Presentory for Windows
Presentory for mac, presentory online.
Rebrand your approach to conveying ideas.
Differentiate your classroom and engage everyone with the power of AI.

Knowledge Sharing
Create inspiring, fun, and meaningful hybrid learning experiences
Create with AI
- AI Tools Tips
Presentation Ideas
- Presentation Topics
- Presentation Elements
- Presentation Software
- PowerPoint Tips
Presentation Templates
- Template Sites
- Template Themes
- Design Ideas
Use Presentory Better
- Creator Hub

More Details
- Basic Knowledge
- Creative Skills
- Inspirational Ideas
Find More Answers
- LOG IN SIGN UP FOR FREE
- A Beginner's Guide to Giving an Oral Presentation

- How to Use Keynote Remote to Control Presentation from iPhone, iPad, or Apple Watch
- 10 Best Sites for Keynote Presentation Templates
- Detailed Explanation of Presentation Tips and Speaking Techniques
- A Comprehensive Guide to Convert PPT to Video with Sound
- Effective Communication and PPT Presentation Skills for HR Managers
- Proven Tips For Better Presentation Writing
- Where Should You Take Your Public Speaking Skills Classes [2024]
- Delivering a Good Interview Presentation With Confidence
- Transforming Leaders Through Executive Presentation Skills
- How To Face the Fear of Public Speaking Classes
- Full Guide To Captivate Your Audience With Good Presentation Qualities
- Techniques for Delivering Good Oral Presentations
- 10 Useful PowerPoint Animation Tips in 2023
- Learn and Explore 5 Best Comparison Slides Templates
- A Comprehensive Guide to Creating Mind Maps in PowerPoint
- A Complete Guide to SWOT Analysis PPT For Proper Professional Growth
- Get The Finest Idea of Designing Perfect Roadmap Templates in No Time!
- How to Create Venn Diagram in PowerPoint, Google Docs, and Google Slides
- Elaborating The Unique Ways of How to Create a Timeline in PowerPoint
- Compelling Presentations: The Essential 5 PPT Elements for Engagement
- Unveiling the Key Elements of a Dynamic and Impactful Presentation
- Mastering Presentation Excellence With Efficient Elements: A How-To Guide
- Everything You Need to Know About the Table of Contents of PowerPoint
- How to Create PowerPoint Presentations with ChatGPT [2023 Update]
- How is AI Revolutionizing Presentations? (Tips & Tool)
- Top 14 AI Presentation Makers in August 2023 [Free & Paid]
- How To Add Animations and Transitions In Google Slides
- How to Use Slides Changing Remote to Control Presentation from Mobile Devices
- Over 100 Inspiring Google Slides Themes and Ideas for Every Occasion
- What is Google Slides? A Comprehensive Guide to Practical Usage
- How to easily import themes into Google Slides
- 10 free and aesthetic Google Slides templates sites
- How to Convert Google Slides to Video? [5 Methods]
- A Comprehensive Guide to Adding Video to Google Slides [Easy Navigation]
- How to Add Slide Transitions in PowerPoint?
- How to Use PowerPoint Morph Transition in 2023
- How to Control Your PowerPoint by Using an Apple Watch?
- How to Enhance Your PowerPoint Presentations with 3D Models
- An In-Depth Guide to Using PowerPoint
- Mastering Slide Transitions in Flutter: A Comprehensive Guide
- Tutorial | How to user Slide Master in PowerPoint
- How to Record Your Screen in PowerPoint? [3 Ways]
- How to Convert PowerPoint to Video Conversion on Windows and macOS?
- How to Add Video to PowerPoint from YouTube and Local Path
- 8 Ways to Solve “PPT Cannot Play Media”
- Top Guide to Play Video Automatically in PowerPoint
Giving an oral presentation is a common part of any business, whether you’re talking to colleagues, clients, or partners. It’s your chance to persuade, inform, or update them. But rushing in unprepared can lead to less-than-stellar results. So, the key to achieving your objective, whatever it may be, depends on one thing: preparation.
This guide is here to help you dedicate the necessary time to make and rehearse your presentation. With the right approach, you’ll deliver an effective oral presentation PPT that leaves a lasting impression. Now, get ready to transform your next meeting into a confident and persuasive experience.
In this article
Part i: what is oral presentation in business communication, informative presentations, instructive presentations, persuasive presentations, sales deck presentations, product marketing presentations, training and development presentations, data-driven presentations, progress report presentations, pitch deck presentations, demonstrations, blackout unnecessary slides, speak slower to avoid filler words, use ai presentation generator, complement texts with visuals, engage your audience.
An oral presentation is a form of verbal communication delivered to an audience. It is a way to share information, persuade them of an idea, or keep them updated. Visual aids like slides, handouts, or demonstrations often support a speaking presentation.
Oral presentations in business communication have several purposes. These include explaining new projects, pitching client ideas, or delivering team updates. Depending on what works, you can do it solo or with a team and keep it short or long.
However, an effective oral presentation doesn’t just happen on its own.
When making oral presentations, ensure they are well-organized, informative, and engaging. They follow a clear structure, with an introduction, body, and conclusion. You should also be confident, enthusiastic, and able to connect with the audience on a personal level.

Now that we’ve laid the groundwork for business oral presentations, let’s dive into the different types you’ll come across. The next part will uncover a variety of business presentations, each with its own goal.
Part II: 10 Different Types of Presentations in Business
Not all speaking presentations are the same. Different business situations call for different styles. Before you think of what you’ll say, figure out which presentation type works best for your audience. Here are the common types of business presentations you can give:
Informative presentations aim to equip attendees with knowledge of a chosen theme. Imagine presenting industry trends to your team or explaining a new company policy. These business presentations focus on clear communication and factual accuracy.
The instructive presentation aims to equip the audience with skills or knowledge they can apply practically. Think of a training session on using a new software program or a workshop on effective negotiation. This business presentation focus shifts to step-by-step guidance and practical exercises.
In a persuasive oral presentation, the goal is to win people over to your viewpoint. Be it convincing investors or pitching a new marketing plan, the deal is to build a solid case. You want compelling arguments, strong data, and a clear call to action.
Designed for sealing the deal, using a sales deck for your oral presentation highlights the value of a product or service. It emphasizes features, benefits, and why it’s better, all while tackling possible concerns. Salespeople often pull these out in client meetings or when pitching to investors.
A product marketing presentation focuses on creating awareness and excitement about a product. It targets a broader audience, not just potential customers, and aims to generate interest and brand recognition. Think of product launches, industry conferences, or social media marketing campaigns.
Training presentations are crucial for giving employees the skills they need. Whether it’s welcoming new hires or boosting leadership skills, the format changes based on the context. Usually, there’s a mix of instruction, practice, and chances to ask questions. You can use this for your oral presentation to ensure everyone’s up to speed in a way that works.

In data-driven presentations, facts and stats take the spotlight. You can add visuals for research, market trends, or data-backed solutions when making oral presentations. The trick is turning complex info into a clear, punchy story with eye-catching charts.
A progress report presentation updates a project, initiative, or campaign. They often involve data and metrics to show progress toward goals and objectives. These business presentations are crucial for maintaining transparency and building trust among stakeholders.
The pitch deck presentation hustles to get funding for a fresh business idea. Picture quick pitches, like selling your vision to venture capitalists. They zoom in on the problem you’re solving, what makes you stand out, and the promise of success. It’s all about packing a punch quickly to make your oral presentation stick.
These oral presentations go beyond words – they show it in action. Whether it’s software, new gear, or tricky procedures, the focus is on demonstrating. It’s a powerful way for the audience to see exactly how things work and throw in questions for a clearer picture.
Knowing the types of business presentations available is crucial. The next section will empower you to deliver effective oral presentations, regardless of your chosen format.
Part III: Techniques for Giving an Effective Oral Presentation
So, you’ve crafted an amazing presentation deck that captures your vision. Or you are starting with an idea for the oral presentation. Now comes the real challenge: delivering it in a way that grabs attention and keeps everyone hooked. Let’s explore some oral presentation techniques to make it a captivating experience.
Imagine a screen packed with text. Boring. No one wants to read a novel on a slide. Instead, blackout slides that reiterate points you’ll cover verbally. Focus on primary points and leave the details for handouts.
Speaking and presenting too fast can sound rushed and nervous. Slow down your pace and articulate clearly. It allows the audience to absorb your message and creates a sense of confidence. Plus, it helps you avoid filler words like “um” and “uh” that can distract from your message.
We all know you’re passionate about your business idea. However, securing investment requires captivating investors and presenting a vision that resonates deeply. Making a compelling pitch deck traditionally meant long hours of wrestling with design software and agonizing over content.
But what if you could lessen the time to create an oral presentation PPT to a few minutes?
Tools like AI presentation generators can help with structure and flow and even suggest visuals. Wondershare Presentory is one of the best in the market that can help automatically create a starting point for your slides. It makes an initial outline for your review. Then, Presentory generates stunning presentations with text, formatting, and imagery in PPT format. All these are based on a keyword or your topic.
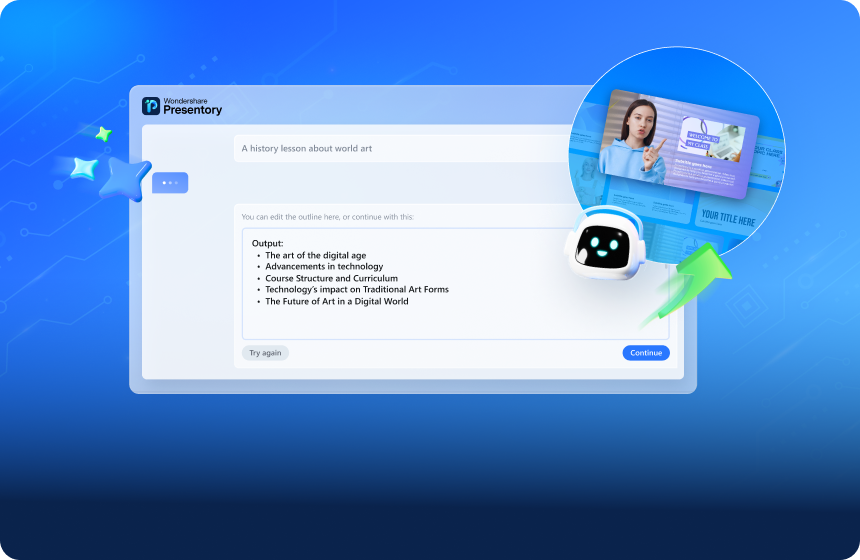
Presentory is valuable for busy professionals and people who need to save time without compromising quality. But it doesn’t stop boosting your work efficiency here. This tool also empowers you to customize the design and content of the AI-generated oral presentation PPT. Furthermore, Presentory offers several additional benefits:
- Online and desktop access: Work on the go. This app lets you access your presentations online or offline, allowing you to work from anywhere.
- Personalized design: Make it your own. This app gives you the tools to customize your slides with layouts and templates that feel fresh and engaging.
- Content optimization: Presentory not only generates content. It also provides suggestions for improvement, ensuring professionalism and persuasiveness.
- Ease of use: No design skills? No problem. This app is user-friendly, and anyone can create professional-looking presentations in no time.
- Integration of resources: Level up your PPT slides. The built-in AI helps you find high-quality images and graphics to make your presentation pop.
- One-click streaming: Reach your audience across platforms. Presentory allows you to stream your oral presentation on Teams, YouTube Live, Facebook Live, Google Meet, and more platforms.
- Enhanced visuals: Import pictures and videos or add animations for a more dynamic presentation.
- Recording: Get your presentation ready for the big day. Use the teleprompter to record yourself practicing and feeling confident.
How To Make an Effective Oral Presentation PPT Using AI?
Presentory empowers you to focus on the speaking and presentation aspects while the AI takes care of the rest. Follow these steps below to create an effective oral presentation PPT for free online:
Step 1: Open the Wondershare Presentory app dashboard in your web browser. Sign in with your Google Account or create a new one.

Step 2: Click Create Presentation AI from the Home page to start.
Step 3: Select Begin with a topic to use AI and generate an outline.

Step 4: Enter your topic in the text box, then click Continue to let AI create the content outline. You can also select from one of the suggested keywords to explore first.

Step 5: Review the AI-generated outline and click Continue if satisfied.

Step 6: Select a template you want to use for the presentation, then click Generating to apply.

Step 7: Tailor your presentation. Edit text, switch slides, add images, and experiment with different layouts and themes to personalize your presentation.

Step 8: Click Share from the upper navigation pane, choose the file format from the pop-up window, then click Export presentation to save the PPT.

Images, infographics, and videos are powerful tools to engage your audience and reinforce your message during oral presentations. But don’t just throw random visuals in there. They should complement your words, not replace them. Choose visuals that are clear, relevant, and support your points.
Giving oral presentations shouldn’t be one-sided lectures. Get your audience involved. Ask questions, encourage participation, and invite discussion. Maybe even throw in a poll or a quick activity to keep them on their toes. Remember, your goal is to present information, connect with your audience, and make them care about your message.
You’ve got the ideas, the passion, the drive. But when it comes to giving an oral presentation , the pressure’s on. Traditional presentation tools can be time-consuming. Relying solely on “best practices” might leave you blending into the background. You need an edge, a way to grab attention and captivate your audience from the get-go.
However, making a compelling oral presentation PPT often takes time and expertise. That’s why you need to incorporate AI tools into your workflow. Try Wondershare Presentory - it is your partner in business communication success. Start creating presentations that win today.
You May Also Like
Related articles.

IMAGES
VIDEO