This browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.

Assignment operators (C# reference)
- 11 contributors
The assignment operator = assigns the value of its right-hand operand to a variable, a property , or an indexer element given by its left-hand operand. The result of an assignment expression is the value assigned to the left-hand operand. The type of the right-hand operand must be the same as the type of the left-hand operand or implicitly convertible to it.
The assignment operator = is right-associative, that is, an expression of the form
Is evaluated as
The following example demonstrates the usage of the assignment operator with a local variable, a property, and an indexer element as its left-hand operand:
The left-hand operand of an assignment receives the value of the right-hand operand. When the operands are of value types , assignment copies the contents of the right-hand operand. When the operands are of reference types , assignment copies the reference to the object.
This operation is called value assignment : the value is assigned.
ref assignment
Ref assignment = ref makes its left-hand operand an alias to the right-hand operand, as the following example demonstrates:
In the preceding example, the local reference variable arrayElement is initialized as an alias to the first array element. Then, it's ref reassigned to refer to the last array element. As it's an alias, when you update its value with an ordinary assignment operator = , the corresponding array element is also updated.
The left-hand operand of ref assignment can be a local reference variable , a ref field , and a ref , out , or in method parameter. Both operands must be of the same type.
A ref assignment means that a reference variable has a different referrent. It's no longer referring to its previous referrent. Using ref = on a ref parameter means the parameter no longer refers to its argument. Any actions that modify the state of the object after ref reassigning it make those modifications to the new item. For example, consider the following method:
The following usage shows that the assignment to the parameter s isn't visible after the method call because s was ref reassigned to refer to sLocal before the string was modified:
Compound assignment
For a binary operator op , a compound assignment expression of the form
Is equivalent to
Except that x is only evaluated once.
The arithmetic , Boolean logical , and bitwise logical and shift operators all support compount assignment.
Null-coalescing assignment
You can use the null-coalescing assignment operator ??= to assign the value of its right-hand operand to its left-hand operand only if the left-hand operand evaluates to null . For more information, see the ?? and ??= operators article.
Operator overloadability
A user-defined type can't overload the assignment operator. However, a user-defined type can define an implicit conversion to another type. That way, the value of a user-defined type can be assigned to a variable, a property, or an indexer element of another type. For more information, see User-defined conversion operators .
A user-defined type can't explicitly overload a compound assignment operator. However, if a user-defined type overloads a binary operator op , the op= operator, if it exists, is also implicitly overloaded.
C# language specification
For more information, see the Assignment operators section of the C# language specification .
- C# operators and expressions
- ref keyword
- Use compound assignment (style rules IDE0054 and IDE0074)
Additional resources

- C# Basic Tutorial
- C# - Overview
- C# - Environment
- C# - Program Structure
- C# - Basic Syntax
- C# - Data Types
- C# - Type Conversion
- C# - Variables
- C# - Constants
- C# - Operators
- C# - Decision Making
- C# - Encapsulation
- C# - Methods
- C# - Nullables
- C# - Arrays
- C# - Strings
- C# - Structure
- C# - Classes
- C# - Inheritance
- C# - Polymorphism
- C# - Operator Overloading
- C# - Interfaces
- C# - Namespaces
- C# - Preprocessor Directives
- C# - Regular Expressions
- C# - Exception Handling
- C# - File I/O
- C# Advanced Tutorial
- C# - Attributes
- C# - Reflection
- C# - Properties
- C# - Indexers
- C# - Delegates
- C# - Events
- C# - Collections
- C# - Generics
- C# - Anonymous Methods
- C# - Unsafe Codes
- C# - Multithreading
- C# Useful Resources
- C# - Questions and Answers
- C# - Quick Guide
- C# - Useful Resources
- C# - Discussion
- Selected Reading
- UPSC IAS Exams Notes
- Developer's Best Practices
- Questions and Answers
- Effective Resume Writing
- HR Interview Questions
- Computer Glossary
C# - Assignment Operators
There are following assignment operators supported by C# −
The following example demonstrates all the assignment operators available in C# −
When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result −
C# Tutorial
C# examples, c# assignment operators, assignment operators.
Assignment operators are used to assign values to variables.
In the example below, we use the assignment operator ( = ) to assign the value 10 to a variable called x :
Try it Yourself »
The addition assignment operator ( += ) adds a value to a variable:
A list of all assignment operators:

COLOR PICKER

Contact Sales
If you want to use W3Schools services as an educational institution, team or enterprise, send us an e-mail: [email protected]
Report Error
If you want to report an error, or if you want to make a suggestion, send us an e-mail: [email protected]
Top Tutorials
Top references, top examples, get certified.

C# Assignment Operators with Examples
In c#, Assignment Operators are useful to assign a new value to the operand, and these operators will work with only one operand.
For example, we can declare and assign a value to the variable using the assignment operator ( = ) like as shown below.
If you observe the above sample, we defined a variable called “ a ” and assigned a new value using an assignment operator ( = ) based on our requirements.
The following table lists the different types of operators available in c# assignment operators.
C# Assignment Operators Example
Following is the example of using assignment Operators in the c# programming language.
If you observe the above example, we defined a variable or operand “ x ” and assigning new values to that variable by using assignment operators in the c# programming language.
Output of C# Assignment Operators Example
When we execute the above c# program, we will get the result as shown below.

This is how we can use assignment operators in c# to assign new values to the variable based on our requirements.
Table of Contents
- Assignment Operators in C# with Examples
- C# Assignment Operator Example
- Output of C# Assignment Operator Example

- Data Structure
- Coding Problems
- C Interview Programs
- C++ Aptitude
- Java Aptitude
- C# Aptitude
- PHP Aptitude
- Linux Aptitude
- DBMS Aptitude
- Networking Aptitude
- AI Aptitude
- MIS Executive
- Web Technologie MCQs
- CS Subjects MCQs
- Databases MCQs
- Programming MCQs
- Testing Software MCQs
- Digital Mktg Subjects MCQs
- Cloud Computing S/W MCQs
- Engineering Subjects MCQs
- Commerce MCQs
- More MCQs...
- Machine Learning/AI
- Operating System
- Computer Network
- Software Engineering
- Discrete Mathematics
- Digital Electronics
- Data Mining
- Embedded Systems
- Cryptography
- CS Fundamental
- More Tutorials...
- Tech Articles
- Code Examples
- Programmer's Calculator
- XML Sitemap Generator
- Tools & Generators

Home » .Net » C# Programs
C# Assignment Operators Example
C# example for assignment operators: Here, we are writing a C# program to demonstrate example of all assignment operators. By IncludeHelp Last updated : April 15, 2023
Assignment Operators
Assignment operators (Assignment ( = ) and compound assignments ( += , -+ , *= , /= , %= )) are used to assign the value or an expression's result to the left side variable, following are the set of assignment operators,
- "=" – it is used to assign value or an expression's result to the left side variable
- "+=" – it is used to add second operand to the existing operand's value and assigns it back (a+=b is equal to a=a+b)
- "-=" – it is used to subtract second operand from the existing operand's value and assigns it back (a-=b is equal to a=a-b)
- "/=" – it is used to divide second operand from the existing operand's value and assigns it back (a/=b is equal to a=a+b)
- "*=" – it is used to multiply second operand with the existing operand's value and assigns it back (a*=b is equal to a=a*b)
- "%=" – it is used to get the remainder by dividing second operand with the existing operand's value and assigns it back (a%=b is equal to a=a%b)
C# code to demonstrate the example of assignment operators
C# Basic Programs »
Related Programs
- C# program to print messages/text (program to print Hello world)
- C# program to demonstrate example of Console.Write() and Console.WriteLine()
- C# program to print a new line
- C# program to print backslash (\)
- C# program to demonstrate the example of New keyword
- C# program to print size of various data types
- C# program for type conversion from double to int
- C# program to convert various data type to string using ToString() method
- C# program to define various types of constants
- C# program to declare different types of variables, assign the values and print
- C# program to input and print an integer number
- C# program to demonstrate example of arithmetic operators
- C# program to demonstrate example of sizeof() operator
- C# program to demonstrate example of equal to and not equal to operators
- C# program to demonstrate example of relational operators
- C# program to demonstrate example of bitwise operators
- C# program to find the addition of two integer numbers
- C# program to swap two numbers with and without using third variable
- C# | print type, max and min value of various data types
- C# program to swap numbers using XOR operator
- C# program to find the magnitude of an integer number
- C# program to demonstrate the example of the left-shift operator
- C# program to demonstrate the example of the right shift operator
- C# program to read the grade of students and print the appropriate description of grade
- C# program to calculate the size of the area in square-feet based on specified length and width
- C# program to find the division of exponents of the same base
- C# program to demonstrate the example goto statement
- C# program to print a message without using the WriteLine() method
- C# program to convert a binary number into a decimal number
- C# program to convert a decimal number into a binary number
- C# program to convert a decimal number into an octal number
- C# program to convert a hexadecimal number into a decimal number
- C# program to convert a decimal number into a hexadecimal number
- C# program to convert a meter into kilo-meter and vice versa
- C# program to convert a temperature from Celsius to Fahrenheit
- C# program to convert a temperature from Fahrenheit into Celsius
- C# program to create gray code
- C# program to change the case of entered character
- C# program to convert entered days into years, weeks, and days
Comments and Discussions!
Load comments ↻
- Marketing MCQs
- Blockchain MCQs
- Artificial Intelligence MCQs
- Data Analytics & Visualization MCQs
- Python MCQs
- C++ Programs
- Python Programs
- Java Programs
- D.S. Programs
- Golang Programs
- C# Programs
- JavaScript Examples
- jQuery Examples
- CSS Examples
- C++ Tutorial
- Python Tutorial
- ML/AI Tutorial
- MIS Tutorial
- Software Engineering Tutorial
- Scala Tutorial
- Privacy policy
- Certificates
- Content Writers of the Month
Copyright © 2024 www.includehelp.com. All rights reserved.

Operators in C#
Back to: C#.NET Tutorials For Beginners and Professionals
Operators in C# with Examples
In this article, I am going to discuss Operators in C# with Examples. Please read our previous article, where we discussed Variables in C# with Examples. The Operators are the foundation of any programming language. Thus, the functionality of the C# language is incomplete without the use of operators. At the end of this article, you will understand what are Operators and when, and how to use them in C# Application with examples.
What are Operators in C#?
Operators in C# are symbols that are used to perform operations on operands. For example, consider the expression 2 + 3 = 5 , here 2 and 3 are operands , and + and = are called operators . So, the Operators in C# are used to manipulate the variables and values in a program.
int x = 10, y = 20; int result1 = x + y; //Operator Manipulating Variables, where x and y are variables and + is operator int result2 = 10 + 20; //Operator Manipulating Values, where 10 and 20 are value and + is operator
Note: In the above example, x, y, 10, and 20 are called Operands. So, the operand may be variables or values.
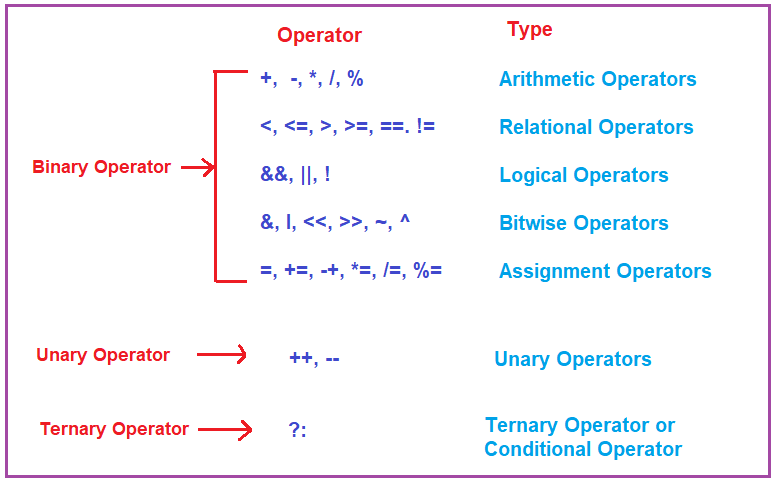
Types of Operators in C#:
The Operators are classified based on the type of operations they perform on operands in C# language. They are as follows:
- Arithmetic Operators
- Relational Operators
- Logical Operators
- Bitwise Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Unary Operators or
- Ternary Operator or Conditional Operator
In C#, the Operators can also be categorized based on the Number of Operands:
- Unary Operator : The Operator that requires one operand (variable or value) to perform the operation is called Unary Operator.
- Binary Operator : Then Operator that requires two operands (variables or values) to perform the operation is called Binary Operator.
- Ternary Operator : The Operator that requires three operands (variables or values) to perform the operation is called Ternary Operator. The Ternary Operator is also called Conditional Operator.
For a better understanding of the different types of operators supported in C# Programming Language, please have a look at the below image.
Arithmetic Operators in C#
The Arithmetic Operators in C# are used to perform arithmetic/mathematical operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, etc. on operands. The following Operators are falling into this category.
Addition Operator (+): The + operator adds two operands. As this operator works with two operands, so, this + (plus) operator belongs to the category of the binary operator. The + Operator adds the left-hand side operand value with the right-hand side operand value and returns the result. For example: int a=10; int b=5; int c = a+b; //15, Here, it will add the a and b operand values i.e. 10 + 5
Subtraction Operator (-): The – operator subtracts two operands. As this operator works with two operands, so, this – (minus) operator belongs to the category of the binary operator. The Minus Operator substracts the left-hand side operand value from the right-hand side operand value and returns the result. For example: int a=10; int b=5; int c = a-b; //5, Here, it will subtract b from a i.e. 10 – 5
Multiplication Operator (*): The * (Multiply) operator multiplies two operands. As this operator works with two operands, so, this * (Multiply) operator belongs to the category of the binary operator. The Multiply Operator multiplies the left-hand side operand value with the right-hand side operand value and returns the result. For example: int a=10; int b=5; int c=a*b; //50, Here, it will multiply a with b i.e. 10 * 5
Division Operator (/): The / (Division) operator divides two operands. As this operator works with two operands, so, this / (Division) operator belongs to the category of the binary operator. The Division Operator divides the left-hand side operand value with the right-hand side operand value and returns the result. For example: int a=10; int b=5; int c=a/b; //2, Here, it will divide 10 / 5
Modulus Operator (%): The % (Modulos) operator returns the remainder when the first operand is divided by the second. As this operator works with two operands, so, this % (Modulos) operator belongs to the category of the binary operator. For example: int a=10; int b=5; int c=a%b; //0, Here, it will divide 10 / 5 and it will return the remainder which is 0 in this case
Example to Understand Arithmetic Operators in C#:
In the below example, I am showing how to use Arithmetic Operators with Operand which are variables. Here, Num1 and Num2 are variables and all the Arithmetic Operators are working on these two variables.

In the following example, I am showing how to use Arithmetic Operators with Operand which are values. Here, 10 and 20 are values and all the Arithmetic Operators are working on these two values.
Note: The point that you need to remember is that the operator working on the operands and the operand may be variables, or values and can also be the combination of both.
Assignment Operators in C#:
The Assignment Operators in C# are used to assign a value to a variable. The left-hand side operand of the assignment operator is a variable and the right-hand side operand of the assignment operator can be a value or an expression that must return some value and that value is going to assign to the left-hand side variable.
The most important point that you need to keep in mind is that the value on the right-hand side must be of the same data type as the variable on the left-hand side else you will get a compile-time error. The different Types of Assignment Operators supported in the C# language are as follows:
Simple Assignment (=):
This operator is used to assign the value of the right-hand side operand to the left-hand side operand i.e. to a variable. For example: int a=10; int b=20; char ch = ‘a’; a=a+4; //(a=10+4) b=b-4; //(b=20-4)
Add Assignment (+=):
This operator is the combination of + and = operators. It is used to add the left-hand side operand value with the right-hand side operand value and then assign the result to the left-hand side variable. For example: int a=5; int b=6; a += b; //a=a+b; That means (a += b) can be written as (a = a + b)
Subtract Assignment (-=):
This operator is the combination of – and = operators. It is used to subtract the right-hand side operand value from the left-hand side operand value and then assign the result to the left-hand side variable. For example: int a=10; int b=5; a -= b; //a=a-b; That means (a -= b) can be written as (a = a – b)
Multiply Assignment (*=):
This operator is the combination of * and = operators. It is used to multiply the left-hand side operand value with the right-hand side operand value and then assign the result to the left-hand side variable. For example: int a=10; int b=5; a *= b; //a=a*b; That means (a *= b) can be written as (a = a * b)
Division Assignment (/=):
This operator is the combination of / and = operators. It is used to divide the left-hand side operand value with the right-hand side operand value and then assign the result to the left-hand side variable. For example: int a=10; int b=5; a /= b; //a=a/b; That means (a /= b) can be written as (a = a / b)
Modulus Assignment (%=):
This operator is the combination of % and = operators. It is used to divide the left-hand side operand value with the right-hand side operand value and then assigns the remainder of this division to the left-hand side variable. For example: int a=10; int b=5; a %= b; //a=a%b; That means (a %= b) can be written as (a = a % b)
Example to Understand Assignment Operators in C#:

Relational Operators in C#:
The Relational Operators in C# are also known as Comparison Operators. It determines the relationship between two operands and returns the Boolean results, i.e. true or false after the comparison. The Different Types of Relational Operators supported by C# are as follows.

Equal to (==):
This Operator is used to return true if the left-hand side operand value is equal to the right-hand side operand value. For example, 5==3 is evaluated to be false. So, this Equal to (==) operator will check whether the two given operand values are equal or not. If equal returns true else returns false.
Not Equal to (!=):
This Operator is used to return true if the left-hand side operand value is not equal to the right-hand side operand value. For example, 5!=3 is evaluated to be true. So, this Not Equal to (!=) operator will check whether the two given operand values are equal or not. If equal returns false else returns true.
Less than (<):
This Operator is used to return true if the left-hand side operand value is less than the right-hand side operand value. For example, 5<3 is evaluated to be false. So, this Less than (<) operator will check whether the first operand value is less than the second operand value or not. If so, returns true else returns false.
Less than or equal to (<=):
This Operator is used to return true if the left-hand side operand value is less than or equal to the right-hand side operand value. For example, 5<=5 is evaluated to be true. So. this Less than or equal to (<=) operator will check whether the first operand value is less than or equal to the second operand value. If so returns true else returns false.
Greater than (>):
This Operator is used to return true if the left-hand side operand value is greater than the right-hand side operand value. For example, 5>3 is evaluated to be true. So, this Greater than (>) operator will check whether the first operand value is greater than the second operand value. If so, returns true else return false.
Greater than or Equal to (>=):
This Operator is used to return true if the left-hand side operand value is greater than or equal to the right-hand side operand value. For example, 5>=5 is evaluated to be true. So, this Greater than or Equal to (>=) operator will check whether the first operand value is greater than or equal to the second operand value. If so, returns true else returns false.
Example to Understand Relational Operators in C#:

Logical Operators in C#:
The Logical Operators are mainly used in conditional statements and loops for evaluating a condition. These operators are going to work with boolean expressions. The different types of Logical Operators supported in C# are as follows:
Logical OR (||):
This operator is used to return true if either of the Boolean expressions is true. For example, false || true is evaluated to be true. That means the Logical OR (||) operator returns true when one (or both) of the conditions in the expression is satisfied. Otherwise, it will return false. For example, a || b returns true if either a or b is true. Also, it returns true when both a and b are true.
Logical AND (&&):
This operator is used to return true if all the Boolean Expressions are true. For example, false && true is evaluated to be false. That means the Logical AND (&&) operator returns true when both the conditions in the expression are satisfied. Otherwise, it will return false. For example, a && b return true only when both a and b are true.
Logical NOT (!):
This operator is used to return true if the condition in the expression is not satisfied. Otherwise, it will return false. For example, !a returns true if a is false.
Example to Understand Logical Operators in C#:

Bitwise Operators in C#:
The Bitwise Operators in C# perform bit-by-bit processing. They can be used with any of the integer (short, int, long, ushort, uint, ulong, byte) types. The different types of Bitwise Operators supported in C# are as follows.
Bitwise OR (|)
Bitwise OR operator is represented by |. This operator performs the bitwise OR operation on the corresponding bits of the two operands involved in the operation. If either of the bits is 1, it gives 1. If not, it gives 0. For example, int a=12, b=25; int result = a|b; //29 How? 12 Binary Number: 00001100 25 Binary Number: 00011001 Bitwise OR operation between 12 and 25: 00001100 00011001 ======== 00011101 (it is 29 in decimal) Note : If the operands are of type bool, the bitwise OR operation is equivalent to the logical OR operation between them.
Bitwise AND (&):
Bitwise OR operator is represented by &. This operator performs the bitwise AND operation on the corresponding bits of two operands involved in the operation. If both of the bits are 1, it gives 1. If either of the bits is not 1, it gives 0. For example, int a=12, b=25; int result = a&b; //8 How? 12 Binary Number: 00001100 25 Binary Number: 00011001 Bitwise AND operation between 12 and 25: 00001100 00011001 ======== 00001000 (it is 8 in decimal) Note : If the operands are of type bool, the bitwise AND operation is equivalent to the logical AND operation between them.
Bitwise XOR (^):
The bitwise OR operator is represented by ^. This operator performs a bitwise XOR operation on the corresponding bits of two operands. If the corresponding bits are different, it gives 1. If the corresponding bits are the same, it gives 0. For example, int a=12, b=25; int result = a^b; //21 How? 12 Binary Number: 00001100 25 Binary Number: 00011001 Bitwise AND operation between 12 and 25: 00001100 00011001 ======== 00010101 (it is 21 in decimal)
Example to Understand Bitwise Operators in C#:

In the above example, we are using BIT Wise Operators with integer data type and hence it performs the Bitwise Operations. But, if use BIT-wise Operators with boolean data types, then these bitwise operators AND, OR, and XOR behaves like Logical AND, and OR operations. For a better understanding, please have a look at the below example. In the below example, we are using the BIT-wise operators on boolean operands and hence they are going to perform the Logical AND, OR, and XOR Operations.

Note: The point that you need to remember while working with BIT-Wise Operator is that, depending on the operand on which they are working, the behavior is going to change. It means if they are working with integer operands, they will work like bitwise operators and return the result as an integer and if they are working with boolean operands, then work like logical operators and return the result as a boolean.
Unary Operators in C#:
The Unary Operators in C# need only one operand. They are used to increment or decrement a value. There are two types of Unary Operators. They are as follows:
- Increment operators (++): Example: (++x, x++)
- Decrement operators (–): Example: (–x, x–)
Increment Operator (++) in C# Language:
The Increment Operator (++) is a unary operator. It operates on a single operand only. Again, it is classified into two types:
- Post-Increment Operator
- Pre-Increment Operator
Post Increment Operators:
The Post Increment Operators are the operators that are used as a suffix to its variable. It is placed after the variable. For example, a++ will also increase the value of the variable a by 1.
Syntax: Variable++; Example: x++;
Pre-Increment Operators:
The Pre-Increment Operators are the operators which are used as a prefix to its variable. It is placed before the variable. For example, ++a will increase the value of the variable a by 1.
Syntax: ++Variable; Example: ++x;
Decrement Operators in C# Language:
The Decrement Operator (–) is a unary operator. It takes one value at a time. It is again classified into two types. They are as follows:
- Post Decrement Operator
- Pre-Decrement Operator
Post Decrement Operators:
The Post Decrement Operators are the operators that are used as a suffix to its variable. It is placed after the variable. For example, a– will also decrease the value of the variable a by 1.
Syntax: Variable–; Example: x–;
Pre-Decrement Operators:
The Pre-Decrement Operators are the operators that are a prefix to its variable. It is placed before the variable. For example, –a will decrease the value of the variable a by 1.
Syntax: –Variable; Example: — x;

Note: Increment Operator means to increment the value of the variable by 1 and Decrement Operator means to decrement the value of the variable by 1.
Example to Understand Increment Operators in C# Language:
Example to understand Decrement Operators in C# Language:
Five Steps to Understand How the Unary Operators Works in C#?
I see, many of the students and developers getting confused when they use increment and decrement operators in an expression. To make you understand how exactly the unary ++ and — operators work in C#, we need to follow 5 simple steps. The steps are shown in the below diagram.

- Step 1: If there is some pre-increment or pre-decrement in the expression, that should execute first.
- Step 2: The second step is to substitute the values in the expression.
- Step 3: In the third step we need to evaluate the expression.
- Step 4: I n the fourth step Assignment needs to be performed.
- Step 5: The final step is to perform post-increment or post-decrement.
Now, if you have still doubt about the above five steps, then don’t worry we will see some examples to understand this step in a better way.
Example to Understand Increment and Decrement Operators in C# Language:
Let us see one complex example to understand this concept. Please have a look at the following example. Here, we are declaring three variables x, y, and z, and then evaluating the expression as z = x++ * –y; finally, we are printing the value of x, y, and z in the console.
Let us evaluate the expression z = x++ * –y; by following the above 5 steps:
- The First step is Pre-Increment or Pre-Decrement . Is there any pre-increment or pre-decrement in the expression? There is no pre-increment but there is a pre-decrement in the expression i.e. –y. So, execute that pre-decrement operator which will decrease the value of y by 1 i.e. now y becomes 19.
- The second step is Substitution . So, substitute the values of x and y. That means x will be substituted by 10 and y will be substituted by 19.
- The third step is Evaluation . So, evaluate the expression i.e. 10 * 19 = 190.
- The fourth step is the Assignment . So, assign the evaluated value to the given variable i.e. 190 will be assigned to z. So, now the z value becomes 190.
- The last step is Post-Increment and Post-Decrement . Is there any post-increment or post-decrement in the expression? There is no post-decrement but there is a post-increment in the expression i.e. x++. So, execute that post-increment which will increase the value of x by 1 i.e. x becomes 11.
So, when you will execute the above program it will print the x, y, and z values as 11, 19, and 190 respectively.
Note: It is not recommended by Microsoft to use the ++ or — operators inside a complex expression like the above example. The reason is if we use the ++ or — operator on the same variable multiple times in an expression, then we cannot predict the output. So, if you are just incrementing the value of a variable by 1 or decrementing the variable by 1, then in that scenario you need to use these Increment or Decrement Operators. One of the ideal scenarios where you need to use the increment or decrement operator is inside a loop. What is a loop, why loop, and what is a counter variable, we will discuss this in our upcoming articles, but now just have a look at the following example, where I am using the for loop and increment operator?
Ternary Operator in C#:
The Ternary Operator in C# is also known as the Conditional Operator ( ?: ). It is actually the shorthand of the if-else statement. It is called ternary because it has three operands or arguments. The first argument is a comparison argument, the second is the result of a true comparison, and the third is the result of a false comparison.
Syntax: Condition? first_expression : second_expression;
The above statement means that first, we need to evaluate the condition. If the condition is true the first_expression is executed and becomes the result and if the condition is false, the second_expression is executed and becomes the result.
Example to understand Ternary Operator in C#:
Output: Result = 20
In the next article, I am going to discuss Control Flow Statements in C# with Examples. Here, in this article, I try to explain Operators in C# with Examples and I hope you enjoy this Operators in C# article. I would like to have your feedback. Please post your feedback, question, or comments about this article.

About the Author: Pranaya Rout
Pranaya Rout has published more than 3,000 articles in his 11-year career. Pranaya Rout has very good experience with Microsoft Technologies, Including C#, VB, ASP.NET MVC, ASP.NET Web API, EF, EF Core, ADO.NET, LINQ, SQL Server, MYSQL, Oracle, ASP.NET Core, Cloud Computing, Microservices, Design Patterns and still learning new technologies.
3 thoughts on “Operators in C#”
Hi Sir.. just noticed.. plz correct result of ternary operator is as 20..
Very clear and concise. Never seen like this before.
VERY GOOD EXPLANATION
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
C# Assignment Operators
- What is C# Assignment Operators?
- How many types of assignment operators in C sharp?
- How to use assignment operator in program?
The C# assignment operator is generally suffix with arithmetic operators. The symbol of c sharp assignment operator is "=" without quotes. The assignment operator widely used with C# programming. Consider a simple example:
result=num1+num2;
In this example, the equal to (=) assignment operator assigns the value of num1 + num2 into result variable.
Various types of C# assignment operators are mentioned below:
Assignment Operators:
In this chapter, you learned about different types of assignment operators in C# . You also learned how to use these assignment operators in a program. In next chapter, you will learn about Unary Operator in C# .
Share your thought
Complete Csharp Tutorial
Please support us by enabling ads on this page. Refresh YOU DON'T LIKE ADS, WE ALSO DON'T LIKE ADS! But we have to show ads on our site to keep it free and updated . We have to pay huge server costs, domain costs, CDN Costs, Developer Costs, Electricity and Internet Bill . Your little contribution will encourage us to regularly update this site.

COMMENTS
In this article. The assignment operator = assigns the value of its right-hand operand to a variable, a property, or an indexer element given by its left-hand operand. The result of an assignment expression is the value assigned to the left-hand operand. The type of the right-hand operand must be the same as the type of the left-hand operand or implicitly convertible to it.
Operator Description Example = Simple assignment operator, Assigns values from right side operands to left side operand: C = A + B assigns value of A + B into C += Add AND assignment operator, It adds right operand to the left operand and assign the result to left operand: C += A is equivalent to C = C + A-=
C# Examples C# Examples C# Compiler C# Exercises C# Quiz C# Server C# Syllabus C# Study Plan C# Certificate. C# Assignment Operators Previous Next Assignment Operators. Assignment operators are used to assign values to variables. In the example below, we use the assignment operator (=) to assign the value 10 to a variable called x:
In c#, Assignment Operators are useful to assign a new value to the operand, and these operators will work with only one operand. For example, we can declare and assign a value to the variable using the assignment operator ( = ) like as shown below.
I think it cannot be overloaded because C# classes are all derived from Object, so they are basically objects, and when you use the assignment operators, you are basically just referencing another object. On the other hand, if you use a structure, then you basically need all the information, so when you use = operator, all fields will be copied.
C# program to demonstrate the example of the right shift operator C# program to read the grade of students and print the appropriate description of grade C# program to calculate the size of the area in square-feet based on specified length and width
Assignment Operators in C#: The Assignment Operators in C# are used to assign a value to a variable. The left-hand side operand of the assignment operator is a variable and the right-hand side operand of the assignment operator can be a value or an expression that must return some value and that value is going to assign to the left-hand side ...
1. Basic Assignment Operator (=) The = operator assigns a value to a variable. This is the simplest form of assignment in C#. Example: using System; public class BasicAssignment { public static void Main() { int a = 5; // Assigns the value 5 to a Console.WriteLine("a = " + a); } }
The C# assignment operator is generally suffix with arithmetic operators. The symbol of c sharp assignment operator is "=" without quotes. The assignment operator widely used with C# programming. Consider a simple example: result=num1+num2; In this example, the equal to (=) assignment operator assigns the value of num1 + num2 into result variable.
The C# Assignment operators are associated with arithmetic operators as a prefix, i.e., +=, -=, *=, /=, %=. The following tables show the available list of C# assignment operators. Symbol