in Java 12
- Exception in Thread Main java.util.NoSuchElementException no line Found
- How to reverse a string using recursion in Java
- Java Program to Reverse a String Using Stack
- Java Program to Reverse a String Using the Stack Data Structure
- Reverse Middle Words of a String in Java
- Sastry Numbers in Java
- Sum of LCM in Java
- Tilde Operator in Java
- 8 Puzzle problems in Java
- Maximum Sum Such That No Two Elements Are Adjacent in Java
- Reverse a String in Place in Java
- Reverse a string Using a Byte array in Java
- Reverse a String Using Java Collections
- Reverse String with Special Characters in Java
- get timestamp in java
- How to convert file to hex in java
- AbstractSet in java
- List vs Set vs Map in Java
- Birthday Problem in Java
- How to Calculate the Time Difference Between Two Dates in Java
- Number of Mismatching Bits in Java
- Palindrome Permutation of a String in Java
- Grepcode java.util.Date
- How to add 24 hrs to date in Java
- How to Change the Day in The Date Using Java
- Java ByteBuffer Size
- java.lang.NoSuchMethodError
- Maximum XOR Value in Java
- How to Add Hours to The Date Object in Java
- How to Increment and Decrement Date Using Java
- Multithreading Scenarios in Java
- Switch case with enum in Java
- Longest Harmonious Subsequence in Java
- Count OR Pairs in Java
- Merge Two Sorted Arrays Without Extra Space in Java
- How to call a concrete method of abstract class in Java
- How to create an instance of abstract class in Java
- Java Console Error
- 503 error handling retry code snippets Java
- Implementation Of Abstraction In Java
- How to avoid thread deadlock in Java
- Number of Squareful Arrays in Java
- One-Time Password Generator Code In Java
- Real-Time Face Recognition In Java
- Converting Integer Data Type to Byte Data Type Using Typecasting in Java
- How to Generate File checksum Value
- Index Mapping (or Trivial Hashing) With Negatives allowed in Java
- Shortest Path in a Binary Maze in Java
- customized exception in Java
- Difference between error and exception in Java
- How to solve deprecated error in Java
- Jagged Array in Java
- CloneNotSupportedException in Java with Examples
- Difference Between Function and Method in Java
- Immutable List in Java
- Nesting Of Methods in Java
- How to Convert Date into Character Month and Year Java
- How to Mock Lambda Expression in Java
- How to Return Value from Lambda Expression Java
- if Condition in Lambda Expression Java
- Chained Exceptions in Java
- Final static variable in Java
- Java File Watcher
- Various Operations on HashSet in Java
- Word Ladder Problem in Java
- Various Operations on Queue in Java
- Various Operations on Queue Using Linked List in Java
- Various Operations on Queue Using Stack in Java
- Get Yesterday's Date from Localdate Java
- Get Yesterday's Date by No of Days in Java
- Advantages of Lambda Expression in Java 8
- Cast Generic Type to Specific type Java
- ConcurrentSkipListSet in Java
- Fail Fast Vs. Fail-Safe in Java
- Get Yesterday's Date in Milliseconds Java
- Get Yesterday's Date Using Date Class Java
- Getting First Date of Month in Java
- Gregorian Calendar Java Current Date
- How to Calculate Time Difference Between Two Dates in Java
- How to Calculate Week Number from Current Date in Java
- Keystore vs Truststore
- Leap Year Program in Java
- Online Java Compiler GDB
- Operators in Java MCQ
- Separators In Java
- StringIndexOutOfBoundsException in Java
- Anonymous Function in Java
- Default Parameter in Java
- Group by Date Code in Java
- How to add 6 months to Current Date in Java
- How to Reverse A String in Java Letter by Letter
- Java 8 Object Null Check
- Java Synchronized
- Types of Arithmetic Operators in Java
- Types of JDBC Drivers in Java
- Unmarshalling in Java
- Write a Program to Print Reverse of a Vowels String in Java
- ClassNotFound Exception in Java
- Null Pointer Exception in Java
- Why Does BufferedReader Throw IOException in Java
- Java Program to Add two Complex Numbers
- Read and Print All Files From a Zip File in Java
- Reverse an Array in Java
- Right Shift Zero Fill Operator in Java
- Static Block in Java
- Accessor and Mutator in Java
- Array of Class Objects in Java
- Benefits of Generics in Java
- Can Abstract Classes Have Static Methods in Java
- ClassNotFoundException Java
- Creating a Custom Generic Class in Java
- Generic Queue Java
- Getting Total Hours From 2 Dates in Java
- How to add 2 dates in Java
- How to Break a Date and Time in Java
- How to Call Generic Method in Java
- How to Increment and Decrement Date using Java
- Java Class Methods List
- Java Full Stack Developer
- Java.lang.NullPointerException
- Least Operator to Express Number in Java
- Shunting Yard Algorithm in Java
- Switch Case Java
- Treeset Java Operations
- Types of Logical Operators in Java
- What is Cast Operator in Java
- What is Jersey in Java
- Alternative to Java Serialization
- API Development in Java
- Disadvantage of Multithreading in Java
- Find the row with the maximum number of 1s
- Generic Comparator in Java
- Generic LinkedList in Java
- Generic Programming in Java Example
- How Can I Give the Default Date in The Array Java
- How to Accept Date in Java
- How to add 4 years to Date in Java
- How to Check Date Equality in Java
- How to Modify HTML File Using Java
- Java 8 Multithreading Features
- Java Abstract Class and Methods
- Java Thread Dump Analyser
- Process vs. Thread in Java
- Reverse String Using Array in Java
- Types of Assignment Operators in Java
- Types of Bitwise Operators in Java
- Union and Intersection Of Two Sorted Arrays In Java
- Vector Operations Java
- Java Books Multithreading
- Advantages of Generics in Java
- Arrow Operator Java
- Generic Code in Java
- Generic Method in Java Example
- Getting a Range of Dates in Java
- Getting the Day from a Date in Java
- How Counter Work with Date Using Java
- How to Add Date in Arraylist Java
- How to Create a Generic List in Java
- Java Extend Multiple Classes
- Java Function
- Java Generics Design Patterns
- Why Are Generics Used in Java
- XOR Binary Operator in Java
- Check if the given string contains all the digits in Java
- Constructor in Abstract Class in Java
- Count number of a class objects created in Java
- Difference Between Byte Code and Machine Code in Java
- Java Program to Append a String in an Existing File
- Main thread in Java
- Store Two Numbers in One Byte Using Bit Manipulation in Java
- The Knight's Tour Problem in Java
- Business Board Problem in Java
- Business Consumer Problem in Java
- Buy as Much Candles as Possible Java Problem
- Get Year from Date in Java
- How to Assign Static Value to Date in Java
- Java List Node
- Java List Sort Lambda
- Java Program to Get the Size of a Directory
- Misc Operators in Java
- Reverse A String and Reverse Every Alternative String in Java
- Reverse a String in Java Using StringBuilder
- Reverse Alternate Words in A String Java
- Size of Empty Class in Java
- Titniry Operation in Java
- Triple Shift Operator in Java
- Types of Conditional Operators in Java
- View Operation in Java
- What is Linked list Operation in Java
- What is Short Circuit && And or Operator in Java
- What is the & Operator in Java
- Why to use enum in Java
- XOR Bitwise Operator in Java
- XOR Logical Operator Java
- Compile-Time Polymorphism in Java
- Convert JSON to Java Object Online
- Difference between comparing String using == and .equals() method in Java
- Difference Between Singleton Pattern and Static Class in Java
- Difference Between Static and Non-Static Nested Class in Java
- Getting Date from Calendar in Java
- How to Swap or Exchange Objects in Java
- Java Get Class of Generic Parameter
- Java Interface Generic Parameter
- Java Map Generic
- Java Program for Maximum Product Subarray
- Java Program To Print Even Length Words in a String
- Logger Class in Java
- Manacher's Algorithm in Java
- Mutable Class in Java
- Online Java IDE
- Package getImplementationVersion() method in Java with Examples
- Set Default Close Operation in Java
- Sorting a Java Vector in Descending Order Using Comparator
- Types of Interfaces in Java
- Understanding String Comparison Operator in Java
- User-Defined Packages in Java
- Valid variants of main() in Java
- What is a Reference Variable in Java
- What is an Instance in Java
- What is Retrieval Operation in ArrayList Java
- When to Use the Static Method in Java
- XOR Operations in Java
- 7th Sep - Array Declaration in Java
- 7th Sep - Bad Operand Types Error in Java
- 7th Sep - Data Structures in Java
- 7th Sep - Generic Type Casting In Java
- 7th Sep - Multiple Inheritance in Java
- 7th Sep - Nested Initialization for Singleton Class in Java
- 7th Sep - Object in Java
- 7th Sep - Recursive Constructor Invocation in Java
- 7th Sep - Java Language / What is Java
- 7th Sep - Why is Java Platform Independent
- 7th Sep - Card Flipping Game in Java
- 7th Sep - Create Generic Method in Java
- 7th Sep - Difference between super and super() in Java with Examples
- 7th Sep - for loop enum Java
- 7th Sep - How to Convert a String to Enum in Java
- 7th Sep - Illustrate Class Loading and Static Blocks in Java Inheritance
- 7th Sep - Introduction To Java
- 7th Sep - Java Lambda foreach
- 7th Sep - Java Latest Version
- 7th Sep - Java Method Signature
- 7th Sep - Java Practice Programs
- 7th Sep - Java SwingWorker Class
- 7th Sep - java.util.concurrent.RecursiveAction class in Java With Examples
- 7th Sep - Largest Palindrome by Changing at Most K-digits in Java
- 7th Sep - Parameter Passing Techniques in Java with Examples
- 7th Sep - Reverse a String in Java Using a While Loop
- 7th Sep - Reverse a String Using a For Loop in Java
- 7th Sep - Short Circuit Operator in Java
- 7th Sep - Java 8 Stream API
- 7th Sep - XOR Operation on Integers in Java
- 7th Sep - XOR Operation on Long in Java
- Array Programs in Java
- Concrete Class in Java
- Difference between Character Stream and Byte Stream in Java
- Difference Between Static and non-static in Java
- Different Ways to Convert java.util.Date to java.time.LocalDate in Java
- Find the Good Matrix Problem in Java
- How Streams Work in Java
- How to Accept Different Formats of Date in Java
- How to Add Date in MySQL from Java
- How to Find the Size of int in Java
- How to Make a Field Serializable in Java
- How to Pass an Array to Function in Java
- How to Pass an ArrayList to a Method in Java
- Implementing the Java Queue Interface
- Initialization of local variable in a conditional block in Java
- isnull() Method in Java
- Java Array Generic
- Java Program to Demonstrate the Lazy Initialization Non-Thread-Safe
- Java Program to Demonstrate the Non-Lazy Initialization Thread-Safe
- Java Static Field Initialization
- Machine Learning Using Java
- Mars Rover Problem in Java
- Model Class in Java
- Nested Exception Handling in Java
- Program to Convert List to Stream in Java
- Static Polymorphism in Java
- Static Reference Variables in Java
- Sum of Two Arrays in Java
- What is Is-A-Relationship in Java
- When to Use Vector in Java
- Which Class cannot be subclassed in Java
- Word Search Problem in Java
- XOR Operation Between Sets in Java
- Burger Problem in Java Game
- Convert Set to List in Java
- Floyd Triangle in Java
- How to Call Static Blocks in Java
- Interface Attributes in Java
- Java Applications in the Real World
- Java Concurrent Array
- Java Detect Date Format
- Java Interface Without Methods
- Java Iterator Performance
- Java Packet
- Java Static Instance of Class
- Java TreeMap Sort by Value
- Length of List in Java
- List of Checked Exceptions in Java
- Message Passing in Java
- Product Maximization Problem in Java
- Terminal Operations in Java 8
- Understanding Base Class in Java
- Difference between Early Binding and Late Binding in Java
- Collectors toCollection() in Java
- Difference between ExecutorService execute() and submit() method in Java
- Difference between Java and Core Java
- Different Types of Recursions in Java
- Initialize a static map in Java with Examples
- Merge Sort Using Multithreading in Java
- Why Thread.stop(), Thread.suspend(), and Thread.resume() Methods are Deprecated After JDK 1.1 Version
- Circular Primes in Java
- Difference Between poll() and remove() Method of a Queue
- EvalEx Java: Expression Evaluation in Java
- Exeter Caption Contest Java Program
- FileInputStream finalize() Method in Java
- Find the Losers of the Circular Game problem in Java
- Finding the Differences Between Two Lists in Java
- Finding the Maximum Points on a Line in Java
- Get Local IP Address in Java
- Handling "Handler dispatch failed" Nested Exception: java.lang.StackOverflowError in Java
- Harmonic Number in Java
- How to Find the Percentage of Uppercase Letters, Lowercase Letters, Digits, and Special Characters in a String Using Java
- Interface Variables in Java
- Java 8 Interface Features
- Java Class Notation
- Java Exception Messages Examples and Explanations
- Java Package Annotation
- Java Program to Find First Non-Repeating Character in String
- Java Static Type Vs. Dynamic Type
- Kaprekar Number in Java
- Multitasking in Java
- Niven Number in Java
- Rhombus Pattern in Java
- Shuffle an Array in Java
- Static Object in Java
- The Scope of Variables in Java
- Toggle String in Java
- Use of Singleton Class in Java
- What is the Difference Between Future and Callable Interfaces in Java
- Aggregate Operation in Java 8
- Bounded Types in Java
- Calculating Batting Average in Java
- Compare Two LinkedList in Java
- Comparison of Autoboxed Integer objects in Java
- Count Tokens in Java
- Cyclomatic Complexity in Java
- Deprecated Meaning in Java
- Double Brace Initialization in Java
- Functional Interface in Java
- How to prevent objects of a class from Garbage Collection in Java
- Java Cast Object to Class
- Java isAlive() Method
- Java Line Feed Character
- java.net.MulticastSocket class in Java
- Keytool Error java.io.FileNotFoundException
- Matrix Diagonal Sum in Java
- Number of Boomerangs Problem in Java
- Sieve of Eratosthenes Algorithm in Java
- Similarities Between Bastar and Java
- Spring vs. Struts in Java
- Switch Case in Java 12
- The Pig Game in Java
- Unreachable Code Error in Java
- Who Were the Kalangs of Java
- 2048 Game in Java
- Abundant Number in Java
- Advantages of Applet in Java
- Alpha-Beta Pruning Java
- ArgoUML Reverse Engineering Java
- Can Constructor be Static in Java
- Can we create object of interface in Java
- Chatbot Application in Java
- Difference Between Component and Container in Java
- Difference Between Java.sql and Javax.sql
- Find A Pair with Maximum Product in Array of Integers
- Goal Stack Planning Program in Java
- Half Diamond Pattern in Java
- How to find trigonometric values of an angle in Java
- How to Override tostring() method in Java
- Inserting a Node in a Doubly Linked List in Java
- Java 9 Immutable Collections
- Java 9 Interface Private Methods
- Java Convert Array to Collection
- Java Transaction API
- Methods to Take Input in Java
- Parallelogram Pattern in Java
- Reminder Program in Java
- Sliding Window Protocol in Java
- Static Method in Java
- String Reverse in Java 8 Using Lambdas
- Types of Threads in Java
- What is thread safety in Java? How do you achieve it?
- xxwxx.dll Virus Java 9
- Java 8 Merge Two Maps with Same Keys
- Java 8 StringJoiner, String.join(), and Collectors.joining()
- Java 9 @SafeVarargs Annotation Changes
- Java 9 Stream API Improvements
- Java 11 var in Lambda Expressions
- Sequential Search Java
- Thread Group in Java
- User Thread Vs. Daemon Thread in Java
- Collections Vs. Streams in Java
- Import statement in Java
- init() Method in Java
- Java Generics Jenkov
- Ambiguity in Java
- Benefits of Learning Java
- Designing a Vending Machine in Java
- Monolithic Applications in Java
- Name Two Types of Java Program
- Random Access Interface in Java
- Rust Vs. Java
- Types of Constants in Java
- Execute the Main Method Multiple Times in Java
- Find the element at specified index in a Spiral Matrix in Java
- Find The Index of An Array Element in Java
- Mark-and-Sweep Garbage Collection Algorithm in Java
- Shadowing of Static Functions in Java
- Straight Line Numbers in Java
- Zumkeller Numbers in Java
- Types of Layout Manager in Java
- Virtual Threads in Java 21
- Add Two Numbers Without Using Operator in Java
- Automatic Type Promotion in Java
- ContentPane Java
- Difference Between findElement() and findElements() in Java
- Difference Between Inheritance and Interfaces in Java
- Difference Between Jdeps and Jdeprscan tools in Java
- Find Length of String in Java Without Using Function
- InvocationTargetException in Java
- Java Maps to JSON
- Key Encapsulation Mechanism API in Java 21
- Placeholder Java
- String Templates in Java 21
- Why Java is Robust Language
- Collecting in Java 8
- containsIgnoreCase() Method in Java
- Convert String to Biginteger In Java
- Convert String to Map in Java
- Define Macro in Java
- Difference Between Lock and Monitor in Java Concurrency
- Difference Between the start() and run() Methods in Java
- Generalization and Specialization in Java
- getChannel() Method in Java
- How to Check Whether an Integer Exists in a Range with Java
- HttpEntity in Java
- Lock Framework Vs. Thread Synchronization in Java
- Niven Number Program in Java
- Passing Object to Method in Java
- Pattern Matching for Switch in Java 21
- Swap First and Last Digit of a Number in Java
- Adapter Design Pattern in Java
- Best Automation Frameworks for Java
- Building a Search Engine in Java
- Bytecode Verifier in Java
- Caching Mechanism in Java
- Comparing Two HashMap in Java
- Cryptosystem Project in Java
- Farthest from Zero Program in Java
- How to Clear Linked List in Java
- Primitive Data Type Vs. Object Data Type in Java
- setBounds() Method in Java
- Unreachable Code or Statement in Java
- What is Architecture Neutral in Java
- Difference between wait and notify in Java
- Dyck Path in Java
- Find the last two digits of the Factorial of a given Number in Java
- How to Get an Environment Variable in Java
- Java Program to open the command prompt and insert commands
- JVM Shutdown Hook in Java
- Semiprimes Numbers in Java
- 12 Tips to Improve Java Code Performance
- Ad-hoc Polymorphism in Java
- Array to String Conversion in Java
- CloudWatch API in Java
- Essentials of Java Programming Language
- Extends Vs. Implements in Java
- 2d Array Sorting in Java
- Aliquot Sequence in Java
- Authentication and Authorization in Java
- Cannot Find Symbol Error in Java
- Compare Two Excel Files in Java
- Consecutive Prime Sum Program in Java
- Count distinct XOR values among pairs using numbers in range 1 to N
- Difference Between Two Tier and Three Tier Architecture in Java
- Different Ways of Reading a Text File in Java
- Empty Array in Java
- FCFS Program in Java with Arrival Time
- Immutable Map in Java
- K-4 City Program in Java
- Kahn's algorithm for Topological Sorting in Java
- Most Popular Java Backend Tools
- Recursive Binary Search in Java
- Set Intersection in Java
- String Reverse Preserving White Spaces in Java
- The Deprecated Annotation in Java
- What is JNDI in Java
- Backtracking in Java
- Comparing Doubles in Java
- Consecutive Prime Sum in Java
- Finding Missing Numbers in an Array Using Java
- Good Number Program in Java
- How to Compress Image in Java Source Code
- How to Download a File from a URL in Java
- Passing an Object to The Method in Java
- Permutation program in Java
- Profile Annotation in Java
- Scenario Based Questions in Java
- Understanding Static Synchronization in Java
- Types of Errors in Java
- Abstract Factory Design Pattern in Java
- Advantages of Kotlin Over Java
- Advantages of Methods in Java
- Applet Program in Java to Draw House with Output
- Atomic Boolean in Java
- Bitset Class in Java
- Bouncy Castle Java
- Chained Exception in Java
- Colossal Numbers in Java
- Compact Profiles Java 8
- Convert Byte to Image in Java
- Convert Set to Array in Java
- Copy ArrayList to another ArrayList Java
- Copy Data from One File to Another in Java
- Dead Code in Java
- Driver Class Java
- EnumMap in Java
- Farthest Distance of a 0 From the Centre of a 2-D Matrix in Java
- How to Terminate a Program in Java
- Instance Block in Java
- Iterative Constructs in Java
- Java 10 var Keyword
- Nested ArrayList in Java
- Square Pattern in Java
- String Interpolation in Java
- Unnamed Classes and Instance Main Method in Java 21
- What is difference between cacerts and Keystore in Java
- Agile Principles Patterns and Practices in Java
- Color Method in Java
- Concurrent Collections in Java
- Create JSON Node in Java
- Difference Between Checkbox and Radio Button in Java
- Difference Between Jdeps and Jdeprscan Tools in Java
- Difference Between Static and Dynamic Dispatch in Java
- Difference Between Static and Non-Static Members in Java
- Error Java Invalid Target Release 9
- Filedialog Java
- String Permutation in Java
- Structured Concurrency in Java
- Uncaught Exception in Java
- ValueOf() Method in Java
- Virtual Thread in Java
- Difference Between Constructor Overloading and Method Overloading in Java
- Difference Between for loop and for-each Loop in Java
- Difference Between Fork/Join Framework and ExecutorService in Java
- Difference Between Local, Instance, and Static Variables in Java
- Difference Between Multithreading and Multiprocessing in Java
- Difference Between Serialization and Deserialization in Java
- Difference Between Socket and Server Socket in Java
- Advantages of Immutable Classes in Java
- BMI Calculator Java
- Code Coverage Tools in Java
- How to Declare an Empty Array in Java
- How To Resolve Java.lang.ExceptionInInitializerError in Java
- Java 18 Snippet Tag with Example
- Object Life Cycle in Java
- print() Vs. println() in Java
- @SuppressWarnings Annotation in Java
- Types of Cloning in Java
- What is portable in Java
- What is the use of an interpreter in Java
- Abstract Syntax Tree (AST) in Java
- Aliasing in Java
- CRUD Operations in Java
- Euclid-Mullin Sequence in Java
- Frame Class in Java
- Initializing a List in Java
- Number Guessing Game in Java
- Number of digits in N factorial to the power N in Java
- Rencontres Number in Java
- Skewed Binary Tree in Java
- Vertical zig-zag traversal of a tree in Java
- Wap to Reverse a String in Java using Lambda Expression
- Concept of Stream in Java
- Constraints in Java
- Context Switching in Java
- Dart Vs. Java
- Dependency Inversion Principle in Java
- Difference Between Containers and Components in Java
- Difference Between CyclicBarrier and CountDownLatch in Java
- Difference Between Shallow and Deep Cloning in Java
- Dots and Boxes Game Java Source code
- DRY Principle Java
- How to get File type in Java
- IllegalArgumentException in Java example
- Is the main() method compulsory in Java
- Java Paradigm
- Lower Bound in Java
- Method Binding in Java
- Overflow and Underflow in Java
- Padding in Java
- Passing and Returning Objects in Java
- Single Responsibility Principle in Java
- ClosedChannelException in Java with Examples
- How to Fix java.net.ConnectException Connection refused connect in Java
- java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException in java with Examples
- Selection Statement in Java
- Difference Between Java 8 and Java 9
- Difference Between Nested Class and Inner Class in Java
- Difference Between OOP and POP in Java
- Difference Between Static and Dynamic in Java
- Difference Between Static Binding and Dynamic Binding in Java
- Difference Between Variable and Constant in Java
- Alternate Pattern Program in Java
- Architecture Neutral in Java
- AutoCloseable Interface in Java
- BitSet Class in Java
- Border Layout Manager in Java
- Digit Extraction in Java
- Dynamic Method Dispatch Java
- Dynamic Variable in Java
- How to Convert Double to string in Java
- How to Convert Meter to Kilometre in Java
- How to Install SSL Certificate in Java
- How to Protect Java Source Code
- How to Use Random Object in Java
- Java Backward Compatibility
- Java New String Class Methods from Java 8 to Java 17
- Mono in Java
- Object to int in Java
- Predefined Streams in Java
- Prime Factor Program in Java
- Transfer Statements in Java
- What is Interceptor in Java
- Java Array Methods
- java.lang.Class class in Java
- Reverse Level Order Traversal in Java
- Working with JAR and Manifest files In Java
- Alphabet Board Path Problem in Java
- Composite Design Pattern Java
- Default and Static Methods in Interface Java 8
- Difference Between Constraints and Annotations in Java
- Difference Between fromJson() and toJson() Methods of GSON in Java
- Difference Between Java 8 and Java 11
- Difference Between map() and flatmap() Method in Java 8
- Difference Between next() and nextLine() Methods in Java
- Difference Between orTimeout() and completeOnTimeOut() Methods in Java 9
- Disadvantages of Array in Java
- How Synchronized works in Java
- How to Create a Table in Java
- ID Card Generator Using Java
- Introspection in JavaBeans
- Java 15 Features
- Java Object Model
- Java Tools and Command-List
- Next Permutation Java
- Object as Parameter in Java
- Optimizing Java Code Performance
- Pervasive Shallowness in Java
- Sequenced Collections in Java 21
- Stdin and Stdout in Java
- Stream count() Function in Java
- String.strip() Method in Java
- Vertical Flip Matrix Problem in Java
- Calling Object in Java
- Characteristics of Constructor in Java
- Counting Problem in Multithreading in Java
- Creating Multiple Pools of Objects of Variable Size in Java
- Default Exception in Java
- How to Install Multiple JDK's in Windows
- Differences Between Vectors and Arrays in Java
- Duplicate Class Errors in Java
- Example of Data Hiding in Java
- Foreign Function and Memory APIs in Java 21
- Generic Tree Implementation in Java
- getSource() Method in Java
- Giuga numbers in Java
- Hessian Java
- How to Connect Login Page to Database in Java
- Difference between BlueJ and JDK 1.3
- How to Solve Incompatible Types Error in Java
- Java 8 Method References
- Java 9 Try with Resources Improvements
- Menu-Driven Program in Java
- Mono Class in Java
- Multithreading Vs. Asynchronous in Java
- Nested HashMap in Java
- Number Series Program in Java
- Object Slicing in Java
- Oracle Java
- Print 1 to 100 Without Loop in Java
- Remove elements from a List that satisfy given predicate in Java
- Replace Element in Arraylist Java
- Sliding Puzzle Game in Java
- Strobogrammatic Number in Java
- Web Methods in Java
- Web Scraping Java
- Window Event in Java
- @Builder Annotation in Java
- Advantages of Abstraction in Java
- Advantages of Packages in Java
- Bounce Tales Java Game Download
- Breaking Singleton Class Pattern in Java
- Building a Brick Breaker Game in Java
- Building a Scientific Calculator in Java
- Circle Program in Java
- Class Memory in Java
- Convert Byte to an Image in Java
- Count Paths in Given Matrix in Java
- Difference Between Iterator and ListIterator in Java with Example
- Distinct Character Count Java Stream
- EOFException in Java
- ExecutionException Java 8
- Generic Object in Java
- How to Create an Unmodifiable List in Java
- How to Create Dynamic SQL Query in Java
- How to Return a 2D Array in Java
- Java 8 Stream.distinct() Method
- Java setPriority() Method
- Mutator Methods in Java
- Predicate Consumer Supplier Java 8
- Program to Generate CAPTCHA and Verify User Using Java
- Random Flip Matrix in Java
- System Class in Java
- Vigenere Cipher Program in Java
- Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) in Java
- CI/ CD Tools for Java
- cint in Java
- Command Pattern in Java
- CSV to List Java
- Difference Between Java Servlets and CGI
- Difference Between Multithreading Multitasking, and Multiprocessing in Java
- Encoding Three Strings in Java
- How to Import Jar File in Eclipse
- Meta Class Vs. Class in Java
- Meta Class Vs. Super Class in Java
- Print Odd and Even Numbers by Two Threads in Java
- Scoped value in Java
- Upper-Bounded Wildcards in Java
- Wildcards in Java
- Zero Matrix Problem in Java
- All Possible Combinations of a String in Java
- Atomic Reference in Java
- Final Method Overloading in Java| Can We Overload Final Methods
- Constructor in Inheritance in Java
- Design Your Custom Connection Pool in Java
- How Microservices Communicate with Each Other in Java
- How to Convert String to Timestamp in Java
- Java 10 Collectors Methods
- Java and Apache OpenNLP
- Java Deep Learning
- Java Iterator Vs. Listiterator Vs. Spliterator
- Pure Functions in Java
- Use of Constructor in Java | Purpose of Constructor in Java
- Implement Quintet Class with Quartet Class in Java using JavaTuples
- Java Best Practices
- Efficiently Reading Input For Competitive Programming using Java 8
- Length of the longest substring without repeating characters in Java
- Advantages of Inner Class in Java
- AES GCM Encryption Java
- Array Default Values in Java
- Copy File in Java from one Location to Another
- Creating Templates in Java
- Different Packages in Java
- How to Add Elements to an Arraylist in Java Dynamically
- How to Add Splash Screen in Java
- How to Calculate Average Star Rating in Java
- Immutable Class with Mutable Object in Java
- Java instanceOf() Generics
- Set Precision in Java
- Snake Game in Java
- Tower of Hanoi Program in Java
- Two Types of Streams Offered by Java
- Uses of Collections in Java
- Additive Numbers in Java
- Association Vs. Aggregation Vs. Composition in Java
- Covariant and Contravariant Java
- Creating Immutable Custom Classes in Java
- mapToInt() in Java
- Methods of Gson in Java
- Server Socket in Java
- Check String Are Permutation of Each Other in Java
- Containerization in Java
- Difference Between Multithreading and Multiprogramming in Java
- Flyweight Design Pattern
- HMAC Encryption in Java
- How to Clear Error in Java Program
- 5 Types of Java
- Design a Job Scheduler in Java
- Elements of Java Programming
- Generational ZCG in Java 21
- How to Print Arraylist Without Brackets Java
- Interface Vs. Abstract Class After Java 8
- Java 9 Optional Class Improvements
- Number of GP sequence Problem in Java
- Pattern Matching for Switch
- Range Addition Problem in Java
- Swap Corner Words and Reverse Middle Characters in Java
- Kadane's Algorithm in Java
- Capture the Pawns Problem in Java
- Find Pair With Smallest Difference in Java
- How to pad a String in Java
- When to use Serialization and Externalizable Interface
- Which Component is responsible to run Java Program
- Difference Between Java and Bastar
- Difference Between Static and Instance Methods in Java
- Difference Between While and Do While loop in Java
- Future Interface in Java
- Invert a Binary tree in Java
- Java Template Engine
- KeyValue Class in JavaTuples
- Quantifiers in Java
- Swapping Pairs of Characters in a String in Java
- Version Enhancements in Exception Handling introduced in Java SE 7
- Find all Palindromic Sub-Strings of a given String in Java
- Find if String is K-Palindrome or not in Java
- Count Pairs from an Array with Even Product of Count of Distinct Prime Factor in Java
- Find if an Array of Strings can be Chained to form a Circle in Java
- Find largest factor of N such that NF is less than K in Java
- Lexicographically First Palindromic String in Java
- LinkedTransferQueue removeAll() method in Java with Examples
- Next Smallest Palindrome problem in Java
| Java is a popular programming language that software developers use to construct a wide range of applications. It is a simple, robust, and platform-independent object-oriented language. There are various types of assignment operators in Java, each with its own function. In this section, we will look at Java's many types of assignment operators, how they function, and how they are utilized. To assign a value to a variable, use the basic assignment operator (=). It is the most fundamental assignment operator in Java. It assigns the value on the right side of the operator to the variable on the left side.
In the above example, the variable x is assigned the value 10. To add a value to a variable and subsequently assign the new value to the same variable, use the addition assignment operator (+=). It takes the value on the right side of the operator, adds it to the variable's existing value on the left side, and then assigns the new value to the variable.
To subtract one numeric number from another, use the subtraction operator. All numeric data types, including integers and floating-point values, can be utilised with it. Here's an illustration:
In this example, we create two integer variables, a and b, subtract b from a, and then assign the result to the variable c. To combine two numerical numbers, use the multiplication operator. All numeric data types, including integers and floating-point values, can be utilised with it. Here's an illustration:
In this example, we declare two integer variables, a and b, multiply their values using the multiplication operator, and then assign the outcome to the third variable, c. To divide one numerical number by another, use the division operator. All numeric data types, including integers and floating-point values, can be utilised with it. Here's an illustration:
In this example, we declare two integer variables, a and b, divide them by one another using the division operator, and then assign the outcome to the variable c. It's vital to remember that when two numbers are divided, the outcome will also be an integer, and any residual will be thrown away. For instance: The modulus assignment operator (%=) computes the remainder of a variable divided by a value and then assigns the resulting value to the same variable. It takes the value on the right side of the operator, divides it by the current value of the variable on the left side, and then assigns the new value to the variable on the left side.
|
Latest Courses

We provides tutorials and interview questions of all technology like java tutorial, android, java frameworks
Contact info
G-13, 2nd Floor, Sec-3, Noida, UP, 201301, India
[email protected] .

Interview Questions
Online compiler.
Browse Course Material
Course info, instructors.
- Adam Marcus
Departments
- Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
As Taught In
- Programming Languages
- Software Design and Engineering
Learning Resource Types
Introduction to programming in java, lecture 4: classes and objects.
Lecture presentation on programming in Java. Topics include: object oriented programming, defining classes, using classes, constructors, methods, accessing fields, primitives versus references, references versus values, and static types and methods.

You are leaving MIT OpenCourseWare
- ▼Java Tutorial
- Introduction
- Java Program Structure
- Java Primitive data type
- ▼Development environment setup
- Download and Install JDK, Eclipse (IDE)
- Compiling, running and debugging Java programs
- ▼Declaration and Access control
- Class, methods, instance variables
- Java Packages
- ▼OOPS Concepts
- Java Object Oriented Programming concepts
- Is-A and Has-A relationship
- ▼Assignments
- Arrays - 2D array and Multi dimension array
- Wrapper classes
- ▼Operators
- Assignment Operator
- Arithmetic Operator
- Conditional Operator
- Logical Operator
- ▼Flow Control
- Switch Satement
- While and Do loop
- Java Branching Statements
- ▼Exceptions
- Handling Exceptions
- Checked and unchecked
- Custom Exception
- Try with resource feature of Java 7
- ▼String Class
- String Class
- Important methods of String class with example
- String buffer class and string builder class
- ▼File I/O and serialization
- File Input and Output
- Reading file
- Writing file
- Java Property File Processing
- Java Serialization
- ▼Java Collection
- Java Collection Framework
- Java ArrayList and Vector
- Java LinkedList Class
- Java HashSet
- Java TreeSet
- Java Linked HashSet
- Java Utility Class
- ▼Java Thread
- Java Defining, Instantiating and Starting Thread
- Java Thread States and Transitions
- Java Thread Interaction
- Java Code Synchronization
- ▼Java Package
- ▼Miscellaneous
- Garbage Collection in Java
- BigDecimal Method
Java Assignment Operators
Description.
Assigning a value to a variable seems straightforward enough; you simply assign the stuff on the right side of the '= 'to the variable on the left. Below statement 1 assigning value 10 to variable x and statement 2 is creating String object called name and assigning value "Amit" to it.
Assignment can be of various types. Let’s discuss each in detail.
Primitive Assignment:
The equal (=) sign is used for assigning a value to a variable. We can assign a primitive variable using a literal or the result of an expression.
Primitive Casting
Casting lets you convert primitive values from one type to another. We need to provide casting when we are trying to assign higher precision primitive to lower precision primitive for example If we try to assign int variable (which is in the range of byte variable) to byte variable then the compiler will throw an exception called "possible loss of precision". Eclipse IDE will suggest the solution as well as shown below. To avoid such problem we should use type casting which will instruct compiler for type conversion.
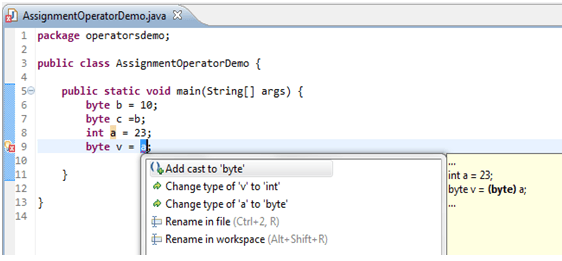
For cases where we try to assign smaller container variable to larger container variables we do not need of explicit casting. The compiler will take care of those type conversions. For example, we can assign byte variable or short variable to an int without any explicit casting.
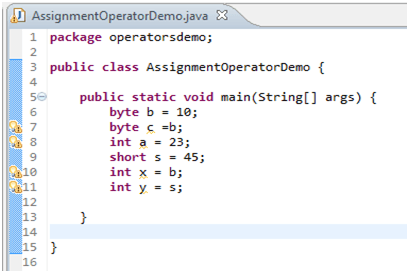
Assigning Literal that is too large for a variable
When we try to assign a variable value which is too large (or out of range ) for a primitive variable then the compiler will throw exception “possible loss of precision” if we try to provide explicit cast then the compiler will accept it but narrowed down the value using two’s complement method. Let’s take an example of the byte which has 8-bit storage space and range -128 to 127. In below program we are trying to assign 129 literal value to byte primitive type which is out of range for byte so compiler converted it to -127 using two’s complement method. Refer link for two’s complement calculation (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Two's_complement)
Java Code: Go to the editor
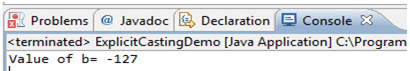
Reference variable assignment
We can assign newly created object to object reference variable as below
First line will do following things,
- Makes a reference variable named s of type String
- Creates a new String object on the heap memory
- Assigns the newly created String object to the reference variables
You can also assign null to an object reference variable, which simply means the variable is not referring to any object. The below statement creates space for the Employee reference variable (the bit holder for a reference value) but doesn't create an actual Employee object.
Compound Assignment Operators
Sometime we need to modify the same variable value and reassigned it to a same reference variable. Java allows you to combine assignment and addition operators using a shorthand operator. For example, the preceding statement can be written as:
The += is called the addition assignment operator. Other shorthand operators are shown below table
| Operator | Name | Example | Equivalent |
|---|---|---|---|
| += | Addition assignment | i+=5; | i=i+5 |
| -= | Subtraction assignment | j-=10; | j=j-10; |
| *= | Multiplication assignment | k*=2; | k=k*2; |
| /= | Division assignment | x/=10; | x=x/10; |
| %= | Remainder assignment | a%=4; | a=a%4; |
Below is the sample program explaining assignment operators:
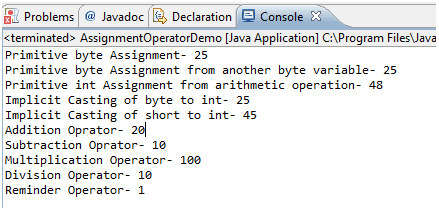
- Assigning a value to can be straight forward or casting.
- If we assign the value which is out of range of variable type then 2’s complement is assigned.
- Java supports shortcut/compound assignment operator.
Java Code Editor:
Previous: Wrapper classes Next: Arithmetic Operator
Follow us on Facebook and Twitter for latest update.
It will be nice if you may share this link in any developer community or anywhere else, from where other developers may find this content. Thanks.
https://www.w3resource.com/java-tutorial/java-assignment-operators.php
- Weekly Trends and Language Statistics
- All Articles List
- 9 January 2023
- 65308 views
- 450 comments
Java Classes: writing your own classes, constructors

Creating your own classes. Abstraction
Constructors.

Museum of Antiquities.
Your task is to design an Artifact class. There are three types of artifacts kept at the museum. We know nothing about the first type except the serial number assigned by the museum (for example: 212121). For the second type, we know the serial number and the culture that created it (for example: 212121, "Aztecs"). For the third type, we know the serial number, the culture that created it, and the century it was created in (for example: 212121, "Aztecs", 12).
Create an Artifact class that describes the antiquities kept at the museum, and write the required set of constructors for the class. Then, in the main() method, create one artifact of each kind.
Dating website
Let's create a user database for a dating website. But here's the problem: you forgot the required order of the arguments, and there's no technical documentation available. Design a User class, which will have the following fields: name ( String ), age ( short ), and height ( int ). Create the appropriate number of constructors, so that the name, age, and height can be specified in any order.
More reading: |
|---|

Java Assignment Operators
| Operators | Example | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| = | x = 9 | Value 25 is assigned to x |
| += | x += 9 | This is same as x = x + 9 |
| -= | x -= 9 | This is same as x = x – 9 |
| *= | x *= 9 | This is same as x = x * 9 |
| /= | x /= 9 | This is same as x = x / 9 |
| %= | x %= 9 | This is same as x = x % 9 |
Java Assignment Operators example

Programming in Java · Computer Science · An Interdisciplinary Approach
Online content. , introduction to programming in java., computer science., for teachers:, for students:.
- Stack Overflow for Teams Where developers & technologists share private knowledge with coworkers
- Advertising & Talent Reach devs & technologists worldwide about your product, service or employer brand
- OverflowAI GenAI features for Teams
- OverflowAPI Train & fine-tune LLMs
- Labs The future of collective knowledge sharing
- About the company Visit the blog
Collectives™ on Stack Overflow
Find centralized, trusted content and collaborate around the technologies you use most.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
Get early access and see previews of new features.
Assigning in Java?
Say I set int A = int B. When I change A after, it will not change the value of B. But when I set a SomeClass A = SomeClass B, and I change A's contents (like a.cost), it changes B.cost as well. Can someone explain this to me?
I thought Java is assigned by value, not reference?
5 Answers 5
Yes, it does - but the value of A is a reference, not a copy of the object itself.
I like to give the following analogy...
Suppose two people both have my address: that's like two variables of type House in Java. Now one of them comes and paints my door red. The second person will still see the red door if they visit:
Basically, remember a few rules and things will become clear:
- The value of an expression in Java is never an object - only ever a reference or a primitive value
- (Corollary of first point) A variable never holds an object - only ever a reference or a primitive value
- Assignment (and argument passing) always copies the value, whether that value is a reference or a primitive value
What does "assigned by value" mean? Are you maybe confusing it with "pass by value/reference"?
At any rate, if you handle a class instance in Java, you are actually handling a reference to that class (much like a pointer in C/C++). Your assignment only copies the reference, so both A and B refer to the same instance, i.e. the data is shared, hence the result.
A is a reference to the object. So if you change the object internal state , it will be reflected to every other variable pointing to it.
If you re-assign A , then B will not change:
(Java is pass by value. Check this article about it.)
- Java is strictly pass by value. When passing a reference by value only the reference is duplicated, not the object being referenced. – Russell Zornes Commented Oct 4, 2010 at 22:03
- @Maven, of course, a stupid mistake, I thought one and wrote the other :) thanks – Bozho Commented Oct 4, 2010 at 22:07
In Java, your variables can be split into two categories: Objects, and everything else (int, long, byte, etc).
A primitive type (int, long, etc), holds whatever value you assign it. An object variable, by contrast, holds a reference to an object somewhere. So if you assign one object variable to another, you have copied the reference, both A and B point to the same object.
NOTE: Strings in Java are actually objects, not primitives, which beginners often assume.
Hope this helps
In java when you assign Object to Object its assign by reference. Int is non an Object in java so when you assign int to int its assign by value.
Your Answer
Reminder: Answers generated by artificial intelligence tools are not allowed on Stack Overflow. Learn more

Sign up or log in
Post as a guest.
Required, but never shown
By clicking “Post Your Answer”, you agree to our terms of service and acknowledge you have read our privacy policy .
Not the answer you're looking for? Browse other questions tagged java or ask your own question .
- The Overflow Blog
- Where developers feel AI coding tools are working—and where they’re missing...
- He sold his first company for billions. Now he’s building a better developer...
- Featured on Meta
- User activation: Learnings and opportunities
- Preventing unauthorized automated access to the network
- Should low-scoring meta questions no longer be hidden on the Meta.SO home...
- Announcing the new Staging Ground Reviewer Stats Widget
Hot Network Questions
- Cost of Laos visa
- Is a private third party allowed to take things to court?
- Does legislation on transgender healthcare affect medical researchers?
- Is “No Time To Die” the first Bond film to feature children?
- Does the Rogue's Evasion cost a reaction?
- Player sprite becomes smaller during attack animation (Java)
- Double 6x6 Beam
- How can moving observer explain non-simultaneity?
- Why would an escrow/title company not accept ACH payments?
- "Chrisma" and "Him"
- What is the simplest formula for calculating the circumference of a circle?
- Tikz template for organization chart
- What is an ellipse in infinite-dimensional spaces?
- Were Soviet doctors and nurses actually as callous as "Voices from Chernobyl" portrays in the prolog?
- Sticky goo making it hard to open and close the main 200amp breaker
- Extract basil seeds from dry husk
- What kind of Fibonacci subword at this offset?
- How was the year spoken in late 1800s England?
- CH in non-set theoretic foundations
- Is BitLocker susceptible to any known attacks other than bruteforcing when used with a very strong passphrase and no TPM?
- How long has given package been deferred due to phasing?
- Is there any reason _not_ to add a flyback diode?
- Is the Star Trek TNG episode Aquiel inspired by The Thing?
- Want a different order than permutation

Fixing ClassCastException: java.math.BigInteger cannot be cast to java.lang.Integer

The ClassCastException occurs when Java attempts to cast an object of one type to another, incompatible type. One common occurrence is the exception message: java.lang.ClassCastException: java.math.BigInteger cannot be cast to java.lang.Integer . This article explores why this exception happens and ways to prevent and fix it.
1. Understanding the Cause of ClassCastException
In Java, a ClassCastException arises when you attempt to cast an object to a type that it cannot be cast to. In the case of BigInteger and Integer , both represent numbers, but they belong to different classes and cannot be cast directly.
1.1 BigInteger vs Integer
- BigInteger : Part of java.math package, which is used to represent arbitrarily large integers.
- Integer : A wrapper class for primitive type int and part of the java.lang package, which stores a fixed 32-bit signed integer.
Because BigInteger can hold larger values than Integer , Java does not allow automatic casting between the two. Forcing such a cast causes a ClassCastException .
1.2 Reproducing the Issue
Consider the following scenario where data is fetched from a database or an external source that stores numeric values as BigInteger . Attempting to cast this to an Integer will throw the exception:
2. Safely Converting BigInteger to Integer in Java
To avoid this issue, we need to convert BigInteger to Integer properly rather than using direct casting.
2.1 Using BigInteger.intValue()
The simplest way to convert a BigInteger to an Integer is by calling the intValue() method on the BigInteger object. This converts the BigInteger to a primitive int , and it can be boxed to an Integer .
In this code snippet, BigInteger.intValue() safely converts the value to int . However, if the value exceeds the range of an int , it will result in data loss (the most significant bits are truncated).
2.2 Checking Value Range Before Conversion
If we are dealing with large numbers, it’s important to check whether the BigInteger can fit into an Integer without data loss.
This example demonstrates a range check to ensure the BigInteger can safely be converted to an int . The code initializes a BigInteger object named bigIntValue with the value "2147483648" . This value is much larger than what a Java Integer can represent, as the Integer type has a maximum capacity far smaller than the BigInteger object in this case.
To ensure the value can safely be converted, the code checks if the BigInteger falls within the range of an Integer . The maximum value an Integer can hold is 2,147,483,647 ( Integer.MAX_VALUE ), and the minimum is -2,147,483,648 ( Integer.MIN_VALUE ). The BigInteger.compareTo() method is used to compare bigIntValue against these limits. Since 2147483648 is greater than 2147483647 , the first comparison ( bigIntValue.compareTo(BigInteger.valueOf(Integer.MAX_VALUE)) <= 0 ) returns false .
Expected Output from running the code above is:

Let’s consider the scenario where the BigInteger value passed is within the range of a Java Integer , i.e., less than 2147483647 .
In this case, since 123,456,789 is less than 2,147,483,647 , the comparison bigIntValue.compareTo(BigInteger.valueOf(Integer.MAX_VALUE)) <= 0 evaluates to true . Additionally, because 123,456,789 is greater than -2,147,483,648 , the second comparison also returns true . With both conditions met, the code safely converts the BigInteger to an int using the intValue() method. This conversion is successful as the value is within the valid range for an Integer .
Expected Output: The converted value, 123,456,789 , is printed as an Integer . There is no data loss or overflow because the value lies within the limits of the Integer type in Java.
3. Conclusion
In this article, we explored how to safely convert a BigInteger to an Integer in Java, particularly focusing on checking the value range to avoid ClassCastException . By verifying that the BigInteger value is within the valid limits of the Integer type, we can confidently perform conversions without the risk of data loss or overflow. This practice enhances the robustness of our Java applications and helps ensure that data remains accurate during numeric operations.
4. Download the Source Code
This was an example of Java ClassCast Exception when converting BigInteger to Integer.

We will contact you soon.

Omozegie Aziegbe
Related articles.

Java 8 Streams – Group By Multiple Fields with Collectors.groupingBy()
Java program to calculate average using arrays, 150 java interview questions and answers – the ultimate list (pdf download & video), java 8 streams filter with multiple conditions examples, java arraylist insert/replace at index, switch as an expression in java with lambda-like syntax, 13 best java decompilers for download and online use for java developers, how to format/parse dates with localdatetime in java 8 – example tutorial.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Java Tutorial
Java methods, java classes, java file handling, java how to's, java reference, java examples, java inheritance, java inheritance (subclass and superclass).
In Java, it is possible to inherit attributes and methods from one class to another. We group the "inheritance concept" into two categories:
- subclass (child) - the class that inherits from another class
- superclass (parent) - the class being inherited from
To inherit from a class, use the extends keyword.
In the example below, the Car class (subclass) inherits the attributes and methods from the Vehicle class (superclass):
Try it Yourself »
Did you notice the protected modifier in Vehicle?
We set the brand attribute in Vehicle to a protected access modifier . If it was set to private , the Car class would not be able to access it.
Why And When To Use "Inheritance"?
- It is useful for code reusability: reuse attributes and methods of an existing class when you create a new class.
Tip: Also take a look at the next chapter, Polymorphism , which uses inherited methods to perform different tasks.
Advertisement
The final Keyword
If you don't want other classes to inherit from a class, use the final keyword:
If you try to access a final class, Java will generate an error:
The output will be something like this:

COLOR PICKER

Contact Sales
If you want to use W3Schools services as an educational institution, team or enterprise, send us an e-mail: [email protected]
Report Error
If you want to report an error, or if you want to make a suggestion, send us an e-mail: [email protected]
Top Tutorials
Top references, top examples, get certified.
- Java Language Updates
- Sealed Classes
6 Sealed Classes
Sealed classes and interfaces restrict which other classes or interfaces may extend or implement them.
For background information about sealed classes and interfaces, see JEP 409 .
One of the primary purposes of inheritance is code reuse: When you want to create a new class and there is already a class that includes some of the code that you want, you can derive your new class from the existing class. In doing this, you can reuse the fields and methods of the existing class without having to write (and debug) them yourself.
However, what if you want to model the various possibilities that exist in a domain by defining its entities and determining how these entities should relate to each other? For example, you're working on a graphics library. You want to determine how your library should handle common geometric primitives like circles and squares. You've created a Shape class that these geometric primitives can extend. However, you're not interested in allowing any arbitrary class to extend Shape ; you don't want clients of your library declaring any further primitives. By sealing a class, you can specify which classes are permitted to extend it and prevent any other arbitrary class from doing so.
Declaring Sealed Classes
To seal a class, add the sealed modifier to its declaration. Then, after any extends and implements clauses, add the permits clause. This clause specifies the classes that may extend the sealed class.
For example, the following declaration of Shape specifies three permitted subclasses, Circle , Square , and Rectangle :
Figure 6-1 Shape.java
Define the following three permitted subclasses, Circle , Square , and Rectangle , in the same module or in the same package as the sealed class:
Figure 6-2 Circle.java
Figure 6-3 Square.java
Square is a non-sealed class . This type of class is explained in Constraints on Permitted Subclasses .
Figure 6-4 Rectangle.java
Rectangle has a further subclass, FilledRectangle :
Figure 6-5 FilledRectangle.java
Alternatively, you can define permitted subclasses in the same file as the sealed class. If you do so, then you can omit the permits clause:
Constraints on Permitted Subclasses
Permitted subclasses have the following constraints:
They must be accessible by the sealed class at compile time.
For example, to compile Shape.java , the compiler must be able to access all of the permitted classes of Shape : Circle.java , Square.java , and Rectangle.java . In addition, because Rectangle is a sealed class, the compiler also needs access to FilledRectangle.java .
They must directly extend the sealed class.
They must have exactly one of the following modifiers to describe how it continues the sealing initiated by its superclass:
final : Cannot be extended further
sealed : Can only be extended by its permitted subclasses
non-sealed : Can be extended by unknown subclasses; a sealed class cannot prevent its permitted subclasses from doing this
For example, the permitted subclasses of Shape demonstrate each of these three modifiers: Circle is final while Rectangle is sealed and Square is non-sealed .
They must be in the same module as the sealed class (if the sealed class is in a named module) or in the same package (if the sealed class is in the unnamed module, as in the Shape.java example).
For example, in the following declaration of com.example.graphics.Shape , its permitted subclasses are all in different packages. This example will compile only if Shape and all of its permitted subclasses are in the same named module.
Declaring Sealed Interfaces
Like sealed classes, to seal an interface, add the sealed modifier to its declaration. Then, after any extends clause, add the permits clause, which specifies the classes that can implement the sealed interface and the interfaces that can extend the sealed interface.
The following example declares a sealed interface named Expr . Only the classes ConstantExpr , PlusExpr , TimesExpr , and NegExpr may implement it:
Record Classes as Permitted Subclasses
You can name a record class in the permits clause of a sealed class or interface. See Record Classes for more information.
Record classes are implicitly final , so you can implement the previous example with record classes instead of ordinary classes:
Narrowing Reference Conversion and Disjoint Types
Narrowing reference conversion is one of the conversions used in type checking cast expressions. It enables an expression of a reference type S to be treated as an expression of a different reference type T , where S is not a subtype of T . A narrowing reference conversion may require a test at run time to validate that a value of type S is a legitimate value of type T . However, there are restrictions that prohibit conversion between certain pairs of types when it can be statically proven that no value can be of both types.
Consider the following example:
The cast expression Polygon p = (Polygon) r is allowed because it's possible that the Rectangle value r could be of type Polygon ; Rectangle is a subtype of Polygon . However, consider this example:
Even though the class Triangle and the interface Polygon are unrelated, the cast expression Polygon p = (Polygon) t is also allowed because at run time these types could be related. A developer could declare the following class:
However, there are cases where the compiler can deduce that there are no values (other than the null reference) shared between two types; these types are considered disjoint . For example:
Because the class UtahTeapot is final , it's impossible for a class to be a descendant of both Polygon and UtahTeapot . Therefore, Polygon and UtahTeapot are disjoint, and the cast statement Polygon p = (Polygon) u isn't allowed.
The compiler has been enhanced to navigate any sealed hierarchy to check if your cast statements are allowed. For example:
The first cast statement UtahTeapot u = (UtahTeapot) s isn't allowed; a Shape can only be a Polygon because Shape is sealed . However, as Polygon is non-sealed , it can be extended. However, no potential subtype of Polygon can extend UtahTeapot as UtahTeapot is final . Therefore, it's impossible for a Shape to be a UtahTeapot .
In contrast, the second cast statement Ring r = (Ring) s is allowed; it's possible for a Shape to be a Ring because Ring is not a final class.
APIs Related to Sealed Classes and Interfaces
The class java.lang.Class has two new methods related to sealed classes and interfaces:
- java.lang.constant.ClassDesc[] permittedSubclasses() : Returns an array containing java.lang.constant.ClassDesc objects representing all the permitted subclasses of the class if it is sealed; returns an empty array if the class is not sealed
- boolean isSealed() : Returns true if the given class or interface is sealed; returns false otherwise
- TECHNOLOGIES
- An Interview Question

How C# Generics is different from Java Generics

- Kautilya Utkarsh
- Sep 24, 2024
- Other Artcile
In this article, we explore the distinctive features of C# generics and how they enhance programming efficiency. We compare generics with non-generic types, focusing on benefits like type safety, code reusability, and performance optimization.
Introduction
Generics in programming refer to a feature that allows a coder to write type-safe, flexible, and reusable code that works with different data types without specifying a concrete data type while coding. It lets you use a placeholder i.e. a “generic type”, which allows a coder to create classes, methods, and data structures that operate on various data types. The popular object-oriented programming languages i.e. “Java” and “C#” support generics, but both handle it in a unique way.
What are Generics?
Generics allows us to write Classes, methods, and interfaces that can work with any data type without losing type safety. Because of this, we don’t require rewriting code for each type; we can write it, and it will work on each type.
Let’s see an example of creating a generic list.
Generic: C# vs. Java
In Java, after compilation, generic type information is removed. This makes Java generics compatible with older versions but limits what you can do with them at runtime, so we say that Java uses type erasure. Where C# generics are reified, that means the type information is kept during both compile-time and runtime. It makes C# more flexible and runtime safety.

Let's understand this with examples,
As type information is retained at runtime in C#, we can inspect the generic type using reflection.
In Java we can’t use primitive type in generics, we use their wrapper classes like ‘Integer’ for “int” but C# supports the primitive classes directly in generics, which makes code simpler and more efficient. Let’s see.
C#’s ability to work with primitive types directly makes it faster and more convenient for developers.
Both languages allow you to make generic types flexible with inheritance, but they handle it differently: Java uses wildcards(?) for both covariance and contravariant, which confuses developers sometimes, whereas C# uses the “out” keyword for covariant types and “in” for contravariant types. This is generally easier to understand. Let’s see
C#’s out and in keywords make it clear whether a type is covariant or contravariant, reducing confusion.
Contravariance: we can pass an Animal to the method.
Constraints on Generics: Java vs. C#
| Feature | Java | C# |
| Basic Constraints | extends keyword for subclasses or interfaces | where T: base class for subclassing |
| Constructor Constraint | Not available | where T : new() ensures a parameterless constructor |
| Reference Type Constraint | Not available | where T: class ensures the type is a reference type |
| Value Type Constraint | Not available | where T: struct ensures the type is a value type |
| Interface Constraint | Can implement interfaces | Can implement interfaces (where T: IInterface) |
| Type Safety | Limited by runtime type erasure | Full-type information is retained at runtime |
Generics in both C# and Java allow for flexible, reusable code, but C# generics stand out due to their ability to handle primitive types, runtime type retention, and more powerful constraints. C#’s support for covariance and contravariance is also easier to understand compared to Java’s wildcard system. Understanding these differences can help you make better decisions when writing or transitioning between C# and Java code. C# generics offer more flexibility and performance benefits in many cases, especially when you need runtime type checks, work with primitive types, or require more control over type constraints.
- C# Generics
- Code Reusability
- Generics Comparison
- Performance
- Type Safety

Programming C# for Beginners
- Java Course
- Java Arrays
- Java Strings
- Java Collection
- Java 8 Tutorial
- Java Multithreading
- Java Exception Handling
- Java Programs
- Java Project
- Java Collections Interview
- Java Interview Questions
- Spring Boot
Java Exercises - Basic to Advanced Java Practice Programs with Solutions
Looking for Java exercises to test your Java skills, then explore our topic-wise Java practice exercises? Here you will get 25 plus practice problems that help to upscale your Java skills.
As we know Java is one of the most popular languages because of its robust and secure nature. But, programmers often find it difficult to find a platform for Java Practice Online. In this article, we have provided Java Practice Programs. That covers various Java Core Topics that can help users with Java Practice.
So, with ado further take a look at our free Java Exercises to practice and develop your Java programming skills. Our Java programming exercises Practice Questions from all the major topics like loops, object-oriented programming, exception handling, and many more.
Topic Wise Java Exercises List
- Pattern Programs in Java
- Array Programs in Java
- String Programs in Java
Java Practice Problems for Searching Algorithms
Practice problems in java sorting algorithms, more java practice exercises.
-768.webp)
Java Practice Programs
This Java exercise is designed to deepen your understanding and refine your Java coding skills, these programs offer hands-on experience in solving real-world problems, reinforcing key concepts, and mastering Java programming fundamentals. Whether you’re a beginner who looking to build a solid foundation or a professional developer aiming to sharpen your expertise, our Java practice programs provide an invaluable opportunity to sharpen your craft and excel in Java programming language .
By diving into these exercises, you’ll not only reinforce key concepts but also gain the practical experience needed to tackle real-world problems effectively. This hands-on practice is essential for mastering Java fundamentals and advancing your career as a proficient Java developer. To further enhance your skills, consider enrolling in our Java Course . This course offers comprehensive lessons and practical exercises, making it an excellent resource for both beginners and experienced developers.
1. Write Hello World Program in Java
The solution to the Problem is mentioned below:
2. Write a Program in Java to Add two Numbers.
Click here for the solution, 3. write a program to swap two numbers, 4. write a java program to convert integer numbers and binary numbers., 5. write a program to find factorial of a number in java., 6. write a java program to add two complex numbers., 7. write a program to calculate simple interest in java, 8. write a program to print the pascal’s triangle in java, 9. write a program to find sum of fibonacci series number, java exercise on pattern.
10. Write a Program to Print Pyramid Number Pattern in Java.
11. write a java program to print pattern., 12. write a java program to print pattern., 13. java program to print patterns., array exercises in java.
14. Write a Java Program to Compute the Sum of Array Elements.
15. write a java program to find the largest element in array, 16. write java program to find the tranpose of matrix, 17. java array program for array rotation, 18. java array program to remove duplicate elements from an array, 19. java array program to remove all occurrences of an element in an array, string exercises in java.

20. Java program to check whether a string is a Palindrome
21. java string program to check anagram, 22. java string program to reverse a string, 23. java string program to remove leading zeros.
-768.webp)
24. Write a Java Program for Linear Search.
Time Complexity: O(N) Space Complexity: O(N)
25. Write a Binary Search Program in Java.
Time Complexity: O(logN) Space Complexity: O(N)

26. Java Program for Bubble Sort.
Time Complexity: O(N 2 ) Space Complexity: O(1)
27. Write a Program for Insertion Sort in Java.
28. java program for selection sort., 29. java program for merge sort..
Time Complexity: O(N logN) Space Complexity: O(N)
30. Java Program for QuickSort.
Time Complexity: O(N logN) Space Complexity: O(1)
After completing these Java exercises you are a step closer to becoming an advanced Java programmer. We hope these exercises have helped you understand Java better and you can solve beginner to advanced-level questions on Java programming.
Solving these Java programming exercise questions will not only help you master theory concepts but also grasp their practical applications, which is very useful in job interviews.
Java Array Exercise Java String Exercise Java Collection Exercise Click Here – To Practice Java Online please check our Practice Portal.
Java Exercise – FAQ
1. how to do java projects for beginners.
To do Java projects you need to know the fundamentals of Java programming. Then you need to select the desired Java project you want to work on. Plan and execute the code to finish the project. Some beginner-level Java projects include: Reversing a String Number Guessing Game Creating a Calculator Simple Banking Application Basic Android Application
2. Is Java easy for beginners?
As a programming language, Java is considered moderately easy to learn. It is unique from other languages due to its lengthy syntax. As a beginner, you can learn beginner to advanced Java in 6 to 18 months.
3. Why Java is used?
Java provides many advantages and uses, some of which are: Platform-independent Robust and secure Object-oriented Popular & in-demand Vast ecosystem
Similar Reads
- Java-Object Oriented
- Java-Strings
- Java-Output
- Java-Library
- Java-Arrays
- Java-Data Types
- Java-Functions
- Output of Java Program
- java-basics
Please Login to comment...
- How to Underline in Discord
- How to Block Someone on Discord
- How to Report Someone on Discord
- How to add Bots to Discord Servers
- GeeksforGeeks Practice - Leading Online Coding Platform
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Note: The compound assignment operator in Java performs implicit type casting. Let's consider a scenario where x is an int variable with a value of 5. int x = 5; If you want to add the double value 4.5 to the integer variable x and print its value, there are two methods to achieve this: Method 1: x = x + 4.5. Method 2: x += 4.5.
A class in Java is a set of objects which shares common characteristics/ behavior and common properties/ attributes. It is a user-defined blueprint or prototype from which objects are created. For example, Student is a class while a particular student named Ravi is an object. Properties of Java Classes. Class is not a real-world entity.
Simple Assignment Operator (=) To assign a value to a variable, use the basic assignment operator (=). It is the most fundamental assignment operator in Java. It assigns the value on the right side of the operator to the variable on the left side. In the above example, the variable x is assigned the value 10.
Lecture presentation on programming in Java. Topics include: object oriented programming, defining classes, using classes, constructors, methods, accessing fields, primitives versus references, references versus values, and static types and methods. ... assignment Programming Assignments. Download Course.
This beginner Java tutorial describes fundamentals of programming in the Java programming language ... You saw this operator in the Bicycle class; it assigns the value on its right to the operand on its left: ... You can also combine the arithmetic operators with the simple assignment operator to create compound assignments. For example, x+=1; ...
Java Class and Objects. Java is an object-oriented programming language. The core concept of the object-oriented approach is to break complex problems into smaller objects. An object is any entity that has a state and behavior. For example, a bicycle is an object. It has. States: idle, first gear, etc. Behaviors: braking, accelerating, etc.
Java provides a class with name Class in java.lang package. Instances of the class Class represent classes and interfaces in a running Java application. The primitive Java types (boolean, byte, char, short, int, long, float, and double), and the keyword void are also represented as Class objects. It has no public constructor. Class objects are cons
Lesson: Classes and Objects. With the knowledge you now have of the basics of the Java programming language, you can learn to write your own classes. In this lesson, you will find information about defining your own classes, including declaring member variables, methods, and constructors. You will learn to use your classes to create objects ...
Classes. The introduction to object-oriented concepts in the lesson titled Object-oriented Programming Concepts used a bicycle class as an example, with racing bikes, mountain bikes, and tandem bikes as subclasses. Here is sample code for a possible implementation of a Bicycle class, to give you an overview of a class declaration.
Compound Assignment Operators. Sometime we need to modify the same variable value and reassigned it to a same reference variable. Java allows you to combine assignment and addition operators using a shorthand operator. For example, the preceding statement can be written as: i +=8; //This is same as i = i+8; The += is called the addition ...
Java Classes/Objects. Java is an object-oriented programming language. Everything in Java is associated with classes and objects, along with its attributes and methods. For example: in real life, a car is an object. The car has attributes, such as weight and color, and methods, such as drive and brake. A Class is like an object constructor, or ...
OOP is faster and easier to execute. OOP provides a clear structure for the programs. OOP helps to keep the Java code DRY "Don't Repeat Yourself", and makes the code easier to maintain, modify and debug. OOP makes it possible to create full reusable applications with less code and shorter development time. Tip: The "Don't Repeat Yourself" (DRY ...
Hi! Today we will talk about classes in Java. You could say that classes form the cornerstone of Java programming. When you become a programmer, nearly your entire job will be writing your own classes that have various functions. Let's see what that means and how it works. :) As you know, Java is an object-oriented programming language.
The Java Assignment operators are used to assign the values to the declared variables. The equals ( = ) operator is the most commonly used Java assignment operator. For example: int i = 25; The table below displays all the assignment operators in the Java programming language. Operators.
For example, + is an operator used for addition, while * is also an operator used for multiplication. Operators in Java can be classified into 5 types: Arithmetic Operators. Assignment Operators. Relational Operators. Logical Operators. Unary Operators. Bitwise Operators. 1.
I am new to Java and I have some questions in mind regarding object assignment. For instance, Test t1 = new Test(); Test t2 = t1; t1.i=1; Assuming variable i is defined inside Test class, am I right to assume both t1 and t2 point to the same object where the modification t1.i=1 affects both t1 and t2?Actually I tested it out and seems like I was right.
Programming assignments. Creative programming assignments that we have used at Princeton. You can explore these resources via the sidebar at left. Introduction to Programming in Java. Our textbook Introduction to Programming in Java [ Amazon · Pearson · InformIT] is an interdisciplinary approach to the traditional CS1 curriculum with Java. We ...
Classes: A class is a user-defined blueprint or prototype from which objects are created. It represents the set of properties or methods that are common to all objects of one type. Classes are required in OOPs because: It provides the template for creating objects, which can bind code into data. It has definitions of methods and data.
In the above example, we have created a constructor named Main(). Inside the constructor, we are initializing the value of the name variable. Notice the statement creating an object of the Main class. Main obj = new Main(); Here, when the object is created, the Main() constructor is called. And the value of the name variable is initialized.
Assignment (and argument passing) always copies the value, whether that value is a reference or a primitive value; Share. Follow ... At any rate, if you handle a class instance in Java, you are actually handling a reference to that class (much like a pointer in C/C++). Your assignment only copies the reference, so both A and B refer to the same ...
The ClassCastException occurs when Java attempts to cast an object of one type to another, incompatible type. One common occurrence is the exception message: java.lang.ClassCastException: java.math.BigInteger cannot be cast to java.lang.Integer. This article explores why this exception happens and ways to prevent and fix it. 1.
Java Inheritance (Subclass and Superclass) In Java, it is possible to inherit attributes and methods from one class to another. We group the "inheritance concept" into two categories: subclass (child) - the class that inherits from another class. superclass (parent) - the class being inherited from. To inherit from a class, use the extends keyword.
Declaring Sealed Classes. To seal a class, add the sealed modifier to its declaration. Then, after any extends and implements clauses, add the permits clause. This clause specifies the classes that may extend the sealed class. For example, the following declaration of Shape specifies three permitted subclasses, Circle, Square, and Rectangle:
Generic: C# vs. Java. In Java, after compilation, generic type information is removed. This makes Java generics compatible with older versions but limits what you can do with them at runtime, so we say that Java uses type erasure. Where C# generics are reified, that means the type information is kept during both compile-time and runtime.
Java is also an object-oriented language, which means that it organizes data and behaviour into reusable units called classes and objects. Java is known for its portability, performance, security, and robust. 2 min read. Java Threading Programs - Basic to Advanced.