Advantages and Disadvantages of Globalization
Globalization is a hotly discussed subject today, with supporters claiming it may lead to economic progress, cultural interchange, and new possibilities. At the same time, opponents suggest it can cause inequality, cultural homogenization, and environmental degradation (Nkang Ogar et al., 2019). This essay will explore the advantages and disadvantages of globalization and provide evidence to support each perspective. The phenomenon of globalization is the result of technological advancements and the growth of international trade and communication (Ramazanov et al., 2021). It has enabled nations to participate in global economic operations, resulting in greater commerce, investment, and cultural interaction. While globalization has brought economic growth and development, cultural exchange and understanding, and technological innovation and progress, it has also increased inequality, threatened local cultures, and created environmental challenges.
Globalization is a dynamic phenomenon changing how people live, work, and connect. While globalization has generated controversy and criticism, it has also had significant advantages. The possibility for economic growth and development is one of the most important benefits of globalization. Globalization has created opportunities for businesses to expand their markets, access resources more efficiently, and increase productivity (Surya et al., 2021). As a result, more investment, job creation, and improved living standards have occurred in many regions of the globe. For example, the rise of multinational firms and foreign investment has aided China’s and India’s fast economic development. In 2020, China’s economy surpassed that of the United States to become the world’s largest economy by purchasing power parity (Vázquez Rojo, 2022). The growth has lifted millions of people out of poverty and improved their standard of living.
Another advantage of globalization is the opportunity for cultural exchange and understanding. Globalization has promoted exchanging ideas, beliefs, and behaviors across civilizations, expanding global variety and understanding. For instance, the popularity of Korean pop music and television dramas, known as K-pop and K-dramas, has spread to many countries worldwide, creating a new form of cultural exchange (Kanozia & Ganghariya, 2021). Similarly, the growth of English as a worldwide language has increased cross-cultural contact and understanding.
A third advantage of globalization is the spread of technology and innovation. Globalization has created opportunities for transferring technology and knowledge across borders, improving communication, healthcare, and education. For example, the development of mobile technology has transformed how people communicate and access information worldwide (Bahrini & Qaffas, 2019). Moreover, globalization has encouraged scientific cooperation and idea sharing, leading to advancements in domains such as health and renewable energy.
Globalization has been the subject of heated controversy in recent years, with detractors pointing to its harmful effects on economies, society, and cultures throughout the globe. Although globalization has excellent benefits, it has substantial drawbacks that cannot be overlooked. One of the most significant shortcomings of globalization is the uneven distribution of wealth and power that it has brought about. While globalization has generated economic growth and development, the benefits have been distributed unevenly. Wealthy corporations and individuals have gained the most, while workers and communities have suffered job losses and decreased wages. For instance, the growth of sweatshop labor in developing countries has led to exploiting workers, unsafe working conditions, and environmental degradation (Lotfi et al., 2021). Furthermore, global businesses often have more power and influence than governments, resulting in a lack of accountability and oversight.
Secondly, globalization has the potential for cultural homogenization and loss of diversity. As global markets become more integrated, local cultures and traditions are often replaced by homogenous global trends. This can lead to a loss of unique cultural practices and a sense of identity for communities worldwide. For example, the proliferation of fast food companies such as McDonald’s and Starbucks has resulted in the homogeneity of culinary culture in many nations, replacing local cuisine with international fast food choices. Similarly, the appeal of Western fashion and entertainment has pushed indigenous forms of creative expression to the margins.
Thirdly, globalization harms the environment and climate change. Globalization has increased consumption and production, leading to more significant resource depletion, pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions. Thus, global trade growth has increased shipping and air transportation, contributing to carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gas emissions (Hulme, 2021). Besides that, natural resource extraction, such as deforestation and mining, has damaged habitats and ecosystems.
Finally, globalization has both positive and negative aspects. Even though globalization has resulted in an uneven distribution of wealth and power, it has also helped millions of people rise out of poverty by improving their access to lower-cost products and services. While globalization could result in a loss of cultural variation and uniformity, it has also promoted more mutual understanding and respect among individuals from many origins. Similarly, whereas technology may cause environmental harm and climate change, it has also created opportunities for environmental betterment and greater collaboration. Consequently, it is critical to recognize and promote globalization’s positive elements while addressing its negative ones. We can advance toward a more equitable and sustainable global system if we can mitigate negative consequences while enhancing positive ones.
In conclusion, the debate over the advantages and disadvantages of globalization is ongoing and complex. Even though globalization has opened up new avenues for economic expansion and cultural interaction, it has also brought new obstacles in the form of inequality, environmental degradation, and cultural uniformity. It is evident from examining these arguments and counterarguments that the influence of globalization is complicated and diverse. Lastly, politicians, corporations, and people must endeavor to mitigate the adverse effects of globalization while promoting its sound effects. Doing so can create a more equitable and sustainable global system that benefits everyone regardless of background or location. In light of this, it is essential to recognize the value of diverse perspectives and engage in open dialogue to solve the complex challenges of globalization.
Bahrini, R., & Qaffas, A. (2019). Impact of information and communication technology on economic growth: Evidence from developing countries. Economies , 7 (1), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/economies7010021
Hulme, P. E. (2021). Unwelcome exchange: International trade as a direct and indirect driver of biological invasions worldwide. One Earth , 4 (5), 666–679. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oneear.2021.04.015
Kanozia, R., & Ganghariya, G. (2021). Cultural proximity and hybridity: Popularity of Korean pop culture in India. Media Asia , 48 (3), 219–228. https://doi.org/10.1080/01296612.2021.1902079
Lotfi, M., Walker, H., & Rendon-Sanchez, J. (2021). Supply Chains’ Failure in Workers’ Rights regarding the SDG COMPASS: A Doughnut Theory perspective. Sustainability , 13 (22), 12526. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132212526
Nkang Ogar, J., Nwoye, L., & Bassey, S. A. (2019). Archetype of globalization: Illusory comfort of neo-colonialism in Africa. International Journal of Humanities and Innovation (IJHI) , 2 (3), 90–95. https://doi.org/10.33750/ijhi.v2i3.46
Ramazanov, I. A., Panasenko, S. V., Cheglov, V. P., Krasil’nikova, E. A., & Nikishin, A. F. (2021). Retail transformation under the influence of Digitalisation and technology development in the context of globalization. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity , 7 (1), 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/joitmc7010049
Surya, B., Menne, F., Sabhan, H., Suriani, S., Abubakar, H., & Idris, M. (2021). Economic growth, increasing productivity of SMEs, and open innovation. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity , 7 (1), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/joitmc7010020
Vázquez Rojo, J. (2022). United States, China and the dispute for Global Hegemony: A Comparative Analysis. HUMAN REVIEW. International Humanities Review / Revista Internacional De Humanidades , 11 (Monográfico), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.37467/revhuman.v11.4302

Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing style below:
Related Essays
Concerns or questions about the doctoral, do curfews keep teens out of trouble, the straight-a conspiracy, anti-terrorism and counterterrorism., transitional justice in georgia, when they see us, popular essay topics.
- American Dream
- Artificial Intelligence
- Black Lives Matter
- Bullying Essay
- Career Goals Essay
- Causes of the Civil War
- Child Abusing
- Civil Rights Movement
- Community Service
- Cultural Identity
- Cyber Bullying
- Death Penalty
- Depression Essay
- Domestic Violence
- Freedom of Speech
- Global Warming
- Gun Control
- Human Trafficking
- I Believe Essay
- Immigration
- Importance of Education
- Israel and Palestine Conflict
- Leadership Essay
- Legalizing Marijuanas
- Mental Health
- National Honor Society
- Police Brutality
- Pollution Essay
- Racism Essay
- Romeo and Juliet
- Same Sex Marriages
- Social Media
- The Great Gatsby
- The Yellow Wallpaper
- Time Management
- To Kill a Mockingbird
- Violent Video Games
- What Makes You Unique
- Why I Want to Be a Nurse
- Send us an e-mail
30 Globalization Pros and Cons

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process
Definition: Globalization refers to the increasing global interconnectedness of nations. It it not only economic integration. It also refers to cultural , technological , social , and political integration (Dincer et al., 2018). A good catch-all definition comes from Hodos (2016), who writes: “Globalization is defined as the process of becoming globally connected.”

Globalization Pros and Cons
The advantages of globalization, 1. increased economic growth.

Globalization facilitates technology, knowledge, and goods transfer, which in turn boosts economic growth (Erixon, 2018).
Through globalization, countries can now purchase the newest technologies and import the most productive machinery from other countries.
This means every country now has access to the most productive machineries, making the whole world more productive. Productivity means more output, which means more economic growth.
2. Cultural exchange and diversity
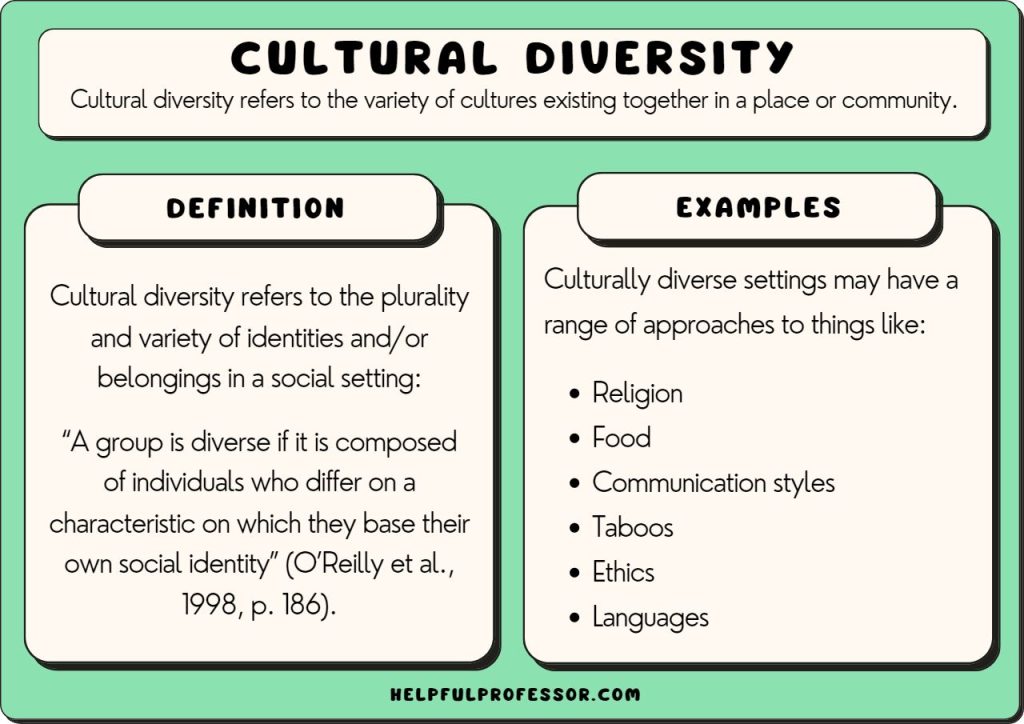
Globalization facilitates cultural exchange and diversity by increasing interactions among people from different parts of the world through trade, travel, and communication.
This exposure leads to the sharing of ideas, traditions, languages, and values across borders, enriching the cultural landscape of participating societies.
Such interactions often lead to the fusion of cuisines, music, art, and fashion, creating new, hybrid forms of cultural expression.
3. Improvement in global communication

Globalization is both caused by and a catalyst for the expansion of global technology and telecommunications. For example, the internet helps facilitate global trade, and demand for a fast and reliable global internet has stimulated its technological development.
The resulting interconnectedness allows for real-time communication across different countries, breaking down geographical and temporal barriers. The result is a more integrated world where cultural and professional exchanges occur more seamlessly.
4. Greater access to foreign investment

Globalization leads to greater access to foreign investment. With broken-down financial barriers, businesses can now source overseas investors for funds. This helps push down the cost of investment and stimulate local business (Erixon, 2018).
It’s also good for investors. They can diversify their portfolios by investing in different countries, and developing countries can benefit from foreign capital to fund growth and development projects.
This influx of foreign investment can lead to economic growth, technological advancements, and increased employment opportunities in the recipient countries.
5. Access to new markets for businesses

200 years ago, everyday small businesspeople could generally only trade with nearby communities. They had to get goods to market via horse and cart and anything perishable had to be consumed fast. There were no refigerators!
Today, with global supply chains, refrigerators, and free trade agreements, even small businesspeople have access to global markets.
Companies can therefore expand their operations and customer base beyond their domestic markets, tapping into demand in different countries (Erixon, 2018).
6. Increased migration opportunities

Globalization has opened up global labor markets. Nowadays, it takes less than 24 hours to move anywhere across the world. No more 3-month boat rides! This has allowed highly-skilled professionals to cross the world and get jobs exactly where there is market demand.
This mobility benefits migrants through better opportunities, the companies by linking them up with the best possible employees, and also contributes to the cultural and economic dynamism of the host countries (Dumont, Rayp & Willemé, 2012).
7. Reduction in prices of goods and services

Globalization leads to a reduction in prices of goods and services by allowing countries to specialize in producing goods where they have a comparative advantage, leading to more efficient production and lower costs (Mir, Hassan & Qadri, 2014).
The removal of trade barriers and the increased competition in global markets drive down prices, making products more affordable for consumers (Erixon, 2018).
Additionally, the global supply chain means consumers have access to a wider variety of goods and services from different parts of the world.
8. Increased competition leading to innovation

Globalization leads to increased competition because you’re no longer just competing with Bob down the road. Businesses are now competing with other businesses from the other side of the world (Erixon, 2018).
While at first this competition sounds bad, it tends to have positive effects. For example, it spurs innovation as companies strive to maintain their competitive edge in a global market.
The exposure to different market needs and technological advancements across borders encourages businesses to innovate and improve their products and services.
This competition not only drives technological advancement but also leads to better quality and diverse options for consumers.
9. Opportunity for developing countries to develop faster

Developing countries need foreign investment and access to foreign markets in order to grow. Globalization provides this access (Mir, Hassan & Qadri, 2014).
This exposure to global markets and capital can accelerate economic growth, create jobs, and promote infrastructure development.
Furthermore, the exchange of knowledge and best practices with developed nations can enhance the skills and capacities of the workforce in developing countries, leading to sustainable development.
10. Spread of democratic values

Some argue that globalization has led to the spread of democratic values. Arjun Appadurai calls this the “ideoscape” of globalization.
The global spread of media and the internet allows for the rapid dissemination of democratic ideals and human rights concepts.
We saw this, for example, during the Arab Spring of 2011, where activist groups multiple countries in the Arab world collaborated via social media to demand democratic reforms.
11. Global talent pool for employment

Globalization leads to a global talent pool for employment as businesses and organizations have access to a wider range of skills and expertise from around the world (Dumont, Rayp & Willemé, 2012).
Enhanced mobility and interconnectedness allow employers to recruit talent from different countries, enabling them to meet specific skill requirements more effectively.
This global workforce diversifies the workplace, fosters innovation, and enhances competitiveness by bringing together diverse perspectives and experiences.
12. Enhanced opportunities for high-skilled workers

Globalization leads to enhanced opportunities for high-skilled workers as it opens up a vast array of international job opportunities in various sectors, including technology, finance, and healthcare (Dumont, Rayp & Willemé, 2012).
These workers can leverage their specialized skills in a broader market, often finding better employment prospects, higher salaries, and advanced career development options globally.
Moreover, the exchange of expertise and knowledge across borders contributes to professional growth and the advancement of specialized fields.
13. Enhanced global cooperation and peace

Globalization could also, in an optimistic scenario, lead to enhanced global cooperation and peace. This is based on the theory that increasing economic interdependence among nations encourages diplomatic relations and collaboration rather than war (Baldwin, 2008).
The shared interests in maintaining stable trade and investment environments promote peaceful interactions and reduce the likelihood of conflicts.
Furthermore, international institutions and agreements foster a platform for dialogue and conflict resolution, contributing to global stability and peace.
14. Widening networking opportunities

Globalization leads to widening networking opportunities as it connects people from different cultures and professional backgrounds through international business, education, and social media platforms.
These connections facilitate the exchange of ideas, collaboration on projects, and the formation of global communities with shared interests and goals.
This extensive networking can lead to new business opportunities, partnerships, and innovations, benefiting individuals and organizations alike (Dumont, Rayp & Willemé, 2012).
15. Access to more goods for consumers

Globalization leads to access to more goods for consumers by breaking down trade barriers and enabling the efficient flow of products across borders (Mir, Hassan & Qadri, 2014).
Amazon Canada doesn’t have the product? No problem, try Amazon UK instead!
This results in a wider variety of goods available in the market, often at lower prices due to increased competition and economies of scale in production.
Consumers benefit from the improved quality, variety, and affordability of products, enhancing their purchasing choices and overall quality of life.
Disadvantages of Globalization
1. widening of economic disparities.

While the above positives sound good, many like Naomi Klein argue that globalization can lead to the widening of economic disparities as it often benefits developed nations and those with competitive advantages, while less developed countries may struggle to keep up.
This can result in increased wealth for certain regions and sectors, while others may experience stagnation or decline in economic growth. The result is a growing gap between the rich and the poor, both within and between countries.
2. Cultural Homogenization (Loss of local cultures)

There is an argument that globalization can lead to the loss of local cultures and identities as global brands and Western media dominate, overshadowing local traditions, languages, and practices.
We call this ‘ cultural homogenization ‘.
The spread of a homogenized global culture can dilute the uniqueness of local cultures, leading to a decrease in cultural diversity. People may adopt global trends at the expense of traditional values and customs, leading to a loss of cultural heritage.
Others dispute this claim, arguing instead that globalization leads to a process called glocalization .
3. Exploitation of labor in developing countries

Globalization can lead to the exploitation of labor in developing countries (Sharma, 2014). Multinational companies may seek to minimize costs by relocating production to regions where labor is cheaper and regulations are less stringent (e.g. opening up factories in Mexico and China instead of midwestern USA).
This can result in poor working conditions, low wages, and a lack of labor rights, exploiting the workforce in these countries. The pursuit of profit by global corporations can overshadow the need for ethical labor practices, leading to exploitation.
4. Environmental degradation

Environmentalists are often concerned that globalization is exacerbating environmental degradation. Increased industrial activity and international transportation contribute to pollution and natural resource depletion (Mir, Hassan & Qadri, 2014).
The global demand for goods encourages mass production, often without adequate environmental safeguards, leading to habitat destruction, loss of biodiversity, and climate change.
The focus on economic growth and consumerism can overshadow the need for sustainable environmental practices, exacerbating global environmental challenges.
5. Increased risk of financial contagion

Globalization leads to an increased risk of financial contagion as economies become more interconnected, meaning that financial crises can quickly spread from one country to another (Mendoza & Quadrini, 2010; Mir, Hassan & Qadri, 2014).
This interdependence is due to global investment and the intertwined nature of banking and financial markets.
A financial problem in one country can lead to investor panic and a loss of confidence, triggering a domino effect that impacts economies worldwide.
6. Over-dependence on global markets
Globalization leads to concerns that countries are over-dependent on foreign markets for essential supplies.
This dependence can make economies vulnerable when supply chains break down. When a major global shock occurs, countries heavily reliant on that market for exports or investment can experience significant economic disruptions (Mendoza & Quadrini, 2010).
For example, most nations in the world are reliant on Taiwan for computer chips. If Taiwan were suddenly invaded by China, the rest of the world won’t be able to produce sufficient computers!
7. Threat to local businesses and industries

In a globalized marketplace, local businesses face intense competition from larger multinational corporations.
These multinationals often have greater resources, technology, and access to larger markets, which can overshadow local enterprises (Burlacu, Gutu & Matei, 2018).
This intense competition can lead to the closure of local businesses, loss of traditional industries, and a decrease in domestic job opportunities.
8. Erosion of national sovereignty

National sovereignty is threatened by a globalized world. Governments may be compelled to alter their policies and regulations to attract global investment and remain competitive in the international market, locking themselves into international trade agreements that require compromise and cooperation (Burlacu, Gutu & Matei, 2018).
This can result in countries losing control over their economic, social, and environmental policies, potentially prioritizing international interests over national priorities.
9. Downward pressure on wages

Globalization can lead to downward pressure on wages as businesses seek to reduce costs by outsourcing jobs to countries where labor is cheaper (Mir, Hassan & Qadri, 2014).
This competition for lower-cost labor markets can result in wage stagnation or decreases in higher-wage countries.
Additionally, the influx of workers willing to accept lower wages can suppress wage growth even in sectors not directly exposed to international competition.
10. Spread of Political Ideologies

While earlier I noted that globalization may have sped up the spread of democracy, the opposite may occur.
While democracy may have been promoted by globalization – especially in the 20th Century – the same could happen with anti-democratic ideologies . For example, recently we have seen the spread of authoritarianism and “illiberal democracy” across the world.
11. Brain drain in developing countries

Globalization leads to brain drain in developing countries as highly educated and skilled professionals migrate to developed countries in search of better job opportunities, salaries, and living conditions (Dumont, Rayp & Willemé, 2012).
This migration of talent results in a significant loss of skilled labor for the originating countries, impacting their development and economic growth.
The departure of these key individuals can also lead to a shortage of expertise necessary for local advancement and innovation.
12. Spread of diseases across borders
Globalization leads to the spread of diseases across borders as increased international travel and trade facilitate the rapid movement of people and goods around the world.
This mobility can enable pathogens to cross geographical boundaries more easily, leading to the faster spread of infectious diseases.
Outbreaks that might have been contained within a region in the past can now quickly escalate into global health emergencies.
13. Vulnerability to global economic fluctuations

A globalized nation may be vulnerable to global economic fluctuations as economies become increasingly interconnected through trade, investment, and financial markets (Mendoza & Quadrini, 2010).
This interconnectedness means that economic issues in one country or region can have ripple effects globally, impacting economies that might not be directly related to the initial problem.
As a result, even local economies can be significantly affected by economic downturns or crises occurring in distant markets.
14. Concentration of corporate power

Some argue that globalization leads to the concentration of corporate power as large multinational corporations expand their reach and influence across multiple countries (Cowling & Tomlinson, 2005).
These corporations can dominate markets, overshadowing smaller local businesses and potentially manipulating markets to their advantage.
This concentration of power can lead to reduced competition, influence over political and economic policies, and an unequal distribution of economic benefits.
15. Potential for global monopolies and oligopolies

Similarly, globalization could lead to the potential for global monopolies and oligopolies as dominant corporations expand their reach across international borders (Burlacu, Gutu & Matei, 2018).
These entities can gain excessive market control, limiting competition and potentially leading to higher prices and fewer choices for consumers.
The global scale of these companies makes it challenging for new entrants to compete, and their influence can extend to shaping market regulations and policies in their favor.
Baldwin, R. (2008). EU institutional reform: Evidence on globalization and international cooperation. American Economic Review, 98(2), 127-132.
Burlacu, S., Gutu, C., & Matei, F. O. (2018). Globalization–pros and cons. Calitatea , 19 (S1), 122-125.
Cowling, K., & Tomlinson, P. R. (2005). Globalisation and corporate power . Contributions to Political Economy , 24 (1), 33-54.
Dincer, H., Yüksel, S., & Hacioglu, Ü. (Eds.). (2018). Strategic Design and Innovative Thinking in Business Operations: The Role of Business Culture and Risk Management . Springer International Publishing.
Dumont, M., Rayp, G., & Willemé, P. (2012). The bargaining position of low-skilled and high-skilled workers in a globalising world . Labour Economics , 19 (3), 312-319.
Erixon, F. (2018). The economic benefits of globalization for business and consumers. European Centre for International Political Economy .
Hodos, T. (Ed.). (2016). The Routledge Handbook of Archaeology and Globalization. Taylor & Francis.
Mendoza, E. G., & Quadrini, V. (2010). Financial globalization, financial crises and contagion . Journal of monetary economics , 57 (1), 24-39.
Mir, U. R., Hassan, S. M., & Qadri, M. M. (2014). Understanding globalization and its future: An analysis. Pakistan Journal of Social Sciences , 34 (2), 607-624.
Sharma, N. K. (2013). Globalization and its impact on the third world economy. Crossing the Border: International Journal of Interdisciplinary Studies , 1 (1), 21-28.

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Free Social Skills Worksheets
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 10 Reasons you’re Perpetually Single
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 20 Montessori Toddler Bedrooms (Design Inspiration)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 21 Montessori Homeschool Setups
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Press ESC to close
Or check our popular categories....
Home » Political Science » Political Economy » 10 Advantages And Disadvantages Of Globalization
10 Advantages And Disadvantages Of Globalization
Globalization is the process of increasing interconnectedness and interdependence among people, businesses, and countries around the world. It is a complex and multifaceted phenomenon that has been shaped by advances in technology, transportation, and communication, as well as economic, political, and cultural factors.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Globalization
Globalization has brought about many advantages, including increased economic growth, access to new markets, and the spread of ideas and innovations. However, it has also had its share of challenges and disadvantages, including job displacement, cultural homogenization, and negative environmental impacts.
In this context, it is important to carefully consider the advantages and disadvantages of globalization in order to understand its impact on the world we live in and work to address any negative effects.
10 Advantages of Globalization
Some of the key advantages of globalization include:
- Increased Economic Growth
- Access To New Markets
- Spread Of Ideas And Innovations
- Increased Cultural Exchange
- Greater Efficiency
- Job Creation
- Improved Living Standards
- Increased Competition
- Greater Access To Information
- Political Benefits

1. Increased economic growth
Globalization has led to increased trade and investment, which has contributed to economic growth around the world. As countries have become more interconnected and trade and investment have increased, businesses have been able to access new markets and sell their products and services to a wider audience. This has led to increased productivity and economic growth, particularly in developing countries that have been able to tap into the global economy.
2. Access to New markets
Globalization has opened up new markets for businesses, allowing them to sell their products and services to a wider audience. This has been facilitated by advances in technology, transportation, and communication, which have made it easier for businesses to connect with customers around the world. The access to new markets has helped businesses to expand their operations and increase their profits.
3. Spread of ideas and innovations
Globalization has facilitated the exchange of ideas and knowledge, leading to the spread of innovations and technological advancements. As people from different parts of the world have come into closer contact with one another, they have been able to share ideas and learn from one another. This has led to the development of new technologies and the spread of innovative ideas, which has had a positive impact on the quality of goods and services available to consumers.
4. Increased cultural exchange
Globalization has brought people from different cultures into closer contact, leading to increased cultural exchange and understanding. As people from different parts of the world have interacted with one another, they have been able to learn about and appreciate different cultures and ways of life. This has helped to promote greater tolerance and understanding among people from different backgrounds and has contributed to a more vibrant and diverse global culture.
5. Greater efficiency
Globalization has allowed for the division of labor, with countries specializing in the production of goods and services in which they have a comparative advantage. This has led to increased efficiency and lower prices for consumers. By specializing in the production of certain goods and services, countries have been able to take advantage of their unique strengths and resources, leading to increased productivity and lower costs.
6. Job creation
Globalization has created new job opportunities, particularly in developing countries. As businesses have expanded their operations internationally, they have created new job opportunities in the countries where they operate. This has helped to reduce poverty and improve living standards for many people around the world.
7. Improved living standards
Globalization has contributed to increased prosperity and improved living standards for many people around the world. As economic growth has increased and access to goods and services has improved, people have been able to enjoy a higher standard of living. This has included increased access to education, healthcare, and other important amenities.
8. Increased competition
Globalization has increased competition among businesses, which has helped to drive innovation and improve the quality of goods and services. As businesses compete with one another on a global scale, they have been forced to continuously improve the quality and value of their products and services in order to stay competitive. This has benefited consumers, who have access to a wider range of high-quality goods and services at lower prices.
9. Greater access to information
Globalization has made it easier for people to access information and connect with others around the world. Advances in technology and communication have made it possible for people to access a wide range of information and connect with others, regardless of their location. This has had a number of benefits, including increased access to education, improved communication and collaboration, and the ability to connect with people from different cultures and backgrounds.
10. Political benefits
Globalization has contributed to increased political stability and cooperation, as countries have become more interconnected and interdependent. As countries have become more reliant on one another for trade and investment, there has been an increased incentive to cooperate and work together to address common challenges. This has led to increased political stability and cooperation, as countries have worked together to solve problems and find mutually beneficial solutions. In addition, the increased economic and cultural exchange facilitated by globalization has helped to promote greater understanding and cooperation among countries.
10 Disadvantages of Globalization
Globalization also had its share of challenges and disadvantages. These includes –
- Job Displacement
- Cultural Homogenization
- Negative Environmental Impacts
- Income Inequality
- Loss of Local Control
- Exploitation Of Workers
- Loss of Cultural Diversity
- Decreased Job Security
- Negative Impact On Small Businesses
- Negative Impact On The Environment
1. Job displacement
Globalization has been associated with job displacement, as some workers have lost their jobs to lower-paid workers in other countries. As businesses have sought to take advantage of lower labor costs in other countries, they have moved some of their operations abroad, leading to job losses in their home countries. This has had a particularly negative impact on workers in developed countries, who may not have the same access to education and training as their counterparts in developing countries.
2. Cultural homogenization
Globalization has been linked to cultural homogenization, as some local cultures have been overshadowed by more dominant global cultures. As people from different parts of the world have come into closer contact with one another, there has been a greater exchange of cultural influences. However, some critics argue that this has led to the erosion of local cultures and the rise of a more dominant global culture. This has had a negative impact on cultural diversity and has led to the loss of some traditional ways of life.
3. Negative environmental impacts
The increased trade and transportation that has accompanied globalization has had negative environmental impacts, including air and water pollution and climate change. The increased movement of goods and people around the world has led to increased emissions of greenhouse gases and other pollutants, which have contributed to climate change and other environmental problems.
4. Income inequality
Globalization has contributed to income inequality, as some people and countries have benefited more from the process than others. While some individuals and countries have experienced increased prosperity and improved living standards as a result of globalization, others have been left behind. This has led to growing income inequality, as the gap between the rich and the poor has widened.
5. Loss of local control
Globalization has led to the loss of local control in some areas, as decision-making has shifted to a global scale. As countries have become more interconnected and interdependent, some argue that local communities and governments have lost control over their own affairs. This has led to a sense of powerlessness and frustration for some people, as global forces have come to shape their lives in ways that they may not be able to influence.
6. Exploitation of workers
Some critics argue that globalization has led to the exploitation of workers in developing countries, as companies seek to take advantage of lower labor costs. In some cases, workers in developing countries have been paid very low wages and have worked in poor conditions in order to produce goods for export to developed countries. This has led to concerns about the exploitation of workers and the erosion of labor standards in some countries.
7. Loss of cultural diversity
Globalization has been linked to the loss of cultural diversity, as some local cultures have been overshadowed by more dominant global cultures. As people from different parts of the world have come into closer contact with one another, there has been a greater exchange of cultural influences. However, some argue that this has led to the erosion of local cultures and the rise of a more dominant global culture, which has had a negative impact on cultural diversity.
8. Decreased job security
The increased competition that has accompanied globalization has led to decreased job security for some workers. As businesses have faced increased competition from abroad, they have been forced to become more efficient in order to stay competitive. This has led to cost-cutting measures, including layoffs and job insecurity, which has had a negative impact on some workers.
9. Negative impact on small businesses
Globalization has benefited large corporations, but it has had a negative impact on small businesses in some cases. As small businesses have faced increased competition from larger, more efficient global corporations, some have struggled to survive. This has led to the closure of some small businesses and the loss of jobs in local communities.
10. Negative impact on the environment
In conclusion, globalization has brought about many positive changes and benefits, including increased economic growth, access to new markets, and the spread of ideas and innovations. However, it has also had its share of challenges and negative impacts, including job displacement, cultural homogenization, and negative environmental impacts.
As we move forward, it is important to carefully consider both the advantages and disadvantages of globalization in order to understand its full impact and work to address any negative effects.
This may involve adopting a more responsible and ethical approach to globalization that takes into account the needs and well-being of people and the environment. By doing so, we can ensure that the benefits of globalization are shared more widely and that its negative impacts are minimized.
Categorized in:
Share Article:
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Other Stories
7 factors for the decline of political theory, the idea of political community: political obligation, please enable javascript in your browser to visit this site..
- Economic Inequality as a Result of Globalisation
- Globalisation Impacts on International Business
- Why some states benefit from globalisation while others fall victim to it
- Impact of Globalisation on Labour
- World Health Organisation and Globalisation
- Globalisation Results: Winners and Losers
- Business Activities Globalisation
- Concept of Globalisation and Cultural Diversity
- Globalisation and Labour Market
- Impacts of Economic Globalisation in Australia since The 1980s
- Globalisation and Cultural Homogeneity
- Commodification and Globalisation in Dubai
- Globalisation Phenomenon: Political and Social Debates
- India and Globalisation Barriers
- Has Globalisation Led To Economic Growth?
- Counterreactions to Globalisation in Local Culture
- Globalisation Effects: the Kelowna International Airport
- Globalisation, Urban Political Economy and Economic Restructuring
- Globalisation and Events Industry Relationship
Benefits of Globalisation Essay
The introduction, some fundamentals on globalisation.
It is impossible to imagine the modern world without such phenomenon as globalisation. Generally, there are many definitions, which cover the term; although the most appropriate one is mostly related to the filed of economy and business.
Thus, globalisation is considered to be a process “by which the world economy is fast becoming a single independent system” (Angiello & Laguerre, 2004). There is a wide range of viewpoints on globalisation: some scientists associate the process with negative outcomes; while others support the opposite opinion and speak about a variety of opportunities globalisation offers.
The thesis statement
The issue of globalisation can be regarded rather ambiguously. For this reason, it seems to be obvious that the international process should be analysed both – from the positive and negative perspectives. A detailed analysis of the consequences globalisation brings about can help clarify whether the phenomenon is considered to be a major driving force of the world economy; or it just generates significant negative effects.
The benefits of globalisation
Some historians are of the opinion that the international process leads to the so-called social inequality; for instance, they consider the gap between rich and poor societies as one of the negative consequences globalisation brought about.
However, in my opinion, it is wrong to compare different societies according to the levels of their prosperity, as the kind of comparison reminds me of comparing round items to square ones.
It should be noted that if societies are ready to accept the international trade, the outcomes will positively affect national incomes; although societies are to practice a wide range of approaches, but not to follow a regular way. In other words, there is a strong need to balance the many competing goals in order to succeed.
A competitive advantage is recognised to be one of the most important variables the benefits of trade depend upon. It is proven that the international process helps countries gain higher incomes.
Thus, in the early nineties a special investigation was conducted; according to the results of the investigation it became evident that rich countries’ GDP increased by 2% annually. That is to say, as far as more globalised countries seemed to undergo a higher increase in GDP per year, less glonalised countires underwent the opposite situation: they experienced economic downfall.
Another negative approach in relation to globalisation is associated with child labour. In poor countries, children are forced to work, as their labour is considered to be the only appropriate way to survive. Rich countries have a wide range of social services and can provide their children with medical care, education, etc. Such benefits are possible partly due to the international process.
However, as far as poor countries can be regarded as less globalised countries, it becomes evident that child labour has nothing in common with globalisation. It cannot be applied to the international influences. The same can be said about the female children’s prostitution in the developing countries.
On the other hand, it must be noted that those poor countries, which domestic conditions (political, social, economical, etc.) are more favourable, have more chances to reduce poverty through globalisation (Srinivasan, 2002).
Generally, one can probably notice that countries have different approaches to globalisation. For instance, China’s attitude to the international process differs from the Western attitude to the concept of the international influence. However, more globalised countries’ higher incomes just prove that globalisation must not be practiced the exact same way.
The issue of globalisation from different perspectives: a brief overview
When discussing the effects of globalisation from the perspectives of the general buyer, one can probably notice that due to the process people are provided with much more goods and services.
Furthermore, the international process affects the pricing policy; for this reason, in most cases the opening price is determined by markets which operate in a global environment. Globalisation gives individuals an opportunity to become familiar with a number of other cultures and experiences.
Most of consumers associate the term with certain radical changes. Of course, the international process affects consumer law in a variety of ways.
Thus, Ronaldo Macedo (2002) points out that the major influences of globalisation on regulation and consumer law involve “changes in the production process and consumption market; transformation from a consumer goods society to a consumer service society, change in the contractual consumer practices and the growth of relational contracts, etc.” (p. 3).
Of course, the influences of globalisation within the perspectives of the general consumer are not limited by the above-mentioned changes. The global economic growth is considered to be a new form of world capitalism; that is why it affects buying attitude in a direct way.
Higher levels of production became possible due to the international process; although such changes in the production process require more financial expenditures. The offer of the standartised goods can be regarded as one of the most common effects the form of the modern capitalism brought about.
Flexible forms of production allow producing goods with unique qualities: as far as buying attitude marks up, higher levels of profitability occur. The flexible form of goods production is a modern industrial technique, which tends to satisfy a variety of consumers’ requirements.
On the other hand, it must be pointed out that the new techniques of production give an opportunity not only to increase the productive capacity, but also to respond to a wide range of alterations in the globalised market in a fast way.
The economic dualism as one of the consequences of globalisation gives an opportunity to combine different consumer markets. Thus, mass consumers along with highly sophisticated ones can satisfy their needs.
When speaking about the effects of globalisation from the perspectives of the company, it becomes evident that the international process can be regarded as the key to competitive advantage.
Of course, the extremely high demands of the modern business world are complicated by globalisation; however, on the other hand, nobody will deny the fact that new business practices appear, technological growth allows reducing the costs of transportation, exchanging of information, etc. Thus, globalisation can be also regarded as a beneficial process in relation to organisations.
Furthermore, it should be noted that the modern business world is deeply interested in globalisation. Thus, capital owners accept globalisation as a business process, which allows making more money. For this reason, the main purpose of a variety of decisions capital owners take is to affect cultural, social and economic approaches of other stakeholders, in favour of the international process.
Most of workers consider the process of globalisation from negative perspectives on the basis of several reasons. Thus, one is to keep in mind that it is workers’ low salary, which is recognised to be one of the major reasons of anti-globalisation positions.
For instance, “a designer jacket may sell for $190 in New York while the worker overseas gets paid 60 cents an hour” (“The Benefits of Globalisation”, n.d.). So, it seems to be evident that there is cheap labour cost, which workers may accept as abnormal.
Despite the fact that globalisation is associated with poverty in developing countries, one is to keep in mind that the supporters of the opinion are totally unfamiliar with the basic points of the international economy; the criticism of the phenomenon is probably related to certain political and economic aspects, but millions of workers go through hardship because of a wide range of domestic problems rather than international influences.
In other words, workers’ ignorance of the issue of globalisation is one of the key reasons of their non-acceptance of the phenomenon.
Most of environmentalists do not consider globalisation as a threat to the environment. On the contrary, the economic stagnation is associated with much more risks as compared with global economic growth.
Moreover, it seems to be evident that global environmental quality improvement is impossible without globalisation processes, as making long-term improvements depends upon the increased income.
Of course, the environment of poor countries is in danger, as there are no resources to implement certain environmental reforms. The fact that globalisation is needed to protect the environment is recognised to be undisputable, as global environmental protection depends upon a variety of economic activities.
Some economists are of the opinion that institutional improvements along with economic growth are needed to resolve a number of contradictions on environmental issues (Mendelsohn, 2003).
The impact of globalisation on domestic policies: a classic example with air pollution
When discussing the impact of globalisation on domestic policies, it is necessary to state that the question is considered to be rather ambiguous.
On the one hand, there is a viewpoint that national policies are greatly determined by the international process; on the other hand, some scientists suppose that globalisation causes no positive or negative outcomes in relation to internal affairs.
Keeping in mind that the global trends can be not only supported, but also neglected by national politics, anti-globalisation activists argue that the global economic growth cannot impact on the national outcomes.
To my mind, anti-globalisation activists’ position is wrong, as the case with environmental pollution shows us how globalisation affects domestic policies. Thus, everybody will accept the fact that environmental problems are of global concern.
For instance, the global character of air pollution is recognised to be “a very suitable indicator for measuring the impact of globalization on national politics” (Jahn 2002).
When analysing the emissions in the OECD-countries, it becomes obvious that national variables are more essential as compared with the international ones; although it should be noted that a variety of international trends are involved into domestic policies.
Despite the fact that national factors seem to be more significant, “a clear positive trend between EU membership and reduction of NOx and CO2 emissions” (Jahn 2002) can be observed. Thus, one can make a conclusion that international factors along with national ones affect domestic policies.
Still, the effect of globalisation on national policy outcomes cannot be rejected, as the investigation, which was conducted on the air-emissions of NOx, CO2, etc. showed the importance of international trends.
When comparing positive and negative attitudes to globalisation, one can probably notice that there are more benefits than harms the global economic growth brings about. Thus, when discussing globalisation from the perspectives of general consumers, environmentalists, workers, and companies, it was proven that the international process offers a variety of opportunities to all parties.
Moreover, the fact that globalisation affects national incomes is also considered to be of great importance, as the fact can be regarded as a proof that the international process is really a major driving force of the modern business world.
The most important argument in favour of globalisation is that “it facilitates an efficient global allocation of savings by channelling financial resources to their most productive uses, thereby increasing economic growth and welfare around the world” (Alfaro et al., 2006).
Of course, there are many other scientists, who consider the international economic integration is a negative way; however, they are unable to argue their viewpoints in a proper way. The international process seems to encourage a wide range of policies that affect people’s life.
It serves the interests of the modern world and facilitates taking decisions. In our days, it is impossible to imagine social, cultural and economic progress without globalisation. It allows greater financial freedom, and therefore, advances people’s living conditions.
Globalisation can be regarded as a natural aspect of capitalism. Competitive advantage the international process stimulates and promotes brings many desirable circumstances to both – the public sphere and the private one. Numerous financial advantages lead to improved financial policies; thus, one can conclude that globalisation contributes to a national prosperity.
Alfaro, L., Kalemli-Ozcan, S., & Volosovych, V. (2006). Capital Flows in a Globalised World: The Role of Policies and Institutions. Hbs.edu . Web.
Angiello, R., & Laguerre, P. (2004). Why Study International Business: The Importance of Globalisation. Bergen.edu. Web.
Jahn, D. (2002). The Impact of Globalisation on Comparative Analysis. Arizona.edu. Web.
Macedo, R. (2002). Globalisation, Regulation and Consumer Law. Yale Law School. Web.
R. (2003). Globalisation and the Environment. Yale.edu . Web.
Srinivasan, T. (2002). Globalisation: Is It Good or Bad? Stanford.edu . Web.
The Benefits of Globalisation. Radford.edu . Web.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2019, April 4). Benefits of Globalisation. https://ivypanda.com/essays/globalisation-4/
"Benefits of Globalisation." IvyPanda , 4 Apr. 2019, ivypanda.com/essays/globalisation-4/.
IvyPanda . (2019) 'Benefits of Globalisation'. 4 April.
IvyPanda . 2019. "Benefits of Globalisation." April 4, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/globalisation-4/.
1. IvyPanda . "Benefits of Globalisation." April 4, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/globalisation-4/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Benefits of Globalisation." April 4, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/globalisation-4/.
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Benefits Of Globalization Essay

Globalization Benefits
The Benefits of Globalization Outweigh the Drawbacks Since the 20th century, people have become globalization in their social life. The actions of people and the view of the city are almost the same with other countries. Globalization is not the fashionable word in the world, it is an important word of human economics. There have some economic professions said it could be dangerous of the transaction in different countries, such as global economic crisis. However, globalization has some positive
Benefits of Globalization
Globalization Introduction Globalization is a term used in literature to refer to the increasing interconnectedness between markets in many countries. With the advantages of new technologies, assets and investments can now flow through international borders faster than they ever have at any point in history. Many corporations have taken advantage of the opportunities to expand internationally and operate on a multinational basis; some span the entire globe in their business operations. The level
Benefit Of Globalization
The term globalization is derived from the word globalize, which refers to the emergence of an international network of social and economic systems. Globalization describes the interplay across cultures of macro-social forces, which include religion, politics, and economics. However over though the same forces still apply, globalization as a whole has transformed due to the technology and resources we have available to us. The main difference between globalization then and now, is that now,
The Benefits Of Globalization
“It has been said that arguing against globalization is like arguing against the laws of gravity” (Kofi Annan, Former Secretary General of the United Nations). Globalization has had and will continue to have a lasting impact on our modern every-day lives. While some United States citizens may not even be able to locate Beijing, China on a map, they sure do purchase many goods that were made there. Globalization is a concept with many meanings and interpretations that have made many people very confused
Benefits of globalization Globalization has created a new opportunity for developing countries The process of globalization has involved many of countries around the world. Developing countries have been affected by globalization. The technology, political influence, social, and natural environment factors have improved under the influence of globalization. Has globalization brought up developing countries many more benefits then detriments? the global healthcare market is both massive and expanding
The Impacts Of Globalization And The Benefits Of Globalization
Globalization is the integration of the worldwide economy in which resources and products move freely across the globe. Globalization has been present for decades however it has predominantly become a more frequent process and has potential good and bad effects on the world of business. Problems can include competition in manufacturing jobs and unemployment in industrialized countries. However, this can also be beneficial in other situations as globalization gives you a larger market trade will be
While some countries have managed to reap the benefits of globalisation, other countries are facing major challenges of income inequality, high levels of unemployment and poverty and the vulnerability of economies to externals shocks. The path of globalisation in its current stage must change to allow more countries to reap the benefits. There is a clear imbalance in the existing workings of the global economy, which has derived from an inequality between the economy, society and political contexts
The advent of modern globalisation has led to unprecedented business and economical developments worldwide. Despite the prevalence of said phenomenon, definitions for the term ‘globalisation’ have been debated extensively. Nevertheless, this process (in a business context) could be defined as the increasing international integration of economies and societies (Berry, 2008; Ch, 2011; International Monetary Fund, 2008; Irani and Noruzi, 2011; OECD, 2013). Both Masson (2001) and Moshirian (2007) suggest
Globalization : A Benefit For America
Globalization: A Benefit to America Globalization. What is it exactly? And why is there so much debate and controversy surrounding it? This topic has sparked protests all over the world. Like with many other topics, some support globalization and what it has accomplished. Others have hatred and believe it should not exist. Why do some people believe that globalization is an essential process and helps the economy immensely, while others see it as the root of pure evil and destruction? The answer
Benefits Of Globalization On Jobs
One of the main benefits of globalization is that it helps to develop trading amongst nations. Some may think that trade causes loss of jobs and believe that we should be more self reliant on our own production of goods. But, what they may not understand is trade comes with added benefits. To date the United States is the largest trading nation in the world. “Most imports have a lower cost and higher quality, and that improves our standard of living” (Marotta, 2003). It is the competitive pressures
Popular Topics
- Benito Mussolini Essay
- Beowulf Comparison Essay
- Beowulf Wiglaf Essay
- John Berger Essay
- Berkshire Hathaway Essay
- Berlin Blockade Essay
- Bermuda Triangle Essay
- Jane Eyre Bertha Mason Essay
- Billing Essay
- Binary Oppositions Essay
- Cultural Globalization as the Americanization of the World’s Cultures Words: 1925
- Globalization Advantages and Negative Cultural Impact Words: 970
- Ways of Eating Around the World: Impact of Globalization Words: 2208
- Interconnection of Globalization and Culture Words: 628
- The Impact of Racism on Globalization Words: 4995
- Globalization: Impact and Consequences Words: 599
- Evaluating Cultural Dimensions of Globalization Words: 3304
- Globalization and Its Pros and Cons Words: 615
- Is Globalization a Threat or an Opportunity to Developing Countries? Words: 1603
- Globalization and its Impact on the World Words: 583
- The Effects of Globalization on Sports Words: 2364
- History of Globalization and World Integration Words: 1432
- Globalization: More Positive Effects Than Negative Ones Words: 1643
- Impacts of Globalization on the Developing Countries Words: 2315
- Globalization: Managing Across Cultures Words: 3025
- Globalization, Its Defenders and Critics Words: 903
- Globalization Impacts on Trade and Employment Words: 1723
- Economic Globalization: The Role of Geography Words: 2100
The Advantages of Globalization
Introduction, accessibility of technology, choice of culture, diverse culture products, sharing knowledge, reference list.
The world is fast becoming a global village, seemingly smaller than it was a decade ago. This scenario has resulted from the development of trade and transport systems, thus making it conducive for movement of people, goods, services, and ideas and creating diversity in social, economic, political, and cultural views across the world. The technological revolution has also played a critical role in advancing globalization.
Globalization is an age-old concept, even though it has elicited great discourses in contemporary times as compared in the past where the idea of a global village seemed farfetched. Globalization is the process of growth and interconnection of world economies and cultures, which are aided by transport and trade. This process has been in progress for hundreds of years although at a much slower pace than in recent years as aforementioned.
It affects the cultural, economic, and social spheres of society. As with every thing else, globalization has both advantages and disadvantages. This paper highlights some of the positive effects that globalization has on all spheres of human interaction including the sharing of cultural products such as music, sports, and movies, knowledge, technology, and foods from different cultures.
A few decades ago, the majority of the contemporary technology was non-existent in most developing countries. People had to do almost everything manually including basic tasks such as doing laundry, cleaning floors, and cooking. However, this scenario was different in most developed countries as they already had some of the technology needed to carry out such tasks with ease.
However, with the improvement and advancement in modes of transport in developing countries, developed countries found new markets in most parts of Africa and Asia and products such as vacuum cleaners, microwaves, and washing machines found their way to developing countries. The main advantage of this development is that it has drastically improved the quality of work done while reducing the amount of time spent doing the same.
This aspect consequently improves the lifestyles of the people using the machines (Rifkin, 2003, Spiritual Perspectives on Globalization, p.176). Nevertheless, western countries are constantly modifying these products and making them more efficient. Today, it does not take a decade for any new technology to be available to consumers in developing countries.
Globalization has opened boundaries across the world, and a new technology in the United States will only take a few months before hitting the market in developing countries. Also, the transport systems have drastically evolved from the use of steam engines and ships to using electric trains and airplanes.
Communication is also easier now with the introduction of hi-tech mobile telephones that connect people both in the same country and with people in different continents at the touch of a button (. The ultimate result of such developments is that people in different areas of the world are in a position to enjoy the benefits of products not ordinarily available to them in their own countries and have expansive markets in other parts of the world.
Marketing forums like Amazon, e-Bay and many other online trading forums enable consumers to purchase goods and services online regardless of one’s location (Pew Global Attitudes Project, 2007, p.177-178).
Globalization has led to the introduction of diverse cultural practices in places where originally there existed only one practice. A century ago, a certain culture was a specific aspect unique to a certain society. For instance, the Chinese culture was specific to people and residents of China, European culture was specific to people living in Europe and African culture specific to Africa.
However, ease of trade and travel has changed this dynamic by making most societies multicultural, with everyone having the freedom to embrace his or her culture of preference rather than being restricted to the culture of birth. For instance, it is Chinese culture that children should not buy food with their own money.
This cultural pursuit seeks to encourage children to eat whatever that their parents place before them, consequently encouraging healthy eating. Nevertheless, since the McDonalds opened its first branch in Beijing in 1992, this cultural requirement has changed drastically.
McDonald’s services, which include hosting birthday parties, appealed to children regardless of the fact that birthdays are not culturally celebrated in China either (The Levin Institute, n.d. Globalization and Culture: Globalization and local culture, p.180).
Also, the introduction of Starbucks, an American coffee retail enterprise, in Italy has given the people of Italy a choice between maintaining their culture of drinking coffee in small and relaxed establishments and ordering coffee at Starbucks to drink on the go at their convenience. There are also other restaurants established for the sole purpose of selling food associated with specific cultures.
There are restaurants that only make Italian cuisine, Chinese cuisine, Japanese cuisine, and French cuisine to mention but a few, while others take pride in being inclusive and serving cuisines from different cultures (Hastings, Thiel & Thomas, 2003, The deadly noodle, p.180). This aspect gives every individual a chance to either try something new or stick to what is familiar.
Another good example is fashion and how different cultures influence their trends. For instance, people associate the Kenyan Maasai kikoi with East Africa and the Ankara with West Africa. Therefore, a person may use any of the two fabrics or use them together to give an African feel to his or her outfit. The beauty of the freedom to choose elements from different cultures is that it creates diversity and nurtures an appreciation for different cultures.
It also creates opportunities to develop new and unique cultures made from the combination of cultures from different societies as well as a means to celebrate similarities. Sports are one such similarity, which is celebrated worldwide through the organization of events that bring different countries together to compete in various disciplines. The Olympics and the FIFA World Cup are examples of such events.
During these events, people from different cultures meet and exchange ideas and practices. Also, some sports are specific to some countries; for instance, the Chinese acrobatics, and through such events, other countries get to learn about these sports, which are specific to some cultures.
Apart from increasing the availability of consumer goods, globalization has increased production and trade of culture products and services such as music and movies. Cultural products and services are products and services that echo the lifestyles and cultural background of a given society. For instance, movies vary depending on the part of the world they come from and the culture in force in that particular part of the world.
For example, the United States developed the ‘Hollywood’ trademark for outstanding movies and other artistic displays that best defined what the culture is like in that part of the world(The Levin Institute, n.d. Globalization and Culture: Globalization and local culture, p.180). They packaged these performances and sold them as a commodity within the American borders.
As globalization progressed, other parts of the world such as Asia and Africa provided a ready market for this commodity. It also created a platform for different cultures around the world to share their experiences whether political, social-cultural, or economical.
It did not take long for Asia and Africa to start producing movies using the knowledge gained from the commodity they bought and incorporating their own cultural experiences into the stories.
Bollywood is the Asian version of this commodity while the Nollywood is the African version produced in the West African region.
Just like the example given earlier on regarding the choice of a culture where people establish restaurants serving specific foods from different parts of the world, the IMAX Company based in the United States is recorded to have opened six hundred and ninety-seven (697) movie theaters in fifty-two countries worldwide by September of 2012.
These theaters provide an avenue for people to enjoy the American movie-watching culture in an authentic American environment (The Levin Institute, n.d. Globalization and Culture: Globalization and local culture, p.180).
Air transportation has made it possible for people to leave one part of the world to learn and gain knowledge in another part of the world.
The Internet and by extension the social media platforms such as Facebook and Twitter have made haring of information, and consequently, knowledge easier and faster as information is relayed in real time to people all over the world (Knickerbocker, 2004, If Poor Get Richer; Does the World See Progress? page 185-186).
The Internet burst has facilitated knowledge sharing by a great margin, and even now, people in developing countries can undertake online studies offered in learning institutions in developing countries. Thanks to globalization, people can have cures to most of the diseases across the world.
A cure discovered in one part of the world now means a cure for the rest of the world. For instance, courtesy of the efforts of Dr. Jonas Salk in the early 1950s who invented the Polio vaccine the disease is now preventable. However, this achievement would not be possible without means of sharing information.
This information-sharing aspect is not only important in issues regarding medicine, but also in political, social, environmental and economic issues. As long as there is an interconnection of interests, through trade, for instance, it is crucial to ensure that there is a flow of information and knowledge.
A good example of why this element is important is the global financial meltdown that occurred throughout the world like a ripple effect to a credit crisis in Europe. Had there been information regarding the credit crunch on the onset, most of the countries with financial links to credit institutions in Europe would have taken necessary measures to prevent a global meltdown.
World leaders hold conventions in different places at different times of the year all over the world to discuss various ways of ensuring conservation and sustainability of the environment because what happens in one part of the world affects the rest of the world.
Carbon emissions, for example, affect the o-zone layer thus causing global warming across the world, regardless of the origin of the emissions (Knickerbocker, 2004, If Poor Get Richer; Does the World See Progress?, page 185-186).
Since every element has a negative side, globalization has numerous positive aspects that have changed the lives of many individuals across the world. The process is continuous and finds new ways of linking various parts of the world together.
Through globalization, culture has defied territorial boundaries, thus allowing the sharing of life-changing knowledge coupled with the development and sharing of technology. Globalization has created diversity in every part of the world and made people to appreciate both what is within and outside their territorial borders.
Hastings, M., Thiel, S., & Thomas, D. (2003). The deadly noodle. Newsweek, 141 (3), 180-182.
Knickerbocker, B. (2004). Globalization and sustainability: If Poor Get Richer, Does World See Progress? The Christian Science Monitor . Web.
Pew Global Attitudes Project. (2007). World publics welcome global trade-But not immigration.
Rifkin, I. (2003). Framing articles: What is globalization: Spiritual Perspectives on Globalization. Woodstock, VT: Skylight Paths Publishers.
The Levin Institute State University. (n.d.). Globalization and Culture: Globalization and local culture. Web.
Cite this paper
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2020, April 16). The Advantages of Globalization. https://studycorgi.com/the-advantages-of-globalization/
"The Advantages of Globalization." StudyCorgi , 16 Apr. 2020, studycorgi.com/the-advantages-of-globalization/.
StudyCorgi . (2020) 'The Advantages of Globalization'. 16 April.
1. StudyCorgi . "The Advantages of Globalization." April 16, 2020. https://studycorgi.com/the-advantages-of-globalization/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "The Advantages of Globalization." April 16, 2020. https://studycorgi.com/the-advantages-of-globalization/.
StudyCorgi . 2020. "The Advantages of Globalization." April 16, 2020. https://studycorgi.com/the-advantages-of-globalization/.
This paper, “The Advantages of Globalization”, was written and voluntary submitted to our free essay database by a straight-A student. Please ensure you properly reference the paper if you're using it to write your assignment.
Before publication, the StudyCorgi editorial team proofread and checked the paper to make sure it meets the highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, fact accuracy, copyright issues, and inclusive language. Last updated: January 27, 2022 .
If you are the author of this paper and no longer wish to have it published on StudyCorgi, request the removal . Please use the “ Donate your paper ” form to submit an essay.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Benefits and Drawbacks of Globalization. Globalization is a complex concept that can be defined by the process of interaction between organizations, businesses, and people on an international scale, which is driven by international trade. Some people may associate it with uniformity, while others can perceive it as the cause of diversification.
Globalization has spurred the spread of new technology, helping to make economies greener and more productive. Globalization has helped to reduce gender wage discrimination and giving new opportunities to women. Globalization has improved the quality of management in firms and the working conditions for people. Globalization has boosted output ...
Apr 11, 2019 · As we enter the fourth wave of globalization, driven by the digital revolution, there is renewed debate over whether it is a beneficial force: powering economic growth, and allowing the spread of ideas to improve people’s lives; or whether it erodes communities, and widens the gap between the elites and the rest of the world.
Globalization is a hotly discussed subject today, with supporters claiming it may lead to economic progress, cultural interchange, and new possibilities. At the same time, opponents suggest it can cause inequality, cultural homogenization, and environmental degradation (Nkang Ogar et al., 2019). This essay will explore the advantages and disadvantages of globalization and provide evidence to […]
Feb 3, 2024 · 3. Improvement in global communication. Globalization is both caused by and a catalyst for the expansion of global technology and telecommunications. For example, the internet helps facilitate global trade, and demand for a fast and reliable global internet has stimulated its technological development.
Feb 16, 2022 · Globalization is a complex phenomenon that has a big influence on various fields of human life, including economics, society, and culture. Even though trade between countries has existed since time immemorial, in the 21st-century, globalization has become an integral part of the world’s development.
Jan 6, 2023 · 10. Political benefits. Globalization has contributed to increased political stability and cooperation, as countries have become more interconnected and interdependent. As countries have become more reliant on one another for trade and investment, there has been an increased incentive to cooperate and work together to address common challenges.
The introduction Some fundamentals on globalisation. It is impossible to imagine the modern world without such phenomenon as globalisation. Generally, there are many definitions, which cover the term; although the most appropriate one is mostly related to the filed of economy and business.
The Benefits of Globalization Outweigh the Drawbacks Since the 20th century, people have become globalization in their social life. The actions of people and the view of the city are almost the same with other countries. Globalization is not the fashionable word in the world, it is an important word of human economics.
Introduction. The world is fast becoming a global village, seemingly smaller than it was a decade ago. This scenario has resulted from the development of trade and transport systems, thus making it conducive for movement of people, goods, services, and ideas and creating diversity in social, economic, political, and cultural views across the world.