
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Unit 13: Research Goals.

43 Basic vs Applied Research
Basic, Applied, and Translational research exist on a spectrum or continuum. In this introductory class we talk about them more as points on a spectrum, and for the purpose of thinking about how the spectrum point influences how you -the competent information consumer- should interpret the study.
Are you wondering why you should care if research is basic or applied? Good, cuz I’d love to tell you. Basic research and Applied research are carried out with different goals in mind, study objectives if you will. Good methodology (aka: research methods) is designed around a study objective. If the study objective is to develop theory, particularly for the benefit of other scholars, YOU (the Competent Information Consumer) should think about the results or findings differently than you would if the primary objective of the research was to solve a problem. Let’s see what your student textbook authors have to say:
Learning Objectives
What are the distinguishing features of Basic and Applied research? What are the differing objectives of each type?
- Basic vs Applied Research
There are two types of research: Basic and Applied.
Basic Research:
- Is traditional research or “pure”
- It is carried out to advance knowledge
- It develops theory
- It focuses on a scholar audience
Applied Research:
- It is used more and more in recent years
- It tests theory in real life
- Its goal is to solve everyday problems
Let’s test your understanding:
Example of Applied Research vs Basic Research
Back to DocMC: Remember when we talked about Translation and the examples from University of Iowa’s Institute for Clinical and Translational Sciences? UI uses the information provided by the National Institutes of Health Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS) as the foundation of their definition. They describe basic, pre-clinical, clinical, clinical implementation, and public health as points on the spectrum. You may be thinking – wait a minute here! If it’s the national institute of health then it’s all about health and it’s all about solving problems! This is part of why when we talk about basic vs. applied in this intro course we use examples that are pretty straightforward – such as theory for building theory. But hear me out with NCAT’s examples. “Basic research involves scientific exploration that can reveal fundamental mechanisms of biology, disease or behavior.” Ok, so you see how it’s really focused on the exploration and how it CAN reveal mechanisms? Compare that to the next stage, Preclinical research, in which “scientists develop model interventions to further understand the basis of a disease or disorder and find ways to treat it. ” That’s more basic (emphasis added by moi), but they continue to talk about how the testing hasn’t gotten to the real deal human testing part. Clinical research is in that basic-applied transitional zone as well, moving steadily toward applied. It’s definitely testing to solve a problem, but also “to obtain data to support regulatory approval for an intervention.” The Clinical Implementation stage then is transitioning from applied to translational – working toward wider adoption of those interventions that clinical research said were legit (and solved problems!). This is another example of how we simplify for this intro course to focusing on the more literal translation – getting the research to people using strategies that allow people to actually understand and implement it.
Is basic better than applied or applied better than basic? Even as a hard-core, highly committed applied researcher I’m going to tell you NO. All these points on the spectrum are a necessary part of healthy research. Basic research informs applied research, which informs basic research, which informs applied research… you get the point. As the NIH says, “The spectrum is not linear or unidirectional; each stage builds upon and informs the others…Every stage…builds upon and informs basic research.”
THIS is what I want you to think about – identify where on the spectrum the research is so that you can figure out if the claims they (or the journalist) are appropriate for that phase. If it’s basic research, and someone is making big claims about something that has not yet been applied, been put to the test in real life (or with humans), it doesn’t mean those claims are wrong necessarily. It means think about “how” right they are, under what circumstances, and for what population? We’ll get deeper into the circumstances and population thing as we continue through this course.
Got ideas for questions to include on the exam?
Click this link to add them !
… Unit 1 … Unit 2 …. Unit 3 … Unit 4 … Unit 5 … Unit 6 … Unit 7 … Unit 8 … Unit 9 … Unit 10 … Unit 11 … Unit 12 … Unit 13 … Unit 14 … Unit 15 … Unit 16 …
Unit 6: Don’t be bashful- interrogate that primary research!
- Lateral vs vertical reading
- The Dreaded Ologies — An Introduction (with a side of paradigm)
Communication Research in Real Life Copyright © 2023 by Kate Magsamen-Conrad. All Rights Reserved.
Share This Book

Basic vs. applied research

- Coding qualitative data for valuable insights
What is the difference between applied research and basic research?
Examples of basic research vs. applied research, basic vs. applied research: a comparative analysis, the interplay between basic and applied research, introduction.
Basic and applied research look at existing knowledge and create new knowledge in different ways. They share the same basic principles of contributing to knowledge through research findings, but their aims and objectives are distinctly different.

In the vast realm of scientific inquiry, research stands as the cornerstone for advancement, driving our understanding of the world and fostering innovation. At its core, research can be bifurcated into two primary types: applied and basic research . While both serve pivotal roles in contributing to our collective knowledge, they operate with distinct objectives and outcomes.
Any approach that is called basic research delves into the foundational principles and theories of science. It is driven by a researcher's curiosity and the aspiration to expand the frontiers of understanding. The primary goal isn't to solve an immediate problem but to garner knowledge for the sake of understanding.
On the other hand, applied research focuses on analysis intended to solve practical problems. Conducting applied research means seeking solutions to specific, tangible challenges that society or industries face. Using the principles derived from basic research, applied research aims to bring about real-world impact and deliver pragmatic solutions.
Basic research
Basic research, often called "pure" or "fundamental" research , is characterized by its intrinsic quest to unravel the mysteries of nature and society. It is an investigation into the very core of phenomena, aiming to discover new principles, theories, or facts without an immediate application in mind. This kind of research is often propelled by the researcher's curiosity, a thirst to understand the "why" and "how" of things, rather than the "what can we do with it."

Basic research has a relatively broad scope and aims to enhance the existing body of knowledge in a particular field. It's not about creating a new product, improving a process, or solving a current societal problem. Instead, it's about laying the groundwork for future investigations, paving the way for applied research to build upon. Basic research poses questions like, "What are the fundamental principles of this phenomenon?" or "How does this process work at different levels?"
Such goals provide the essential framework upon which much of our modern understanding and technological advancement rests. Without the exploratory and explanatory nature of basic research, the foundational knowledge needed to drive innovation would be missing.
Applied research
While basic research focuses on curiosity and the pursuit of knowledge for its own sake, applied research takes a different approach by examining how real-world phenomena or outcomes can be altered. At its core, applied research is oriented towards identifying practical solutions to specific problems. Its primary objective is not just to add to the existing knowledge base but to leverage that knowledge to develop solutions, innovations, or interventions that can be directly applied in the real world.

Applied research is deeply rooted in real-world issues. Whether it's finding a cure for a specific disease, developing a new technological solution for environmental challenges, or creating strategies to improve education in underprivileged communities, the primary goal is to generate practical outcomes that can be directly implemented. Its relevance is often immediately apparent, as it's tailored to answer particular challenges faced by society, industries, or organizations.
The line between basic and applied research can sometimes blur, especially when foundational discoveries from basic research lead directly to tangible applications. However, the main distinction lies in the intent: while basic research seeks to understand the fundamental nature of phenomena, applied research aims to harness that understanding for tangible benefits.
Applied research is invaluable as it accelerates the transition of theoretical knowledge into practical, impactful solutions. Through applied research, the abstract findings of basic research are transformed into actionable insights, tools, and technologies that shape our daily lives and address pressing challenges.

Make the most of your data with ATLAS.ti
Powerful tools in an intuitive interface, ready for you with a free trial today.
Research in the social sciences encompasses a broad spectrum of topics, ranging from understanding human behavior and societal structures to exploring the dynamics of interpersonal relationships. Basic and applied research methods in the social sciences offer unique insights into these areas. Let's delve into some examples to understand their distinct approaches.
Basic research examples
The social construction of reality
A classic area of investigation in sociology is understanding how societies construct reality. This kind of research delves deep into the ways cultures, languages, and institutions shape our understanding of the world. It doesn't immediately aim to solve societal problems but provides essential insights into how perceptions and beliefs are formed. Research methods often used for this type of study include in-depth interviews , participant observations , and ethnographic studies .
Attachment theory in psychology
Attachment theory seeks to understand the deep emotional and physical attachment between a child and at least one primary caregiver. It delves into the nature of attachment and its implications for personal development. The research often involves longitudinal studies that observe behaviors over extended periods.
Applied research examples
Interventions for at-risk youth
Applied researchers might design programs or interventions to help at-risk youth, building on the foundational knowledge of psychology, sociology, and education. The research might involve evaluating the effectiveness of a particular program, using methods like surveys , focus groups , and pre-and-post assessments.
Communication strategies for public health
Understanding human behavior is crucial for successful public health campaigns. Researchers might study the best ways to communicate vital health information to various populations, especially in times of crisis like pandemics. Methods often include A/B testing of messages, surveys to assess message efficacy, and observational studies to gauge real-world behavior following communication campaigns.
The distinction between basic and applied research is not just a matter of intent or outcome; it also encompasses differences in methodologies , scopes, and approaches. Let's undertake a comparative analysis to illuminate these distinctions further, particularly in the context of the social sciences.
Purpose and motivation
Basic research is motivated by the quest for knowledge. It seeks to answer fundamental questions about human behavior, societal structures, and the interplay between various social factors. The driving force here is curiosity. In contrast, applied research is driven by the need to address specific societal or practical problems. Its purpose is to take the theoretical knowledge derived from basic research and convert it into actionable solutions.
Methodological approaches
It's important to acknowledge that there is no one universal research method that can address all potential research inquiries. Moreover, the same research methods, such as conducting interviews or engaging in inductive and deductive reasoning , can be utilized in basic and applied research, but they will differ in their scope and objectives. While applied research is more experimental or confirmatory, a basic research approach is often exploratory or explanatory in nature. Basic research methods include ethnography , in-depth interviews , or longitudinal studies to gain a deep understanding of a topic. The focus is on generating theories and understanding patterns.

Applied research, on the other hand, often employs more structured and targeted methodologies. Surveys , experiments, and evaluations are commonly used to verify propositions, assess the efficacy of interventions, or gauge public opinion. The approach is more pragmatic, seeking results that can inform decisions and guide actions.
Outcomes and results
Basic research outcomes are usually theoretical contributions: new concepts, theories, or insights into existing phenomena. The results expand the academic literature and provide a foundation for future studies.
Applied research results in tangible solutions or recommendations. The outcomes might include a new social program, policy recommendations, interventions, or communication strategies. The results are geared towards immediate implementation and often have direct implications for organizations, governments, or communities.
The discourse on basic and applied research often sets them apart, emphasizing their distinct objectives and methodologies. However, it's crucial to recognize that these research types aren't isolated from each other. They coexist in a symbiotic relationship, where the findings from basic research often provide the foundational knowledge for applied research, and the results of applied research can inspire further basic investigations.
The transition of knowledge
One of the most notable instances of the interplay is how basic research's findings become the bedrock for applied research projects. For example, a basic research study on cognitive development in children might reveal specific patterns or stages. An applied researcher, recognizing the implications of these findings, could then design educational interventions tailored to these developmental stages.
How one complements the other
Basic research pushes the boundaries of our understanding, expanding the horizon of what we know. Applied research, on the other hand, can reframe this expansive knowledge and make it relevant and actionable for society's immediate needs.

But the relationship is reciprocal. Applied research can also highlight gaps in our understanding, pointing out areas where basic research is needed. For instance, if an intervention designed based on current knowledge fails to achieve its intended results, it signals to basic researchers that there might be underlying factors or dynamics not yet understood.
The dynamic continuum
Instead of viewing basic and applied research as two separate entities, it's more accurate to see them as points on a continuum. The knowledge generated by basic research flows towards applied projects, which in turn can inspire further basic investigations. This dynamic loop ensures that research in the social sciences remains both grounded in fundamental understanding and relevant to real-world challenges.

Conduct applied and basic research through ATLAS.ti
Whatever your research objectives, make it happen with ATLAS.ti. Download a free trial today.


- My presentations
Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
Basic vs. applied research
Published by Tordis Eliassen Modified over 5 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "Basic vs. applied research"— Presentation transcript:

Using the Internet as a Tool. Introduction to the Internet Industry Trends Labor Market Information.

Evaluation Procedures

Striving for Alignment: One Funder's Lessons in Supporting Advocacy.

Healthy and Active Before 5 Community Summit PLEDGE the Practice. PASS the Policy! PLEDGE the Practice. PASS the Policy!

© Nuffield Foundation 2013 Practical Work for Learning Combustion of iron wool.

Comparative Social Welfare Approaches, Focus and Issues.

Role of Program Theory in Building Program Evaluations Joe E. Heimlich, Ph.D. The Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio, USA The Institute for Learning.

Economics of Research and Surveillance: Value of Information David Hutton.

Scientific Notation Review

Instructional Design Abdullah Alsowyan. Instructional Design A science works in solving problems by using translation pedagogical research in many models.

Define Human Performance Technology › Foundational Aspects › Specific Concepts Connections with Housing/Residence Life › Higher Education and Student.

Answering the inference question Inference cannot be lifted, paraphrased or quoted. It is the underlying idea in the extract. How to structure the first.

Inquiry 1 written AND oral reports due Th 9/24 or M 9/28.

Extra Review for Metric Quiz

Scientific Notation. Simplify: Scientific Notation Expressed as a number between 0 and 10 times a power of positive - a very large number 10 negative.

Working with Industry: Culture and Expectations Jim Capistran November 18, 2010.

Equality Impact Assessments (EQIAs) Jacqueline Rae Equalities Research.

What is randomization and how does it solve the causality problem? 2.3.

Warm UP: Factor: 1) 4v 2 – 4v – 82) 3p 2 – 2p – 5 3) 5n n + 124) 2n 2 + 5n + 2.

Research Problem Students have a difficult time with critical thinking, especially the aspects of analysis and evaluation necessary to evaluate data.
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.

The difference between basic and applied research – Key differences
In a rapidly evolving landscape of scientific and technological innovation, understanding the inner workings of research is increasingly vital.
Whether you’re a seasoned academic, an industry professional, or simply a curious individual, comprehending the difference between applied and basic research is used to provide critical insights into how knowledge is both generated and utilized.
These two kinds of research, while distinct in their aims and methodologies, often serve as two sides of the same coin, each with its unique contributions and challenges.
By examining research outcomes, funding sources, criticisms, and examples from both categories, this comprehensive blog demystifies the often blurry line that separates basic research vs applied research methods.
If you’ve ever pondered which type of research to use for a project or questioned how basic principles derived from foundational studies turn into real-world applications, this exploration offers a lens into the multifaceted world of research.
Key Differences Between Basic and Applied Research
In the realm of scientific inquiry, understanding the key differences between basic and applied research is crucial. These two types of research serve distinct purposes and often utilize different research methods, but they are interconnected in the quest for new knowledge.
| Attribute | Basic Research | Applied Research |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Objective | To acquire new knowledge and understanding | To solve a specific, practical problem |
| Focus | Theoretical, general concepts | Real-world applications |
| Research Methods | Observational, theoretical, experimental | Controlled experiments, surveys, case studies |
| Immediate Application | Typically no | Yes |
| Examples | Einstein’s theories in physics | Health campaigns to reduce heart disease |
| Criticisms | May lack immediate practical use | May not contribute to theoretical understanding |
| Time Horizon | Long-term, foundational | Short-term, actionable |
| Funding Source | Often academic or government grants | Typically industry, private sector, or targeted grants |
| Real-world Impact | May lead to unforeseen applications | Directly aimed at current issues |
| Interconnectedness | Can lay the groundwork for applied research | May contribute to general understanding |
Basic Research
Basic research focuses on the acquisition of fundamental understanding without immediate application in mind.
For example, when Einstein was formulating his theories in physics, he was conducting basic research.
He sought to explain the laws governing the universe but didn’t necessarily aim to solve a practical problem.
Basic research often gets criticized for not having apparent applications, but it lays the groundwork for future advancements. Years after Einstein, his theories paved the way for the development of laser technology, used in everything from DVDs to medical procedures.
Applied Research
Applied research focuses on solving specific, practical problems. It’s the type of research used when health psychologists want to tackle rising rates of cardiovascular diseases, for instance. Conducting applied research, they may investigate effective messaging strategies to encourage healthier diets, aiming to produce tangible benefits in public health.
Applied research seeks to utilize scientific understanding for a particular real-world issue.
The line between basic and applied research is not always clear-cut. While applied research may yield new knowledge that contributes to a broader understanding of human behavior, basic research may inadvertently lead to practical applications.
For instance, research in quantum mechanics, which was initially considered highly theoretical, has found applications in modern computing.
It’s also worth noting that the research methods employed may differ based on the type of research being conducted.
Applied research often employs methods like case studies, surveys, or controlled experiments aimed at resolving a specific issue, whereas basic research might involve more theoretical or observational methods aimed at general understanding.
While basic research often explores theoretical concepts without an immediate application, applied research focuses on real-world issues. Both are integral in advancing our collective knowledge and sometimes unexpectedly complement each other in offering solutions to challenges we face.
What’s better? Basic vs applied research?
The debate between the impact of basic and applied research is an enduring one, and both sides have compelling arguments. The key differences between the two types of research are their aims and methods.
- Basic research focuses on generating new knowledge and understanding fundamental principles, often without an immediate application in mind.
- Applied research, on the other hand, seeks to solve specific problems and is often guided by practical outcomes.
One could argue, as some experts do, that basic research often has a more profound long-term impact. For instance, the discovery of the structure of DNA was a feat of basic research.
Today, it serves as the cornerstone for a multitude of applied research projects in genetics, forensics, and medicine. Another example of basic research is the development of quantum mechanics, which initially appeared to be an abstract field but has led to the invention of technologies like semiconductors and MRI machines.
Conversely, applied research focuses on immediate needs and therefore, its impact can be more immediately visible.
Examples of applied research include the development of COVID-19 vaccines or the creation of energy-efficient technologies. This type of research often uses methods and knowledge generated by basic research to achieve its goals.
The contention that applied research can be counterproductive due to its narrow focus and the push to monetize findings is a nuanced issue.
While entrepreneurship courses in academic settings may appear to detract from the purity of research, they can also offer researchers tools to transform basic research into applied solutions, bridging the gap between theory and practice.
The two aren’t mutually exclusive; basic research and applied research often go hand in hand.
Researchers conducting applied research may stumble upon findings that contribute to new knowledge, just as those conducting basic research may see their work result in unexpected applications.
Examples of basic research vs applied research
Basic research:.
- Genetic Sequencing : Research to understand the sequences of DNA and what each gene does.
- Particle Physics : Experiments in places like CERN to understand the basic building blocks of the universe.
- Social Psychology Theories : Studying human behavior in a controlled environment to understand basic social interactions.
- Climate Models : Researching the fundamental mechanisms that control climate change without necessarily looking for immediate solutions.
- Pure Mathematics : Investigating abstract mathematical concepts that may not have an immediate application.
- Astronomy : Observing and mapping distant celestial bodies to understand the universe’s structure.
- Brain Mapping : Basic research on how neurons communicate within the brain, without a targeted application.
- Evolutionary Biology : Studying how organisms evolve over time to adapt to their environment.
Applied Research:
- Pharmaceuticals : Developing new drugs based on an understanding of disease mechanisms.
- Renewable Energy : Researching better solar panels or wind turbines to harness energy more efficiently.
- Market Research : Understanding consumer behavior to improve product design or advertising strategies.
- Educational Methods : Evaluating teaching strategies to improve educational outcomes.
- Medical Procedures : Research to develop new surgical techniques or medical devices.
- Cybersecurity : Designing new types of encryption or security measures based on vulnerabilities.
- Agricultural Techniques : Researching better ways to increase crop yield or protect against pests.
- Transportation : Developing new materials for lighter, more fuel-efficient vehicles.
Careers in basic research and applied research
Here are some examples of careers that use mainly basic or applied research – but some scientists do a mixture of both.
Careers in Basic Research:
- Theoretical Physicist : Focuses on understanding the fundamental laws governing physical phenomena.
- Astrophysicist : Studies the properties and behaviors of celestial bodies and the universe.
- Mathematician : Conducts research in pure mathematics, exploring abstract concepts.
- Geneticist : Investigates genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.
- Neuroscientist : Researches the complexities of the nervous system, including the brain.
- Biochemist : Studies the chemical processes within and related to living organisms.
- Cognitive Psychologist : Explores the mental processes behind human behavior.
- Archaeologist : Conducts research to understand human history and pre-history through the excavation of sites and the analysis of artifacts.
- Geologist : Studies the Earth’s physical structure and substance, its history, and the processes that act on it.
Careers in Applied Research:
- Pharmaceutical Researcher : Develops new drugs or medical treatments.
- Environmental Consultant : Provides advice on environmental regulations and conducts research to solve environmental problems.
- Data Scientist : Uses statistical models to analyze data for actionable insights, often for businesses.
- Mechanical Engineer : Designs and tests new devices, often focused on solving specific mechanical problems.
- Market Research Analyst : Conducts research to understand market trends and consumer behavior.
- Clinical Psychologist : Applies psychological research to treat mental health disorders.
- Agricultural Scientist : Researches ways to improve the sustainability and productivity of agricultural systems.
- Software Developer : Creates new software based on research into user needs, technological advancements, or problem-solving.
- Nutritional Epidemiologist : Studies the relationship between diet and health outcomes, often aiming for public health applications.
Wrapping up – applied research and basic research
As we’ve journeyed through this comprehensive exploration of applied research and basic research, it’s clear that each holds its unique place in the expansive world of research.
The two are like siblings—different in personality but stemming from the same family of intellectual inquiry.
Basic research is theoretical and often provides the foundation for applied research. On the flip side, applied research is practical in nature and focuses on solving immediate real-world problems.
Despite their differences, one can’t exist optimally without the other.
Basic research helps pave the way for advancements in applied research, while findings from applied research can loop back to enrich our foundational knowledge.
While basic research tends to engage with more conceptual questions, applied research is driven by practical problems that require immediate solutions. These different types of research methods can serve different purposes but are not mutually exclusive.
The world of research is enriched by the interplay between basic and applied research methods. Whether theoretical or practical, long-term or immediate, both contribute significantly to our understanding and make up the vibrant tapestry of research that seeks to answer questions, solve problems, and improve our lives.
And there we have it—your guided tour through the landscape of applied and basic research is complete!
Whether you’re an aspiring researcher, an industry professional, or a curious individual, understanding these key differences between basic and applied research will surely add a valuable layer to your perspective.

Dr Andrew Stapleton has a Masters and PhD in Chemistry from the UK and Australia. He has many years of research experience and has worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow and Associate at a number of Universities. Although having secured funding for his own research, he left academia to help others with his YouTube channel all about the inner workings of academia and how to make it work for you.
Thank you for visiting Academia Insider.
We are here to help you navigate Academia as painlessly as possible. We are supported by our readers and by visiting you are helping us earn a small amount through ads and affiliate revenue - Thank you!

2024 © Academia Insider

Please log in to save materials. Log in
- Resource Library
- Research Methods
- VIVA Grant Recipients
- Vgr-social-work-research
Education Standards
Radford university.
Learning Domain: Social Work
Standard: Basic Research Methodology
Lesson 10: Sampling in Qualitative Research
Lesson 11: qualitative measurement & rigor, lesson 12: qualitative design & data gathering, lesson 1: introduction to research, lesson 2: getting started with your research project, lesson 3: critical information literacy, lesson 4: paradigm, theory, and causality, lesson 5: research questions, lesson 6: ethics, lesson 7: measurement in quantitative research, lesson 8: sampling in quantitative research, lesson 9: quantitative research designs, powerpoint slides: sowk 621.01: research i: basic research methodology.
The twelve lessons for SOWK 621.01: Research I: Basic Research Methodology as previously taught by Dr. Matthew DeCarlo at Radford University. Dr. DeCarlo and his team developed a complete package of materials that includes a textbook, ancillary materials, and a student workbook as part of a VIVA Open Course Grant.
The PowerPoint slides associated with the twelve lessons of the course, SOWK 621.01: Research I: Basic Research Methodology, as previously taught by Dr. Matthew DeCarlo at Radford University.
Version History
Instant insights, infinite possibilities
Basic vs. applied research: what’s the difference?
Last updated
27 February 2023
Reviewed by
Cathy Heath
Short on time? Get an AI generated summary of this article instead
Research can be used to learn new facts, create new products, and solve various problems. Yet, there are different ways to undertake research to meet a desired goal.
The method you choose to conduct research will most likely be based on what question you want to answer, plus other factors that will help you accurately get the answer you need.
Research falls into two main categories: basic research and applied research. Both types of research have distinct purposes and varied benefits.
This guide will help you understand the differences and similarities between basic and applied research and how they're used. It also answers common questions about the two types of research, including:
Why is it called basic research?
What is more important, basic research or applied research?
What are examples of pure (basic) research and applied research?
Analyze basic and applied research
Dovetail streamlines analysis to help you uncover and share actionable insights
- What is basic research?
Basic research (sometimes called fundamental or pure) advances scientific knowledge to completely understand a subject, topic, or phenomenon. It's conducted to satisfy curiosity or develop a full body of knowledge on a specific subject.
Basic research is used to bring about a fundamental understanding of the world, different behaviors, and is the foundation of knowledge in the scientific disciplines. It is usually conducted based on developing and testing theories.
While there is no apparent commercial value to the discoveries that result from basic research, it is the foundation of research used for other projects like developing solutions to solve problems.
Examples of basic research
Basic research has always been used to give humans a better understanding of all branches of science and knowledge. However, it's not specifically based on identifying new things about the universe.
Basic research has a wide range of uses, as shown in the following examples:
Investigation into how the universe began
A study searching for the causes of cancer
Understanding the components that make up human DNA
An examination into whether a vegetarian diet is healthier than one with meat
A study to learn more about which areas in the world get the most precipitation

Benefits of conducting basic research
Called basic research because it is performed without an immediate or obvious benefit, this type of research often leads to vital solutions in the future. While basic research isn't technically solution-driven, it develops the underlying knowledge used for additional learning and research.
There are many benefits derived from basic research, including:
Gaining an understanding of living systems and the environment
Gathering information that can help society prepare for the future
Expanding knowledge that can lead to medical advances
Providing a foundation for applied research
- What is applied research?
Applied research studies particular circumstances to apply the information to real-life situations. It helps improve the human condition by finding practical solutions for existing problems.
Applied research builds off facts derived from basic research and other data to address challenges in all facets of life. Instead of exploring theories of the unknown, applied research requires researchers to use existing knowledge, facts, and discoveries to generate new knowledge.
Solutions derived from applied research are used in situations ranging from medical treatments or product development to new laws or regulations.
Examples of applied research
Applied research is designed to solve practical problems that exist under current conditions. However, it's not only used for consumer-based products and decisions.
Applied research can be used in a variety of ways, as illustrated by the following examples:
The investigation of ways to improve agricultural crop production
A study to improve methods to market products for Gen Z consumers
Examination of how technology can t make car tires last longer
Exploration of how to cook healthy meals with a limited budget
A study on how to treat patients with insomnia
Benefits of using applied research
Although applied research expands upon a foundation of existing knowledge, it also brings about new ideas. Applied research provides many benefits in various circumstances, including:
Designing new products and services
Creating new objectives
Providing unbiased data through the testing of verifiable evidence
- Basic research vs. applied research: the differences
Both basic and applied research are tactics for discovering specific information. However, they differ significantly in the way research is conducted and the objectives they achieve.
Some of the most notable differences between basic and applied research include the following:
Research outcomes: curiosity-driven vs. solution-driven
Basic research is generally conducted to learn more about a specific subject. It is usually self-initiated to gain knowledge to satisfy curiosity or confirm a theory.
Conversely, applied knowledge is directed toward finding a solution to a specific problem. It is often conducted to assist a client in improving products, services, or issues.
Research scope: universal scope vs. specific scope
Basic research uses a broad scope to apply various concepts to gain more knowledge. Research methods may include studying different subjects to add more information that connects evidence points in a greater body of data.
Meanwhile, applied research depends on a specific or narrow scope to gather specific evidence to address a certain problem.
Research approaches: expanding existing knowledge vs. finding new knowledge
Researchers conduct basic research to fill in gaps between existing information points. Basic knowledge is an expansion of existing knowledge to gain a deeper understanding. It is often based on how, what, or why something is the way it is. Although applied research may be based on information derived from basic research, it's not designed to expand the knowledge. Instead, the research is conducted to find new knowledge, usually in the form of a solution.
Research commercialization: Informational vs. commercial gain
The main basis of product development is to solve a problem for consumers.
Basic research might lead to solutions and commercial products in the future to help with this. Since applied research is used to develop solutions, it's often used for commercial gain.
Theory formulation: theoretical vs. practical nature
Basic research is usually based on a theory about a specific subject. Researchers may develop a theory that grows and changes as more information is discovered during the research process. Conversely, applied research is practical in nature since the goal is to solve a specific problem.
- Are there similarities between applied and basic research?
While some obvious differences exist, applied and basic research methods have similarities. For example, researchers may use the same methods to collect data (like interviews, surveys , and focus groups ) for both types of research.
Both types of research require researchers to use inductive and deductive reasoning to develop and prove hypotheses . The two types of research frequently intersect when basic research serves as the foundation for applied research.
While applied research is solution-based, basic research is equally important because it yields information used to develop solutions to many types of problems.
- Methods used in basic research and applied research
While basic and applied research have different approaches and goals, they require researchers or scientists to gather data. Basic and applied research makes use of many of the same methods to gather and study information, including the following:
Observations: Studying research subjects for an extended time allows researchers to gather information about how subjects behave under different conditions.
Interviews: Surveys and one-to-one discussions help researchers gain information from other subjects and validate data.
Experiments: Researchers conduct experiments to prove or disprove certain hypotheses based on information that has been gathered.
Questionnaires: A series of questions related to the research context helps researchers gather quantitative information applicable to both basic and applied research.
- How do you determine when to use basic research vs. applied research?
Basic and applied research are both helpful in obtaining knowledge. However, they aren't usually used in the same settings or under the same circumstances.
When you're trying to determine which type of research to use for a particular project, it's essential to consider your product goals. Basic research seeks answers to universal, theoretical questions. While it works to uncover specific knowledge, it's generally not used to develop a solution. Conversely, applied research discovers answers to specific questions. It should be used to find out new knowledge to solve a problem.
- Bottom line
Both basic and applied research are methods used to gather information and analyze facts that help build knowledge around a subject. However, basic research is used to gain understanding and satisfy curiosity, while applied research is used to solve specific problems. Both types of research depend on gathering information to prove a hypothesis or create a product, service, or valuable process.
By learning more about the similarities and differences between basic and applied research, you'll be prepared to gather and use data efficiently to meet your needs.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 18 April 2023
Last updated: 27 February 2023
Last updated: 22 August 2024
Last updated: 5 February 2023
Last updated: 16 April 2023
Last updated: 9 March 2023
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 4 July 2024
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
- Key Differences
Know the Differences & Comparisons
Difference Between Basic and Applied Research

On the contrary, applied research implies the research that is put to practical use and is beneficial to solve practical problems. This article might help you in understanding the difference between basic and applied research.
Content: Basic Research Vs Applied Research
Comparison chart.
| Basis for Comparison | Basic Research | Applied Research |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Basic Research refers to the study that is aimed at expanding the existing base of scientific knowledge. | Applied Research is the research that is designed to solve specific practical problems or answer certain questions. |
| Nature | Theoretical | Practical |
| Utility | Universal | Limited |
| Concerned with | Developing scientific knowledge and predictions | Development of technology and technique |
| Goal | To add some knowledge to the existing one. | To find out solution for the problem at hand. |
Definition of Basic Research
Basic Research or otherwise called as pure or fundamental research, is one that focuses on advancing scientific knowledge for the complete understanding of a topic or certain natural phenomenon, primarily in natural sciences. In a nutshell, when knowledge is acquired for the sake of knowledge it is called basic research.
Basic Research is completely theoretical, that focuses on basic principles and testing theories. It tends to understand the basic law.
Basic Research deals with generalization and formulation of theory about human behaviour. It is aligned towards collecting information that has universal applicability. Therefore, basic research helps in adding new knowledge to the already existing knowledge.
Definition of Applied Research
Applied Research can be defined as research that encompasses real life application of the natural science. It is directed towards providing a solution to the specific practical problems and develop innovative technology.
In finer terms, it is the research that can be applied to real-life situations. It studies a particular set of circumstances, so as to relate the results to its corresponding circumstances.
Applied research includes research that focuses on certain conclusions experiencing a business problem. Moreover, research that is aligned towards ascertaining social, economic or political trends are also termed as applied research.
Key Differences Between Basic and Applied Research
The points given below explain the differences between basic and applied research:
- Basic Research can be explained as research that tries to expand the already existing scientific knowledge base. On the contrary, applied research is used to mean the scientific study that is helpful in solving real-life problems.
- While basic research is purely theoretical, applied research has a practical approach.
- The applicability of basic research is greater than the applied research, in the sense that the former is universally applicable whereas the latter can be applied only to the specific problem, for which it was carried out.
- The primary concern of the basic research is to develop scientific knowledge and predictions. On the other hand, applied research stresses on the development of technology and technique with the help of basic science.
- The fundamental goal of the basic research is to add some knowledge to the already existing one. Conversely, applied research is directed towards finding a solution to the problem under consideration.
The type of research may vary on the basis of the level at which research is carried out and its purpose. One can choose basic research over applied research when the purpose is to add certain scientific knowledge, whereas when it is important to identify a proper solution to the problem under study, applied research is preferable.
You Might Also Like:

Ghulam Mustafa Safi says
October 22, 2017 at 2:52 pm
I found the information very informative and useful. Want to receive the information on regular basis if possible.
January 25, 2023 at 11:19 am
i am satisfied with the information given it has addressed my concern
Rick Tayebwa says
February 22, 2018 at 8:36 pm
This has really settled the confusion i had between these two terms
Jamila Shabnam says
November 7, 2018 at 5:41 pm
Please guide me about research & impact evaluation…..to me impact evaluation is an assessment procedure & it’s formatted differently than research…what r the basic differences between the two? Thank u.
January 29, 2019 at 2:48 pm
I found this very useful, except that i have not seen the name of the author etc for referencing.
Surbhi S says
January 30, 2019 at 9:44 am
The name of the author is given at the top, below the title
G Zimba says
April 5, 2022 at 10:36 am
Author’s name?
June 16, 2023 at 5:05 pm
Meseret says
September 13, 2019 at 1:19 pm
Am so much satisfied. thanks a lot.
Charles says
February 2, 2020 at 9:27 pm
This website is very useful.
Bolanle samson falade says
May 6, 2020 at 3:36 pm
someone help to answer this question the Research is a veritable tools to economic growth and development thank you.
Ogbeche ojochide says
March 27, 2021 at 9:49 am
The information is very useful and educative
Abdullahi A. Bakare says
July 14, 2021 at 4:30 pm
I found this very informative. It has helped me a lot in my Research Methodology teaching.
Marietha says
November 8, 2021 at 2:31 am
I found it is very useful and accurate.
J. M. Mlangwa says
January 4, 2022 at 4:36 pm
This article is very useful to me because it Helps to answer my assignment Explain the distinctions between basic research and applied research. Thank you
Richard Essuman says
March 20, 2022 at 8:19 pm
Much Regards. Thank you.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser. For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser.
- My Wish List
- Compare Products
- Presentations
Applied Vs Fundamental Research
You must be logged in to download this file*
item details (2 Editable Slides)
(2 Editable Slides)
Related Products
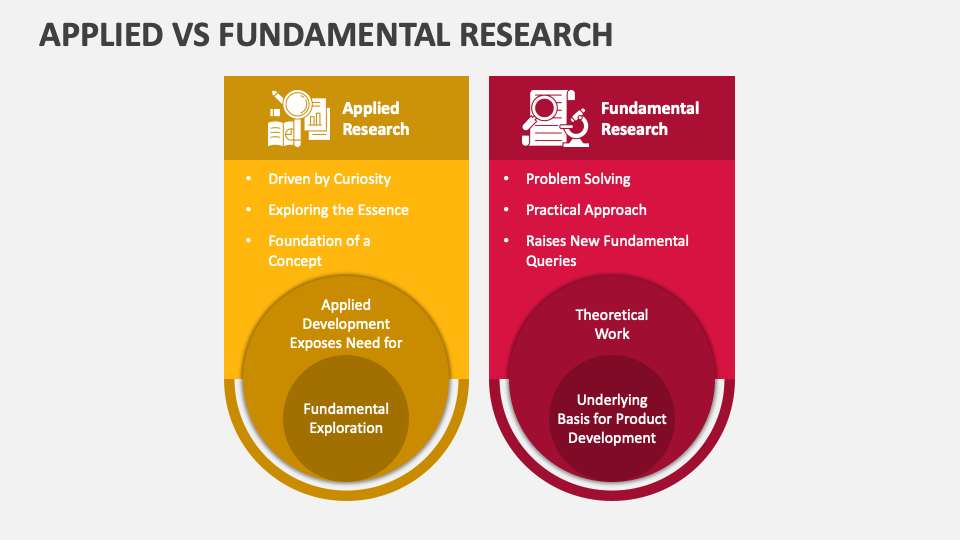
Applied research and fundamental research are two distinct approaches within the realm of scientific inquiry. Shed light on the differences between Applied vs. Fundamental Research using our presentation template for MS PowerPoint and Google Slides.
Researchers can harness our customizable PPT to explain that fundamental research is driven by curiosity to uncover underlying principles without an immediate practical application in mind. In contrast, applied research takes into account the existing scientific principles, knowledge, or theories and applies them to practical situations or industries. You can further depict how applied research differs from fundamental research in terms of factors such as timeframe, focus, knowledge, innovation, and more.
Sizing Charts
| Size | XS | S | S | M | M | L |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EU | 32 | 34 | 36 | 38 | 40 | 42 |
| UK | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 |
| US | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 |
| Bust | 79.5cm / 31" | 82cm / 32" | 84.5cm / 33" | 89.5cm / 35" | 94.5cm / 37" | 99.5cm / 39" |
| Waist | 61.5cm / 24" | 64cm / 25" | 66.5cm / 26" | 71.5cm / 28" | 76.5cm / 30" | 81.5cm / 32" |
| Hip | 86.5cm / 34" | 89cm / 35" | 91.5cm / 36" | 96.5cm / 38" | 101.5cm / 40" | 106.5cm / 42" |
| Size | XS | S | M | L | XL | XXL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UK/US | 34 | 36 | 38 | 40 | 42 | 44 |
| Neck | 37cm / 14.5" | 38cm /15" | 39.5cm / 15.5" | 41cm / 16" | 42cm / 16.5" | 43cm / 17" |
| Chest | 86.5cm / 34" | 91.5cm / 36" | 96.5cm / 38" | 101.5cm / 40" | 106.5cm / 42" | 111.5cm / 44" |
| Waist | 71.5cm / 28" | 76.5cm / 30" | 81.5cm / 32" | 86.5cm / 34" | 91.5cm / 36" | 96.5cm / 38" |
| Seat | 90cm / 35.4" | 95cm / 37.4" | 100cm / 39.4" | 105cm / 41.3" | 110cm / 43.3" | 115cm / 45.3" |

- Organizations
- Planning & Activities
- Product & Services
- Structure & Systems
- Career & Education
- Entertainment
- Fashion & Beauty
- Political Institutions
- SmartPhones
- Protocols & Formats
- Communication
- Web Applications
- Household Equipments
- Career and Certifications
- Diet & Fitness
- Mathematics & Statistics
- Processed Foods
- Vegetables & Fruits
Difference Between Basic Research and Applied Research
• Categorized under Planning & Activities , Psychology , Science | Difference Between Basic Research and Applied Research
Research is commonly defined as a systematic investigation with the intent to verify facts and generate updated conclusions. Regarding its utility, research is divided into two: basic and applied. Many researchers suggest that these are closely working with each other as basic research is a platform which applied research often uses to solve real life problems. Also, basic research employs technology (which was developed by applied research) to address its objectives. Thus, these inquiries form a cycle of advancement.
Generally, applied research deals with particular topics which have direct practical relevance. On the contrary, basic research is mainly motivated by the expansion of knowledge and seek to answer questions that are not related to direct applications. The following concepts delve into such distinctions.
What is Basic Research?
Basic research is also known as fundamental or pure research since it is mainly concerned with the improvement of scientific knowledge. The purpose of basic research is simply to gather more information to further understand existing phenomena specially in the field of natural sciences. Its focus is on supporting as well as challenging assumptions which aim to explain various phenomena. Pure research looks at the “big picture” in the sense that it looks for overall factors and related postulates. Hence, fundamental research is purely theoretical as it delves into basic laws and principles.
Though the engendered ideas may not be directly applied to current situations, such conclusions from basic research are highly fundamental in enhancing future applied studies. For instance, previous studies on mathematical theories have been utilized in programming and other information technology processes.
What is Applied Research?
The purpose of applied research is to know more about a certain real-world problem and take steps to solve it. It focuses on the application of natural science principles on practical difficulties as well as enhancing innovations. Such studies are often associated with the fields of business, economics, health, and politics. For instance, a company may hire an applied researcher to look into the best way of hiring applicants and placing employees in connection with the organization’s various positions.
Many applied researchers utilize the naturalistic observation method to verify existing social difficulties and then conduct experiments to ascertain solutions. However, data gathering challenges such as ethics and validity issues may arise specially when testing procedures may pose harm for humans and animals. Thus, restrictions are applied in employing the respective study procedures.
Difference between Basic and Applied Research
Purpose of basic and applied research.
Basic research is meant to expand one’s current knowledge while applied research is aiming to solve particular life problems.
Basic research is more theoretical since it generally generates theories and explores information which may not be presently applied. It is also focused on improving current academic concepts. On the other hand, applied research is more practical and descriptive in nature as it seeks to alleviate current problems in various fields and is mostly concerned with end-usage.
The scope of basic research is often universal as it may bae applied to diverse concepts. However, applied research is largely particular as it is focused on very specific topics which seek to answer certain problems.
As compared to basic research, applied research is more often linked with the improvement of technology as it covers the direct application of knowledge.
While basic research aims to predict future phenomena, applied research seeks to prevent predicted problems or come with solutions for future challenges. The former deals with knowing what could happen while the latter goes beyond by coming up with probable actions.
Basic research is driven by curiosity while applied research is driven by clients as the former is conducted to understand fundamental concepts while the latter is done to help solve individuals’ or groups’ problems.
Commercial Objectives
As compared to basic research, applied research is closely associated with commercial processes since it aims to create relevant products and services.
As compared to basic research, applied research is more closely connected with the development of economy as numerous surveys, experiments, and case studies are conducted to verify the efficacy of products, market strategies, and other economically related procedures.
Academic Publications
As compared to applied research, basic researches more often appear in academic publications as they delve into generating new knowledge.
Environment
Basic research occurs in a sterile or highly-controlled environment such as laboratories. Conversely, applied research mainly takes place in real world settings where other unexpected variables may intervene.
Basic vs Applied Research: Comparison Chart

Summary of Basic and Applied Research
- As to purpose, research is generally divided into two: basic and applied.
- Basic research can provide valuable information that applied research can use.
- Such inquiries form a cycle of advancement.
- Basic research is also known as fundamental or pure research since it is mainly concerned with the improvement of scientific knowledge.
- The purpose of applied research is to know more about a certain real-world problem and take steps to solve it.
- Basic research is theoretical in nature while applied research is practical; hence, it is associated with technology.
- As compared to applied research, basic research has a wider scope.
- While basic research predicts future phenomena, applied research creates solutions or preventions for probable problems.
- Basic research is curiosity-driven while applied research is client-driven.
- As compared to basic research, applied research is more closely associated with economically related objectives.
- Basic research mostly appears in academic publications.
- While basic research takes place in a sterile environment, applied research is often conducted in messy real-world settings.
- Recent Posts
- Difference Between Hematoma and Melanoma - February 9, 2023
- Difference Between Bruising and Necrosis - February 8, 2023
- Difference Between Brain Hematoma and Brain Hemorrhage - February 8, 2023
Sharing is caring!
- Pinterest 453
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
- The Differences Between Research Methods and Research Methodology
- Difference Between Primary and Secondary Research
- Difference Between Subject Matter and Content
- Difference Between Study and Experiment
- Difference Between Supercomputing and Quantum Computing
Cite APA 7 Brown, g. (2018, May 22). Difference Between Basic Research and Applied Research. Difference Between Similar Terms and Objects. http://www.differencebetween.net/science/difference-between-basic-research-and-applied-research/. MLA 8 Brown, gene. "Difference Between Basic Research and Applied Research." Difference Between Similar Terms and Objects, 22 May, 2018, http://www.differencebetween.net/science/difference-between-basic-research-and-applied-research/.
information helped a great deal… thank you.
The Summary says: Basic research mostly appears in academic publications. The chart inverted the information.
Helps a lot….thnaks.
Dear Ms Gene Balinggan,
The article of yours has been of very much help. I hope this note of thanks motivates you to write more of such articles. Once again Thank You Very Much.
Best regards, Syed Mehdi
It’s very important web site and utilities
So helpful But why in the table you write that basic is less often apear in acadmic site? is that right?
Leave a Response
Name ( required )
Email ( required )
Please note: comment moderation is enabled and may delay your comment. There is no need to resubmit your comment.
Notify me of followup comments via e-mail
References :
Advertisments, more in 'planning & activities'.
- Difference Between Budgeting and Forecasting
- Difference Between Takt Time and Cycle Time
- Difference Between Shipping and Billing Address
- Difference Between Pension and Retirement
- Difference between Analyzing and Evaluating
More in 'Psychology'
- Difference Between INTP and INFP
- Difference Between Aversion Therapy and Flooding
- Difference Between Availability Heuristic and Representative Heuristic
- Difference Between Anchoring Heuristic and Adjustment Heuristic
- Difference Between Akinetic Mutism and Locked-In Syndrome
More in 'Science'
- Difference Between Rumination and Regurgitation
- Difference Between Pyelectasis and Hydronephrosis
- Difference Between Cellulitis and Erysipelas
- Difference Between Suicide and Euthanasia
- Difference Between Vitamin D and Vitamin D3
Top Difference Betweens
Get new comparisons in your inbox:, most emailed comparisons, editor's picks.
- Difference Between MAC and IP Address
- Difference Between Platinum and White Gold
- Difference Between Civil and Criminal Law
- Difference Between GRE and GMAT
- Difference Between Immigrants and Refugees
- Difference Between DNS and DHCP
- Difference Between Computer Engineering and Computer Science
- Difference Between Men and Women
- Difference Between Book value and Market value
- Difference Between Red and White wine
- Difference Between Depreciation and Amortization
- Difference Between Bank and Credit Union
- Difference Between White Eggs and Brown Eggs
Newly Launched - AI Presentation Maker

AI PPT Maker
Powerpoint Templates
PPT Bundles
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories

Basic vs applied research ppt powerpoint presentation layouts portfolio cpb
Our Basic VS Applied Research Ppt Powerpoint Presentation Layouts Portfolio Cpb are topically designed to provide an attractive backdrop to any subject. Use them to look like a presentation pro.

- Add a user to your subscription for free
You must be logged in to download this presentation.
PowerPoint presentation slides
Presenting our Basic VS Applied Research Ppt Powerpoint Presentation Layouts Portfolio Cpb PowerPoint template design. This PowerPoint slide showcases five stages. It is useful to share insightful information on Basic VS Applied Research. This PPT slide can be easily accessed in standard screen and widescreen aspect ratios. It is also available in various formats like PDF, PNG, and JPG. Not only this, the PowerPoint slideshow is completely editable and you can effortlessly modify the font size, font type, and shapes according to your wish. Our PPT layout is compatible with Google Slides as well, so download and edit it as per your knowledge.

People who downloaded this PowerPoint presentation also viewed the following :
- Diagrams , Business , Strategy , Icons , Business Slides , Flat Designs , Linear Process Diagrams , Process Management
- Basic VS Applied Research
Basic vs applied research ppt powerpoint presentation layouts portfolio cpb with all 6 slides:
Use our Basic VS Applied Research Ppt Powerpoint Presentation Layouts Portfolio Cpb to effectively help you save your valuable time. They are readymade to fit into any presentation structure.
Ratings and Reviews
by Coleman Henderson
March 18, 2022
by Devon Ferguson
March 17, 2022


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Basic Research Identify functional relationships or regularities May not have immediate relevance Critical to the survival of applied research. Applied Research Aimed to solve problems, help clients Based on basic research. Types of research: Basic vs. Applied. Slideshow 6525966 by gail-wilson.
There are two types of research: Basic and Applied. Basic Research: Is traditional research or "pure". It is carried out to advance knowledge. It develops theory. It focuses on a scholar audience. Applied Research: It is used more and more in recent years. It tests theory in real life.
While applied research is more experimental or confirmatory, a basic research approach is often exploratory or explanatory in nature. Basic research methods include ethnography, in-depth interviews, or longitudinal studies to gain a deep understanding of a topic. The focus is on generating theories and understanding patterns.
Presentation on theme: "Basic vs. applied research"— Presentation transcript: 1 Basic vs. applied research. 2 Similarities and differences Both use scientific method Differ in: Goals Audience Problems. 3 Examples of how they can go together Brockner, Grover, Reed, DeWitt, & O'Malley, 1987 ...
The two are like siblings—different in personality but stemming from the same family of intellectual inquiry. Basic research is theoretical and often provides the foundation for applied research. On the flip side, applied research is practical in nature and focuses on solving immediate real-world problems.
DeCarlo and his team developed a complete package of materials that includes a textbook, ancillary materials, and a student workbook as part of a VIVA Open Course Grant. The PowerPoint slides associated with the twelve lessons of the course, SOWK 621.01: Research I: Basic Research Methodology, as previously taught by Dr. Matthew DeCarlo at ...
Basic research is generally conducted to learn more about a specific subject. It is usually self-initiated to gain knowledge to satisfy curiosity or confirm a theory. Conversely, applied knowledge is directed toward finding a solution to a specific problem. It is often conducted to assist a client in improving products, services, or issues.
The applicability of basic research is greater than the applied research, in the sense that the former is universally applicable whereas the latter can be applied only to the specific problem, for which it was carried out. The primary concern of the basic research is to develop scientific knowledge and predictions.
Researchers can harness our customizable PPT to explain that fundamental research is driven by curiosity to uncover underlying principles without an immediate practical application in mind. In contrast, applied research takes into account the existing scientific principles, knowledge, or theories and applies them to practical situations or ...
Basic research is theoretical in nature while applied research is practical in nature. In this sense, basic research generates theories and improves on existing theories with the aim of contributing to an existing knowledge bank. Applied research, on the other hand, is practical and more descriptive in nature.
Basic research is theoretical in nature while applied research is practical; hence, it is associated with technology. As compared to applied research, basic research has a wider scope. While basic research predicts future phenomena, applied research creates solutions or preventions for probable problems. Basic research is curiosity-driven while ...
Presenting our Basic VS Applied Research Ppt Powerpoint Presentation Layouts Portfolio Cpb PowerPoint template design. This PowerPoint slide showcases five stages. It is useful to share insightful information on Basic VS Applied Research. This PPT slide can be easily accessed in standard screen and widescreen aspect ratios.
Applied Research. * exploratory. * concentrates on the need to advance knowledge. * lays the foundation for applied research. chain sampling. * descriptive. * aims to solve a specific question or problem. * an investigation of the findings of basic research. referral sampling.