
How is a hypothesis tested quizlet?
We evaluate hypotheses by using sample statistics about population parameters and all statistical tests assume “random sampling.” A substantive hypothesis expressed in terms of population parameters. We use our sample statistics to make statements about population parameters.
Table of Contents
What is a hypothesis in biology quizlet?
Hypothesis. is a scientific explanation for a set of observations that can be tested in ways that support or reject it.
How do you test a hypothesis in biology?
Experiments and further observations are often used to test the hypotheses. A scientific experiment is a carefully organized procedure in which the scientist intervenes in a system to change something, then observes the result of the change. Scientific inquiry often involves doing experiments, though not always.
What is a hypothesis biology?
Most commonly in scientific research, a hypothesis is a tentative, testable, and falsifiable statement that explains some observed phenomenon in nature. We more specifically call this kind of statement an explanatory hypothesis.
What is hypothesis in research quizlet?
A research hypothesis is a. specific, precise, testable, and falsifiable prediction about the relationship between 2 or more variables: a precise statement of the presumed relationship among specific parts of a theory.
Which type of reasoning is used in hypothesis testing quizlet?
Deductive reasoning or deduction is the type of logic used in hypothesis-based science.
In what two ways can a hypothesis be tested?
A hypothesis can be tested in two ways: a controlled experiment or by gathering more information.
What is a hypothesis simple definition?
A hypothesis (plural: hypotheses), in a scientific context, is a testable statement about the relationship between two or more variables or a proposed explanation for some observed phenomenon.
What is the purpose of a hypothesis quizlet?
What is the purpose of a hypothesis for any study? To provide direction for research by identifying the expected outcome. A hypothesis posed as a declarative statement predicts an expected outcome.
What is the best way to test hypothesis?
The most common way to test a hypothesis is to create an experiment. A good experiment uses test subjects or creates conditions where you can see if your hypothesis seems to be true by evaluating a broad range of data (test results).
How do you test a hypothesis in data science?
- Start with specifying Null and Alternative Hypotheses about a population parameter.
- Set the level of significance (α)
- Collect Sample data and calculate the Test Statistic and P-value by running a Hypothesis test that well suits our data.
What is the test for whether a hypothesis is scientific or not?
What is the test for whether a hypothesis is scientific or not? A hypothesis is scientific if it is possible to prove it wrong. If one cannot be proved wrong, it cannot be proved right, and is then “speculation”.
What makes a hypothesis testable?
To be considered testable, some essential criteria must be met: There must be a possibility to prove that the hypothesis is true. There must be a possibility to prove that the hypothesis is false. The results of the hypothesis must be reproducible.
What is a hypothesis in biology examples?
For example, a scientist can form a hypothesis stating that if a certain type of tomato has a gene for red pigment, that type of tomato will be red. During research, the scientist then finds that each tomato of this type is red.
What is a simple hypothesis quizlet?
Simple hypothesis. A statement explaining and or predicting a relationship between one independent and one dependent variable. Variable. A measurable characteristic that varies among the subjects being studied. Hypothesis.
What is a characteristic of a hypothesis quizlet?
has to state the direction of the expected relationship. consistency. the hypothesis is consistent with the data and with how you plan to test it. testability. data should be feasible to obtain and would indicate if the hypothesis is defensible.

What is meant by a hypothesis quizlet astronomy?
hypothesis. a testable idea that explains an observation about nature.
How is deductive reasoning tested?
A deductive reasoning test is intended to be abstract – it does not need specific job-related skills, nor does it need any culturally specific knowledge. All the information that you need to answer the question correctly is provided in the test, and there is only one answer that is correct.
What is the logical basis for hypothesis testing?
The Logic of Hypothesis Testing As just stated, the logic of hypothesis testing in statistics involves four steps. State the Hypothesis: We state a hypothesis (guess) about a population. Usually the hypothesis concerns the value of a population parameter.
What is reasoning in biology?
However, at a simpler level, “reasoning” is derived from “reason,” and implies exploration of the causality of events. Biological reasoning also involves searching (and researching) the causes of biological phenomena, including human diseases.
What are four ways to test a hypothesis?
- State the hypotheses. Every hypothesis test requires the analyst to state a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis.
- Formulate an analysis plan. The analysis plan describes how to use sample data to accept or reject the null hypothesis.
- Analyze sample data.
- Interpret the results.
How hypothesis is formed?
Try to imagine possible solutions to explain your observations. Once you come up with a possible explanation, ask yourself if it could be proven wrong by an experiment. If it could be proven wrong, then you have formed a hypothesis.
What is the method of hypothesis?
In science, a hypothesis is part of the scientific method . It is a prediction or explanation that is tested by an experiment. Observations and experiments may disprove a scientific hypothesis, but can never entirely prove one.
What is a hypothesis quizlet psychology?
Hypothesis A tentative and testable explanation of the relationship between two (or more) events or variables; often stated as a prediction that a certain outcome will result from specific conditions. Confirmation Bias.
What is a purpose of a hypothesis?
The Purpose of a Hypothesis A hypothesis is used in an experiment to define the relationship between two variables. The purpose of a hypothesis is to find the answer to a question.
Craving More Content?
Read our latest blog posts
What are the different approaches to personality.
There are four major theoretical approaches to the study of personality. Psychologists call them the psychoanalytic, trait, humanistic and social cognition approaches. What is the biological…
Why are enzymes called biological catalysts?
The enzymes are called biocatalyst because it increases the speed of biochemical reaction in an organism. As, the enzymes accelerate the chemical reaction, without changing the…
Are adopted children more like their biological parents or adoptive parents?
In terms of weight, adopted children tend to resemble their biological parents more than they do their adoptive parents. Are adopted children like their biological parents?…
Notifications
- Science, Tech, Math ›
- Chemistry ›
Scientific Hypothesis, Model, Theory, and Law
Understanding the Difference Between Basic Scientific Terms
Hero Images / Getty Images
- Chemical Laws
- Periodic Table
- Projects & Experiments
- Scientific Method
- Biochemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Medical Chemistry
- Chemistry In Everyday Life
- Famous Chemists
- Activities for Kids
- Abbreviations & Acronyms
- Weather & Climate
- Ph.D., Biomedical Sciences, University of Tennessee at Knoxville
- B.A., Physics and Mathematics, Hastings College
Words have precise meanings in science. For example, "theory," "law," and "hypothesis" don't all mean the same thing. Outside of science, you might say something is "just a theory," meaning it's a supposition that may or may not be true. In science, however, a theory is an explanation that generally is accepted to be true. Here's a closer look at these important, commonly misused terms.
A hypothesis is an educated guess, based on observation. It's a prediction of cause and effect. Usually, a hypothesis can be supported or refuted through experimentation or more observation. A hypothesis can be disproven but not proven to be true.
Example: If you see no difference in the cleaning ability of various laundry detergents, you might hypothesize that cleaning effectiveness is not affected by which detergent you use. This hypothesis can be disproven if you observe a stain is removed by one detergent and not another. On the other hand, you cannot prove the hypothesis. Even if you never see a difference in the cleanliness of your clothes after trying 1,000 detergents, there might be one more you haven't tried that could be different.
Scientists often construct models to help explain complex concepts. These can be physical models like a model volcano or atom or conceptual models like predictive weather algorithms. A model doesn't contain all the details of the real deal, but it should include observations known to be valid.
Example: The Bohr model shows electrons orbiting the atomic nucleus, much the same way as the way planets revolve around the sun. In reality, the movement of electrons is complicated but the model makes it clear that protons and neutrons form a nucleus and electrons tend to move around outside the nucleus.
A scientific theory summarizes a hypothesis or group of hypotheses that have been supported with repeated testing. A theory is valid as long as there is no evidence to dispute it. Therefore, theories can be disproven. Basically, if evidence accumulates to support a hypothesis, then the hypothesis can become accepted as a good explanation of a phenomenon. One definition of a theory is to say that it's an accepted hypothesis.
Example: It is known that on June 30, 1908, in Tunguska, Siberia, there was an explosion equivalent to the detonation of about 15 million tons of TNT. Many hypotheses have been proposed for what caused the explosion. It was theorized that the explosion was caused by a natural extraterrestrial phenomenon , and was not caused by man. Is this theory a fact? No. The event is a recorded fact. Is this theory, generally accepted to be true, based on evidence to-date? Yes. Can this theory be shown to be false and be discarded? Yes.
A scientific law generalizes a body of observations. At the time it's made, no exceptions have been found to a law. Scientific laws explain things but they do not describe them. One way to tell a law and a theory apart is to ask if the description gives you the means to explain "why." The word "law" is used less and less in science, as many laws are only true under limited circumstances.
Example: Consider Newton's Law of Gravity . Newton could use this law to predict the behavior of a dropped object but he couldn't explain why it happened.
As you can see, there is no "proof" or absolute "truth" in science. The closest we get are facts, which are indisputable observations. Note, however, if you define proof as arriving at a logical conclusion, based on the evidence, then there is "proof" in science. Some work under the definition that to prove something implies it can never be wrong, which is different. If you're asked to define the terms hypothesis, theory, and law, keep in mind the definitions of proof and of these words can vary slightly depending on the scientific discipline. What's important is to realize they don't all mean the same thing and cannot be used interchangeably.
- Scientific Method Lesson Plan
- What Is an Experiment? Definition and Design
- How To Design a Science Fair Experiment
- Chemistry 101 - Introduction & Index of Topics
- What Is the Difference Between Hard and Soft Science?
- What Is a Control Group?
- Henry's Law Definition
- Chemistry Vocabulary Terms
- Hess's Law Definition
- What Does pH Stand For?
- How to Write a Lab Report
- What Is Chemical Engineering?
- Teach Yourself Chemistry Today
- Check Out These Chemistry Career Options Before You Get a Degree
- Here's How to Calculate pH Values
- Setting Up a Home Chemistry Lab
- For educators
- English (US)
- English (India)
- English (UK)
- Greek Alphabet
This problem has been solved!
You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts.
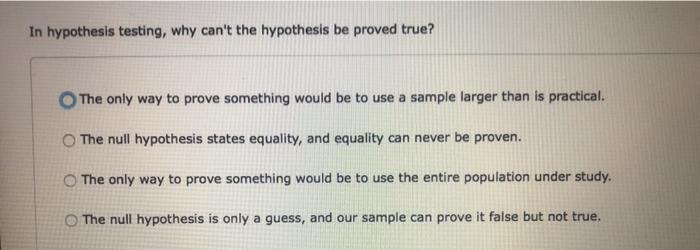
Question: In hypothesis testing, why can't the hypothesis be proved true? The only way to prove something would be to use a sample larger than is practical. The null hypothesis states equality, and equality can never be proven. The only way to prove something would be to use the entire population under study. The null hypothesis is only a guess, and our sample can
Not the question you’re looking for?
Post any question and get expert help quickly.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Answer: B A) You can prove a hypothesis to be true. B) You can accept or reject a hypothesis, but never prove it to be true. C) You can prove a hypothesis to be false. D) Accepting or rejecting a hypothesis is the same thing as proving whether or not the hypothesis is true.
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like null hypothesis, alternative hypothesis, can you prove a hypothesis? and more.
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Can you prove a hypothesis?, a group of similar cells working together to perform a specific function is a, what is the advantage of using a chart or graph rather than a table and more.
Mar 6, 2017 · You can accept or reject a hypothesis, but never truly prove it to be true. You can prove a hypothesis to be true. Accepting or rejecting a hypothesis is the same as proving whether or not the hypothesis is true.
Nov 18, 2019 · When a research hypothesis stands the test of time, it can then develop into a theory. Is it possible to prove a null hypothesis? In statistics, the only way of supporting your hypothesis is to refute the null hypothesis. A null hypothesis is a working hypothesis that is to be disproved by a statistical test in favour of the alternative hypothesis.
Sep 15, 2022 · Observations and experiments may disprove a scientific hypothesis, but can never entirely prove one. What is a hypothesis quizlet psychology? Hypothesis A tentative and testable explanation of the relationship between two (or more) events or variables; often stated as a prediction that a certain outcome will result from specific conditions.
Sep 1, 2022 · The answer depends on whether you are using a pre-defined critical value (or p-value threshold like p<0.05) in a hypothesis test that yields a decision (a Neyman–Pearsonian hypothesis test), or whether you are using the magnitude of the actual p-value as an index of the evidence in the data (a [neo-]Fisherian significance test).
But you got the main problem: I would say that a Bayesian approach could work if you can Prove that you're randomly sampling, and that you had sampled enough in order to be 100% sure that, if it existed, you could have sampled the right sample which falsify your hypothesis. Which, again, impossible.
Nov 5, 2019 · This hypothesis can be disproven if you observe a stain is removed by one detergent and not another. On the other hand, you cannot prove the hypothesis. Even if you never see a difference in the cleanliness of your clothes after trying 1,000 detergents, there might be one more you haven't tried that could be different.
The only way to prove something would be to use a sample larger than is practical. The null hypothesis states equality, and equality can never be proven. The only way to prove something would be to use the entire population under study. The null hypothesis is only a guess, and our sample can prove it false but not true.