- EssayBasics.com
- Pay For Essay
- Write My Essay
- Homework Writing Help
- Essay Editing Service
- Thesis Writing Help
- Write My College Essay
- Do My Essay
- Term Paper Writing Service
- Coursework Writing Service
- Write My Research Paper
- Assignment Writing Help
- Essay Writing Help
- Call Now! (USA) Login Order now
- EssayBasics.com Call Now! (USA) Order now
- Writing Guides

Unemployment Problem And Solution (Essay Sample) 2023
Unemployment problem and solution.

We use cookies to enhance our website for you. Proceed if you agree to this policy or learn more about it.
- Essay Database >
- Essay Examples >
- Essays Topics >
- Essay on Market
Essay On Unemployment In Saudi Arabia
Type of paper: Essay
Topic: Market , Social Issues , Unemployment , Middle East , Politics , Workplace , Human Resource Management , Saudi Arabia
Words: 2000
Published: 01/26/2020
ORDER PAPER LIKE THIS
Unemployment is a state of joblessness that takes different dimensions and forms. It begins from the time and individual starts looking for jobs relentlessly hopping into one office after another. It is a very dynamic concept that even incorporates the period between which a person dumps one job and when he or she secures another one. Saudi Arabia is one of the wealthiest nations in the Middle East with some of the world’s largest oil reserves. However, a greater percentage of her population is jobless. Some employees in Saudi Arabia receive low wages and are thus not satisfied with their jobs. This country has a lot of immigrants who work in non-skilled jobs in small-scale businesses and construction. Her private sector is highly occupied by foreigners. Currently, Saudi Arabia is experiencing an unemployment rate of approximately 10.5%.
Causes of unemployment
Job dissatisfaction is one the basic causes of unemployment in Saudi Arabia. Many people are in jobs that they are not happy with. This dissatisfaction may be a result is underutilization of skills that such workers gained during their training of due to mismatch of wages entered and the qualification. Workers may also be discontented with their jobs due to poor tittles at their work places. Most of the jobless persons in Saudi Arabia are victims of job dissatisfaction. They have pulled out of the labor market simply because the jobs they secure do not satisfy their payment satisfactions and work conditions. For any worker to gain substantive progress and growth in his or her job, he or she must first of all be part of that job. A worker’s positivity towards whatever he or she is doing. Immigrant labor has taken over the local human resource in Saudi Arabia. Unlike the developed countries which restrict labor import, Saudi Arabia is a recipient of high numbers of foreign workers. Of these workers, many are unskilled and stream into odd and manual jobs. This results into two distinct labor market trends. The first trend comprises of Saudi Arabians who mainly occupy the few white collar government jobs. This category of workers also takes up a very big share in the highly regulated industries such financial services and oil and natural gas industries. However, this number is very slim owing to the fact that most Saudi Arabians do not have the adequate professional qualifications to serve in such high profile jobs. Only a few citizens can manage these positions. The second category is made up of unskilled foreigners who mainly dominate the low-skill and technical jobs which are also lowly remunerated and are accompanied by difficult working conditions. (Ramady 356) Gender is another big issue that has enhanced unemployment in this country. Job placement is not equally distributed between male and female Saudis. Men are most favored by the Islamic culture that dominates the Saudi Arabian society. In real essence, women are victims of legislative, occupational, educational and social obstacles to full incorporation into the Saudi Arabian labor market. Currently, women make up to less than 15% of the total public and private human resource in Saudi Arabia. This is scaling quite very low on the general figures of the region. (Abdulaziz Al-Saud ) The poor quality of higher education in the country has been a worrying. Professional training programs that institutions of higher education are offering does not appeal to the Saudi Arabia’s labor market. This means that these institutions do not consider the societal economic needs and gaps. A good education system should aim at solving the problems faced by the society. However, things are different in Saudi Arabia and fresh graduates are always victims of rude shock as these institutions usher them into the labor market. This ends up in creating an artificial shortage in the labor market because graduates are available but with inappropriate skills that cannot fit in the Saudi Arabia’s economy. A survey from major Arab countries reveals that their educational standards fall way below the international professional thresholds. Anderson 2013, asserts that these countries still lag behind in the comparative assessment of international achievement of students. (Andersson and Abdelkader 211) High population in the Saudi Arabian country is also another factor escalating unemployment rates in Saud Arabia. Young age population profile has lowered the Saudi Arabia’s labor participation rate. This implies that the young population that dominates the Saudi Arabia’s population is not yet in the job-seeking bracket. This population is very different from the people who are not employed but fall in the working age bracket. Such people can be said to be jobless since there are either voluntarily jobless or are victims of some economic forces which are beyond their control. In the Gulf Cooperation Council and the United States of America rankings, the Saudi Arabia labor participation rate ranks very low at about 35 percent. This statistics cuts across the female and the male labor participation. If the greater percentage of the Saudi Arabia’s population is not economically productive in the labor market then this country cannot consider her human resource base as stronger. The key implication of this is that this population is mainly the dependents of the foreign workers in Saudi Arabia who the law prohibits from joining the Saudi Arabia’s labor market. Besides, they are unskilled and their educational level is very low and are the most affected by the economic downturn. (Ghafour 31) Poor working conditions and poor remuneration by the Saudi employers is enhancing unemployment. Many workers in Saudi Arabia are victims of low wages and poor working conditions. The average hours that an employee works for in a week does not correspond to the wages he or she receives. This is the basis of ascertaining good or bad working conditions of a particular job. Research shows that working hours in Saudi Arabia’s government jobs are proportionate to their earnings or wages. People having government job placements can only work for a maximum of 30 hours per week. This is professionally justifiable and encouraging and many employees would go for nothing less than it. Much over exploitation comes from the private sector which strains their workers potentials more than they reward them. One of the reasons that can back up this claim is that most private employers are profit maximisers and would tactfully scheme for maximum benefit. The persons who look forward into joining the private sectors are greatly discouraged by this situation and they would rather stay away jobless that sign into them. They look at such working conditions as difficult. (Andersson and Djeflat 212)
Effects of Unemployment
Generally, lack of adequate employment opportunities in any country is a big problem. It affects all the sectors of economy. It also waters down the need for professional training in that country. Person who are within the working age bracket yet are jobless are the most traumatized by unemployment. Poverty is always an ally of unemployment in any nation which suffers this menace. When people live bellow one dollar a day, they are globally considered poor. Such people cannot cater for all their needs thus wade in poverty. Many Saudi Arabia’s citizens are falling within this category. Despite her rich and lucrative oil fields, the per capita income of her citizens is very low. Unemployment leads to an increase in social injustice. Many idle yet trained youths are opting to violence and crime to survive. As the say goes that an idle mind is the devils workshop, these youths remain very idle and thus brew crime associated plans. Most of them end up into bank robbers, prostitutes, drug traffickers and pornographic artists and artistes. This implies that even the working class is not safe since there are the targets of these rowdy and jobless youths. They terrorize investors and rob them of their ventures. There has been many crime related issues that accrue from unemployment. Many people fallen victims of Saudi conmen, who unsuspectingly rob them of millions of dollars. These are what the jobless community in the Saudi Arabian economy resort to. (Ramady 380)
One of the key tools that the Saudi government is adopting to curb this escalating rate of unemployment is the Saudinization. This operation aims at replacing the foreign labor force with the Saudi locals or other citizens. It is conducted through dual program that entails use of incentives to boost the morale of native human resource. The government is also backing up this effort with the restriction of visa issuance to the foreign workers who endeavor to stay and work in Saudi Arabia. This is a strategy that would ensure inclusive labor force in Saudi Arabia. However, it is worth noting that this is a long process which needs proper planning and excursion. As stated before, this foreign human resource is currently dominating the Saudi labor market and facing them out must require proper preparedness. It is quite remarkable that this is a strategy that is already on course and the government is committing its resources into it to ensure its success. The second step towards the resolution of this problem is to refine and put the private sector under check and balance. It is quite clear that the government jobs cannot cater for the entire Saudi working age bracket. The private sector has a greater responsibility to play in the labor market. The government should therefore ensure that it control the private sector’s acquisition and maintenance of labor force. The private employers must ensure that they attract workers through creating good working conditions and terms of service. Many workers voluntarily choose to remain jobless due to the oppression that they get in the private sectors. If the government simply neglects their crucial responsibility to serve and protect its citizens, the private entrepreneurs would such the blood to the last drop. They are profit oriented and thus would over exploit their workers just but to earn maximum profits at lower production costs. Labor is therefore a major constituent of this production cost. Another most important way of solving unemployment problem in Saudi Arabia is by changing the Saudi’s perception towards culture and work ethics. Young and fresh graduates should understand very what the labor market expect of them. They must appropriately apply and integrate the skills they have acquired to suit their job specifications and the market labor demands. The poor women participation in the Saudi labor market is also as a result of poor ethical practices. Ramady emphasizes that the government must only and directly involve women in the nation building to bridge the gap between men and women human resource. (Abdulaziz Al-Saud ) Saudi Arabia should adequately address her higher educational standards to meet the global professional standards. She should do a complete overhaul of her educational curriculum to suit the current trends in the labor market. There is no need of producing thousands of graduates who can barely fit in any job market. This is a big wastage. Again, higher education should be made affordable and accessible to ensure that this rich labor market gets enough professionals to serve it needs. Thorough research is very paramount in this issues and the Saudi government should commit herself into this. (Ghafour ) In conclusion, unemployment is a very big setback to every government. When a government is unable to provide enough jobs opportunities to its citizens then its governance is questionable. However, whenever a government is undergoing such economic setbacks it should immediately strategize to counteract the situation. Saudi Arabia’s immigration department should adopt firm regulations to control influx of foreign workers into this country.
Works Cited
Alwaleed Bin Talal Bin Abdulaziz Al-Saud. “A Saudi Prince’s Plea for Reform.” New York Times 24 February, 2011: Print. Ghafour, Abdul. "Central Department of Statistics and Information, Ministry of Economy and Planning; Saudi Arabian Monetary Agency (SAMA)." Forty-Fourth Annual Report. August 2008. Otto, Jan Michiel. Sharia Incorporated: A Comparative Overview of the Legal Systems of Twelve Muslim Countries in Past and Present. illustrated. Leiden: Amsterdam University Press, 2010. Ramady, Mohamed A. The Saudi Arabian Economy: Policies, Achievements, and Challenges. 2, illustrated. New York: Springer, 2010. Sara Hamdan. “Saudi Arabia to Fine Firms with Too Many Foreign Workers.” New York Times 21 November, 2012: Print. Thomas Andersson and Abdelkader Djeflat. The Real Issues of the Middle East and the Arab Spring. New York: Springer, 2013.

Cite this page
Share with friends using:
Removal Request

Finished papers: 2489
This paper is created by writer with
If you want your paper to be:
Well-researched, fact-checked, and accurate
Original, fresh, based on current data
Eloquently written and immaculately formatted
275 words = 1 page double-spaced

Get your papers done by pros!
Other Pages
Church personal statements, shoot book reviews, craft book reviews, canal book reviews, clone book reviews, exile book reviews, turnover book reviews, delay book reviews, loop book reviews, counterpart book reviews, brokaw essays, entrances essays, dumex essays, cruzi essays, coxs essays, astral essays, furniss essays, braunwald essays, fili essays, kla tencor essays, ego defense essays, ans 1 considered as major elements for any agricultural companies essay 2, movie review on ted videos, case study on internal swot analysis on the kraft foods group, why are spain ireland greece and italy sometimes referred as the euro zones book review example, global warming and its effects argumentative essay examples, example of case study on quot into the mouths of babes quot by james traub nytimes magazine 7 24 88, sample essay on love as a theme in different texts, name research paper samples, free competition and society argumentative essay sample, good example of literature review on the story of an hour, single sex vs coed education essay, othello term papers examples, free hypertension essay example, free data standards and security course work example, good nursing admission questions admission essay example, criminal law essay examples 7, annotated outline essays examples, good essay on economic impact of tourism in the united kingdom.
Password recovery email has been sent to [email protected]
Use your new password to log in
You are not register!
By clicking Register, you agree to our Terms of Service and that you have read our Privacy Policy .
Now you can download documents directly to your device!
Check your email! An email with your password has already been sent to you! Now you can download documents directly to your device.
or Use the QR code to Save this Paper to Your Phone
The sample is NOT original!
Short on a deadline?
Don't waste time. Get help with 11% off using code - GETWOWED
No, thanks! I'm fine with missing my deadline
Unemployment in Saudi Arabia Research Paper
Introduction.
Unemployment puts a bad taste in the thoughts of everybody who is affected directly or indirectly by it. No one government has been fully able to tame unemployment. The reasons to unemployment vary from one country to another. Besides, the approaches that each country may employ in the struggle to address unemployment may also vary. Cultural, social and religious and or economic causes the immediate variables that distinguish each country’s unemployment state.
Although these could be the differences, unemployment basically has a general definition, with its impacts almost the same across all the nations involved. This problem solution research is aimed looking into the unemployment situation in Saud Arabia. The research will focus on unemployment on a general perspective in Saudi Arabia while narrowing down, partially to focus on unemployment of women in the country.
Literature review
Unemployment situation in Saudi Arabia has drawn much attention in the recent years. It has come to be appreciated as a factor that oils the occurrence of social unrest in the region as put by Bosbait and Wilson, (2005). Much effort has been in place to from the government of Saudi Arabia in order to address the question of unemployment despite the fact that the nation is full of vast deposits of crude oil. The country is one of the leading nations in oil production on a world ranking scale.
Unemployment data provided by the government for the year 2002 showed that the overall unemployment for all gender was pegged at 6.1%, with Saudi male unemployment figure estimated at 8.1% while female unemployment was at 15.8 per cent, almost twice the male unemployment figure (Niblock, 2006. Pp. 115). However, the figures provided above are a small representation since they do not the expanse population of Saudi (Niblock, 2006, pp 116).
The lack representation of this information has its roots in the culture of Saudi as a nation, thus leading to unaccountability of the real number of women in the labor force it is asserted that the effect of culture exerts a substantial impact on human resource management practices in Saudi Arabia. With respect to this, Budhwar and Debra, (2001, p.143) posited that cultural values and social attitudes to work and management are absolutely different from those practiced in the western world especially their European neighbors.
Additionally, they lay a further emphasis on tribal and family values. Religion has had a big influence on the employment of women in Saudi Arabia. For this reason, Budhwar and Debra, (2001, pp 143) established that this is a big counter-effect to the employment of women contrary to the fact the government of Saudi Arabia has of late invested substantially in education and training of women.
On the other hand, there is a view that the policy designed by the State personnel in Saudi Arabia has a bias towards sex segregation in education and to a great extend gave a rebirth to older familial relations that give a raw deal to a woman’s employability, despite skill being present to a woman being in question (Moghadam, V.M., 2003, pp 65).
Unemployment in Saudi Arabia is not only a core factor of social and unemployment- related crimes but also an awakening to the government’s overdependence on the expatriates for foreign labor (Cordesman, A.H., 2003, P. 22).
The high number of foreign workers is an attribute that characterizes Middle Eastern countries including Saudi Arabia. This is especially notable in the foreign sectors of these countries. This has undermined the employment efforts by the Saudi government in providing a balance between creations of employment opportunities for Saudi citizens.
Statistical data for Saudi Arabia for instance show that its private sector have about one fourth of Saudi population working as foreign expatriates in the private sector (Maisel &Shoup, 2009.p. 439). Regarding employment, Wilson (2004, p. 94), wrote that issues that affect employment have a complex nature, more so, when societies that are undergoing a spontaneous change like the Saudi Arabian situation.
He further notes that, reduction of unemployment by creation of jobs Saudi way is just a means to meet ends in the short term, which has an undermining result to the labor market. A good remedy to the unemployment situation in Saudi Arabia, as suggested by Wilson (2004, p 94), should help build capacity to the economy of the Saudi government rather than just being viewed as a means of reducing social unrest that come along with unemployment. Unemployment has had a profound effect on the education of a girl-child in Saudi Arabia.
Despite its introduction, there has been a slow progress in the labor market competitiveness of females. There is a big gap in equal opportunity between male and female. On this, Rao, (2004, p. 265), observed that the policy of female education presents discouraging impacts on the learning process of a girl-child. The effects are more notable when the level of education. The effect is more pronounced by the restrictions barring women to live alone in residential campuses, in the country.
Accomplishment of diversity especially with the use of vocational education has not been harnessed. This part of education is so limited that the only notable profession that has shown recent signs of adopting it in its system is the school of nursing. There has also been a question of high youth unemployment rates in Saudi Arabia. In the recent years, Saudi Arabia has prospered due to oil deposits, but youth unemployment still remains a challenge for the Saudi government to solve (Bowen, 2008., p. 129).
Definition of the problem
Unemployment is not only a problem facing Saudi Arabia as a government, but it is spread almost all over the world. Difference in the impacts resulting from unemployment is the type of world one belongs, which is third of the first world. Although, unemployment affects a particular question, we may be interested to investigate if it is spread evenly across a population or there exist a segment of the population that is affected most.
Besides, there may evidence of unemployment rampant to some gender. The above knowledge presents a road map to investigate unemployment in Saudi Arabia. Students graduating from institutions of higher learning comes to labor markets with infinite ambitions of securing white-collar jobs in their mother countries or in foreign countries.
A government like Saudi Arabia is endowed with vast deposits of “black gold” but it has unemployment so high that, despite its efforts to curb the effects, little change has been noticed. Locals attain education to higher levels, but they are not employable in their own country. Saudi Arabia has high numbers of foreigners as employees in its private sector; does it have implications that it has locally made labor market, does not favor the absorption of force?
Factors such as religion and culture are suspect causes of unemployment. Although they may not be directly associated with unemployment, perceptions of culture and religion by communities are direct hindrances to education of some segments of Saudi Arabia’s population-gender. Gender to this extend is brought to focus. Access to formal education may be impeded by radicalism and sectarian beliefs directed to some marginalized groups-women.
To address such like misconceptions, Saudi Arabia put in place policies to help female gender access a formal education. Nevertheless, this was not enough a solution because the problem still exists. As a consequence, it is questionable as to who was the policy-maker; instead of providing a solution, he only ended up affecting the learning process of females.
Female unemployment
Female unemployment is still a nightmare in the Arab world, especially, Saudi Arabia. The society is male dominated. Important positions are dominated by males both in the private and public sector. The cause of lies in three causes; religion and social setting; culture and education policy. Many societies in the western world adopted women in their workforce earlier than most of the third world societies which are still struggling with a culture miasma.
Culture in a country like Saudi Arabia is like a grave to burry employment of women alive. In the first place, strict rules still exist that dictates the social conduct of men and women. A society which has a man as an absolute leader in the family affairs, public place appearance and schooling levels, marginalizes the progress of females in matters of national economic building and well being of a country.
For a woman in Saudi Arabia, modernization is just a dream both awake and a sleep. Statics on employment/unemployment shows a great imbalance to equal opportunities between males and females in all sectors in Saudi Arabia. Education reforms were enacted into the government system in Saudi Arabia, in 1960. However, the system lacks freedom because the education sector is still under the control religious leaders in Saudi Arabia.
The competitiveness of a woman in the labor market is low as compared. Statistical data show that as late as 2002, unemployment stood at 8.1% on the overall. Gender wise, male unemployment was estimated at 6.8% while female unemployment was recorded to be standing at 15.8 % (Niblock, 2006, p. 115) as shown in chart 5.14 in the appendix. Assuming a high reliability of this figures, there is prove of inequality or gender imbalance to the access of education and employment.
It is alleged that education policy is a disguise of old familial and tribal practices that do not favor substantial education of females. Education of women in Saudi Arabia exposes a woman to a basic education that only takes her back domestic duties. Even if, they attain a university education; there are limited employment opportunities in the sex- segregated environments.
Sex segregation begins from secondary schools to higher institutions of learning like colleges and universities. Girls are not taught by male teachers, but only female teachers, sometimes scarcities hit these female institutions, but male teachers are not hired as a remedy for this scarcity.
There is also a general trend in the selection of courses at higher levels of learning. Most students are likely to select conservative studies like history and Islamic studies. This limits their competitive advantage on the job market. One reason this limits their competitiveness is that, in the modern information world, there are little chances that one will get a white collar job in a world where science and technical skills are required.
At present, women are restricted to work in places like where there are can very easily interact with other male clients. Customs in Saudi Arabia dictate that this is an embarrassment both to the female and the client.
As a result, most female employees in such places as banks are more likely to be employed for back office duties, even if with a reputable university. Besides, there is no clear work-family policy to give opportunities to women to balance between work and family commitments at home. Most of them are more likely to lose employment due maternity.
Saudi Arabia should still address this problem for the rates of female unemployment are not favorable. The place of a woman in the job market is, therefore, a big puzzle to solve. Education of the female has a slow progress almost five decades education of women was accepted in the 1960s. Like western cultures, a woman must be given freedom, and her skills harnessed in order to build capacity in the economy of Saudi Arabia.
Research questions
In the light of the problem above, research questions will be distributed for males and females. The ones that are directly dealt with here shall be for the males while those pertaining to women/female unemployment shall be referred to in appendix 1.
- What are the social, religious, cultural and economic causes of unemployment in Saudi Arabia?
- Is the education policy hindering the production of graduates well suited for the job market in Saudi Arabia?
- What are the impacts of foreign expatriates to youth employment in Saudi Arabia?
- What are the work-family policy bottlenecks that hinder flexibility in balancing between work and family obligations?
- How is the government effort of replacing foreign labor with locals in Saudi Arabia suitable in solving long-term unemployment in Saudi Arabia?
- What are the negative and positive impacts of unemployment to the economy of Saudi Arabia?
Research methodology
Data collection.
This research will employ both primary and secondary data collection process. Secondary data collection process shall employ usage of data the usage of already store statistical data on the unemployment situation in Saudi Arabia particularly in the 21st century. Caution will be taken during the data collection process by secondary means. To ensure that secondary data used is valid, the following aspects shall be considered.
Sufficiency
Adequacy of secondary data to use shall be considered to question the applicability of the collected secondary data to the current research situation. Any inadequacies in the secondary data will render insufficient and unsuitable to be used in the current research. Secondary data will also be employed based on its reduced bias if there is the difference in scope of research today and before.
Appropriateness
Appropriateness will be considered to investigate if the data used in the former research fits the current research situation. Inappropriate data will not be employed in this current situation.
Emphasis will be accorded to the way the primary data was compiled. This will look into the way some of the terms used were defined; was there any theories employed in the extraction of the data from their parent primary sources? Are there any changes or differences in the object, environment and spectrum of the initial knowledge claim? If changes are encountered, the data will be rendered unfit for incorporation into the current research.
Data dependability
Data used in the project was tested for its reliability as for the person who carried out the research, the sources that these data were obtained from, the methods employed during the collection of the data, the former accuracy degree, the attainment of the intended degree and possible biases during data compilation.
Data collection will involve usage questionnaires for primary data collection. Since this is a qualitative research process, total of 300 questionnaires will be distributed to the participants across selected institutions in Saudi Arabia. The target group of participants will be sampled from the population using simple random sampling technique. The groups to be investigated will comprise of three potential categories: university students, unemployed, and those in employment.
Of the employed and unemployed, the category would be subdivided further to investigate the proportion of gender for the two categories. Since there are three categories of intended respondents, there will be 100 hundred questionnaires distributed for each group. For the category of employed and unemployed, some level stratification of the sample was employed to distinguish between those in employment on the basis of gender.
Some considerations were made during the administration of the questionnaires. These were ethical considerations on the part of the participants. They were assured of anonymity in the study; thus there was no place on the questionnaire requesting them to sign or write a name. As a result, this was a tool to raise the validity and confidence in the data collected from our respondents.
Out of the three hundred questionnaires, we shall have an analysis of the proportion of male and female respondents to determine the highest. Besides, there will also be age grouping that is 18-20, 21-23 and 24-26. Since there is knowledge claim that there is a high proportion of males in the higher institutions of learning than there are females, we shall also investigate the proportion of female respondents from the questionnaires.
This will be carried out by investigating the gender age group response of those aged between 18-20 years. This group will be chosen as an indicator based on the allegation that if early on in the course of education there was some dropping out of school of females, then the proportion will show up in the remnant. This age limit is also chosen because most of them will still be in school having not attained an employment chance due to the fact that they will probably be still in school.
There is knowledge claim that dropping out of secondary level decreases the chances of getting employed. On the contrary, graduates also find it difficult to secure employment – in high paying positions either in the government institutions or private sector. To investigate this, we will analyze the age group of 24-26 years for the proportion of those in employment and that, not in employment.
This age group will be chosen since it is the time most of them shall have completed school at tertiary levels of learning if any. Besides, at this age, most of them shall be arranging to marry or shall have already married. Marital status shall be included at this stage as it has been found that most unemployed youth in Saudi Arabia are more likely not be married at the stated age because most of them do not afford the costs associated with marriage.
To investigate the effects of religion, society and culture, questions will be deliberately administered based on gender. This will employ interviews with a randomly chosen sample of female and male respondents from Saudi Arabia. We shall target the educated and married women but males will be included at all levels. The reason for this approach is that married women are more likely to be unemployed despite the fact that they have education sufficient enough to enable them secure employment.
The aim of this is to investigate the truth in the claim that religion and culture undermines the status of a woman in society to undertake work positions that have long been held by males. Besides, this choice on investigation method would allow us to investigate the extent of the effect work-family policy in the Saudi Arabian government. We shall investigate females married and employed, unemployed due to family responsibilities and unemployed due to replacement after maternity leave.
Secondary data shall come in use particularly in the provision of data pertaining to foreign labor force in the labor markets of Saudi Arabia. Data from these sources will used to provide insights into the general trends concerning the salaries paid to foreigners, and their representation in the lour force the period of 2000 to 2010.
However, a glance shall also be given to foreign labor force trends for years before the period above. Table 1 in the appendix section will supply this information followed by an analysis using graphs 1, also located in the appendix section.

Analysis of survey answers for women
The questions targeted women’s employment and education. The perspectives that were given to this approach were the influence of culture, religion and the social setting of Saudi Arabia. On the aspect of culture, most respondents expressed a dislike of the impacts of culture especially when combined with religious interpretations concerning a woman in Islam.
Most of their answers expressed a concern of change in the cultural practices like sex segregation at places of work in order to create equal opportunities for employment of both men and female. Furthermore, on the same issue of sex segregation, schools should be given freedom of mixing both sexes at all levels instead of creating a separation in terms of students and teachers.
Most blamed the policy of education in Saudi Arabia that they claimed marginalizes the learning process of females in institutions of learning. There is a general distaste among women in Saudi Arabia concerning the dominance of males in all institutions of learning and as well as home setting. This they expressed in view familial and traditional values that they felt are subject to abolishment
With respect to work family policy, almost 95% of the respondents disagreed with the current policy which does not favor formal maternity leave for women. They expressed their heartfelt concern that most women are likely to lose employment in the event of application of maternity leave.
On the same note, most of them aired their concern at the lack of absorption of a part time work system that will solve the work-family imbalances that do exist. Alluding to the western style of part time arrangement that permits even women to work at odd hours of the night, the women wished that restrictions should lifted to create room for a Saudi woman to make decisions(work related decisions) that would fully absorb a Saudi woman into the economic circles of the nation.
In the light of women graduate women taking up conservative subjects like history and religion as opposed to sciences and technical subjects, the response shows that they do not make the decision willingly but they do so with a mind that even if they take the subjects, they end up marginalized in employment, being relegated to near casual work and back office chores in promising institutions like banking institutions.
Generally, there is a genera disagreement to the education system, chances of employment for women as compared to men and the cultural implications of the position of a woman in Saudi Arabian society at large.
Solutions to the problem
Solutions to the unemployment problem in Saudi Arabia can be categorized as those that can take long period and those that can take a shorter. The long term solutions are directed at economic reforms. Owing to the fact that much of revenue for the country comes from oil, long term-economic reforms should geared towards macroeconomic management reforms. This is just an introductory note. To begin with, long term solutions are as shown below.
Long – term solutions
One of the causes of unemployment in Saudi Arabia emerging from the research process is that there is a sizable proportion of foreign workers in Saudi Arabia’s labor market. Chart 5.7 in the appendix shows that a greater percentage of the nation’s Per-capita income comes from outside the population. This has for a long time constituted frictional unemployment as a result of regional immobility of the labor markets.
As a means to reform this, the Saudi government must device a model to replace up to about 75% of the foreign labor force with the locals. The reason behind not fully replacing the foreign labor with local one is because we are seeking to resolve the unemployment in the long term. Due to challenges in the education sector in Saudi Arabia, the country may lack a matched replacement for foreign workers with locals.
The 75% percent level should not be replaced by causing a dismissal of a foreign worker but it should be an international system, where, local workers work alongside foreign workers in order to transfer skill and knowledge from the more experienced foreign worker to the local. With time, the foreigner shall be replaced fully by the local worker.
This process should not just be left to take a natural course, but should be triggered by the government through devising a functional implementation commission composed of professionals sourced locally and consultancy services of foreign experts.
In the light of integration of locals into the labor force, the government policy should also reform the private sector so that a faire Wage and salary is paid to the locals to mitigate a high – salary levels of expatriates which are a source of frequent unrest related to unemployment. Although, the system of increasing salaries for local workers will come with an associated cost, the government of Saudi Arabia should nevertheless enforce the implementation of this policy (Ramady, 2005).
Secondly, reforms in the educational sector should be adopted as a long – term remedy to unemployment. These reforms must be geared to improve the numbers and quality of education being offered to meet the demands of the labor market, not just for literacy. In order to improve on the number of students graduating from colleges and other university levels of learning (oxford business group, 2009. P 213).
Increased spending by the government through allocation of sizable amounts for the education sector can act as a good stimulus for these reforms. Education infrastructure building is also one other way of introducing reforms in the sector.
New additional colleges, universities and technical institutions should be established to act as knowledge reservoir for the country. The needs should not be limited for the creation of force that satisfies the local market a lone but also developing skill which is marketable on the international, if not global level. That is creation of a surplus labor forces.
Thirdly, another long – term solution to the unemployment would be to address the sex segregation problem facing Saudi Arabia. This particular problem is faced particularly by women both in schools and public places of work (Petmesidou et al. 2006). The school impact is at all levels of learning especially at tertiary institutions of learning.
In schools, there is segregation female and male gender even in classrooms. This has a big impact on the education a girl child as it relegates the status of a woman both socially and academically. By so doing, accessibility of a woman to formal education is limited. In fact, it is not only accessibility but also access to marketable courses in tertiary institutions of learning in Saudi Arabia.
A woman thus has limited right of choice due to male dominance hidden in a veil of preservation of religious values only to impede women from participating in a fair learning process. To address this, the government of Saudi Arabia should not look at the surface value of sex segregation but should, to a greater extent, resolve the effects on this on the labor market if a woman is included. Western systems have proofed beyond doubt that a woman can contribute as a man to economic development of a country.
The solution of this should not be pegged in the name of “addressing sex segregation” but total abolishment. This has a lasting effect to the economy by providing employment chances to a woman; not only in the back – office positions but also in any public places skill is required (Arya, & Roy, 2006).
Population growth control
Population growth is a blessing is a blessing in disguise in that it identifies people of Saudi Arabia. However, the population of Saudi Arabia has statistically been found to be the fastest growing in the region. If the population growth is controlled, provision of basic amenities by the government will present Saudi with problems of control.
Besides, lack of population control may mean that many people graduate from colleges but may end unemployed due to lack of institutions to absorb the graduates. Consequently, population control is a means to curb associated future unemployment issues facing Saudi Arabia.
Short – term solutions
The short-term solutions to unemployment in Saudi Arabia should be employed in order to solve the unemployment problem aimed at engaging the youth in activities that can help them in the creation of self employment. One way of perpetuating unemployment is through over reliance of employment in the private sector or in the civil service of any given country owing to the nature of competition in the job market, there exists likelihood that not all people with a required skill will be employed by the same employer.
However, one way of solving this is through the creation of small and medium scale enterprises targeting the youth. Creation of these enterprises requires some capital input which may be a challenge for the youth to acquire. Luckily, micro financing can enable beginners to access small business loans which can be repaid for a specified period of time. This will not only solve unemployment but will also reduce unemployment related crimes.
Secondly, a portion of the schooling population does not finish school but drop out as early as secondary level. To address this problem, particularly for those students who may not re-enroll, this class presents the involved with a near permanent unemployment situation. Research showed that there is a general attitude in Saudi Arabia with youth evading employment in casual labor.
An example given in support of this is that work like carpentry, is generally not embraced warmheartedly by Saudi youth leading to the work being taken up mostly by foreigners. Encouraging the youth who dropped out of school will take an attitude-changing training of the youth across Saudi Arabia. This has a far reaching impact on the population of the country at large.
Conclusions/recommendations
In conclusion, the problem of unemployment in Saudi Arabia is a problem that has national outcry. The implementation of some reformations should be considerate enough to address the problem. It has been established that culture and social setting of the Saudi society has a negative impact on the resolutions put in place to address the problem. The most hit person in the region is a woman, who feels the impacts of religion and culture to a substantial extend.
The part that has been found to be most devastating is sex segregation related to employment. As a fact that has been established and found to have far reaching effects, segregation, if handled the way given in the solutions will mitigate the impacts of unemployment to a large scale thus giving a Saudi woman a significant place In the economic building of that nation.
With regard to the research process, information given may be limiting in the sense that research looked at time frame of 10 years data. Any useful research can therefore, be incorporated or carried out to investigate further into the problem of women unemployment problem facing women not only in Saudi Arabia but also in other developing countries.
With regard to research, the following recommendations are suggested.
- Further research should be undertaken to establish the plight of women in the labor market of Saudi Arabia.
- The implementation process regarding the suggested reforms in the education sector should be taken with immediate effect in order to address the unemployment problem facing Saudi Arabia
- Sex segregation should not only be taken as a problem facing Saudi Arabia, but it should be viewed on a global scale since there could be other victims elsewhere in the world.
- A recommendation is made to separate religion and learning as a process.
Reference list
Arya, S & Roy, A. (2006). Poverty, gender and migration . New Delhi: Sage Publications India Pvt, Ltd.
Bosbait, M. & Wilson, R. (2005). Education, School to work Transitions and Unemployment in Saudi Arabia. Middle Eastern Studies. Vol. 41(4). Pp 533-545. Web.
Bowen, H. W. (2008). The history of Saudi Arabia . Westport: Greenwood Publishing Group, Inc.
Budhwar, S. P. & Debra, A. Y. (2001). Human resource management in developing countries. New York: Routledge.
Cordesman, A. H. (2003). Saudi Arabia enters the twenty-first century: the political, foreign policy, economic and energy dimensions . Westport: Praeger Publishers.
Maisel, S. & Shoup, J. A. (2009). Saudi Arabia and the gulf Arab states today: A-J . Westport: Greenwood Publishing Group, Inc.
Moghadam, V. M., (2003). Women: gender and social change in the Middle East Colorado: Lynne Rienner, Publishers, Inc.
Niblock, T. (2006). Saudi Arabia: power, legitimacy, and survival . New York: Routledge.
Petmesidou, M. et al. (2006). Poverty and social deprivation in the Mediterranean: trends, policies and welfare prospects in the new millennium . New York: Zed Books.
Ramady, A. M. (2005). the economy of Saudi Arabia: policies, achievements and challenges . New York: Springer.
Rao, D. B. (2004). Education for women . New Delhi. Discovery Publishing House. New York: Routledge.
Wilson, R. (2004 ). Economic development in Saudi Arabia . New York: Routledge.
Table 1. Employment in Saudi Arabia, 000s

Table 2. Average Saudi monthly salaries, SR (1US$=3.75 SR)
Chart 5.4: Women as a percentage of the labor force
It shows that the most of the labor force (about 75%) comprises of foreigners.
- Effects of Increasing Interest Rates in Africa
- Understanding Recession and Expansion: Economic Impact on Businesses
- Inflation in Saudi Arabia
- The Saudi Arabian Market Macro-Analysis
- Foreign Direct Investment in Saudi Arabia
- Australia's Economy and Major Events
- Islamic Business
- Major Reasons for Food Prices Increase
- Emiritization Efforts and Recommendations
- The Implication of Population Demographics on Businesses
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2020, April 25). Unemployment in Saudi Arabia. https://ivypanda.com/essays/unemployment-in-saudi-arabia/
"Unemployment in Saudi Arabia." IvyPanda , 25 Apr. 2020, ivypanda.com/essays/unemployment-in-saudi-arabia/.
IvyPanda . (2020) 'Unemployment in Saudi Arabia'. 25 April.
IvyPanda . 2020. "Unemployment in Saudi Arabia." April 25, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/unemployment-in-saudi-arabia/.
1. IvyPanda . "Unemployment in Saudi Arabia." April 25, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/unemployment-in-saudi-arabia/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Unemployment in Saudi Arabia." April 25, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/unemployment-in-saudi-arabia/.
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment

Band 5+: Unemployment is the one of the biggest problems of contemporary society. What do you think are the main causes of unemployment? What solutions can you suggest?
Unemployment is one of the biggest problems faced by many people around the world.Many different reasons can cause unemployment.I am going to mention some of the main reasons and solutions.
Population growth can cause unemployment when there are more people looking for jobs ,than there are jobs available.If economy doesn’t create enough jobs,unemployment can increase. also it can happen if companies use more machines instead of hiring people. So when there are too many people and not enough job,unemployment goes up.
Technological improvements can cause unemployment when machines or automation replace human workers.This happens because new technologies can do tasks more quickly than people.For example automated check in systems at airports or check out systems in stores,reduce the need of the human resources. Or maybe it requires some different skills that not all workers have. Because of that people lose their jobs and can’t find jobs that matches to their skills.
If government support small businesses and give loans and grants to help them.these jobs can grow and hire people. By offering more training classes on popular and in-demend skills in the world,people can learn new skills and find job opportunities to work in that field.
So if the government support people and people help each other to find suitable job,everyone can have a job and an income and the unemployment problem will be solved.
Check Your Own Essay On This Topic?
Generate a band-9 sample with your idea, overall band score, task response, coherence & cohesion, lexical resource, grammatical range & accuracy, essays on the same topic:, unemployment is the one of the biggest problems of contemporary society. what do you think are the main causes of unemployment what solutions can you suggest.
It is said that unemployment is one of the major problems of modern society. In my opinion, there are two main causes of the aforementioned problem, associated with changes in economic policies and the seasons of the year. Although the problem of unemployment affects people’s lives to a greater extent, it remains unnoticed. Firstly, I […]
In this day and age, one of the most significant challenges that has emerged among individuals is unemployment. This essay will first outline the root causes of this issue before suggesting remedies to address it. There are numerous reasons why joblessness has become widespread today. The primary factor is limited professional experience. Research indicates that […]
Seeking livelihood has become the most challenging pursuit in today’s world. In this essay, I will discuss the reasons and provide some solutions to alleviate this situation. To start with, two main causes for unemployment are lack of techincal skills and low employment opportunities.Candidates, for instance focus on academic preparation, however, neglect the fact that […]
In these days, unemployment is part of issues faced by society. Causes of this are limited job vacancy and lack of specific personal skill that people have. Regulation from government and courses related to job needs are needed in order to solve the problem. To start with, working opportunity is narrow and there are not […]
Other Topics:
Task 2: many people believe that the best way to produce a happier society is to ensure that there are only small differences in earning between the richest and the poorest members. to what extent do you agree or disagree give reasons for your answer and include any relevant examples from your own knowledge or experience..
One school of thought believes that reducing the income disparity between the rich and the poor is a key approach to create a contented society. From my perspective, I disagree with that view due to its potential impacts on human rights and a nation’s development To begin with, this method can result in unfairness among […]
Some people believe that governments should spend more money on improving the appearance of cities, such as building impressive buildings and public spaces. Others argue that this money should be spent on more practical issues, such as housing and education. Discuss both views and give your own opinion.
The allocation of government funds is a perennial debate, with opinions diverging on whether to prioritize aesthetic improvements or practical necessities. While there is merit in investing in urban beautification, I contend that addressing fundamental issues like housing and education should take precedence. On one hand, aesthetically pleasing cities can enhance a city’s appeal and […]
Some people believe that entertainers are paid too much and their impact on society is negative, while others disagree and believe that they deserve the money that they make because of their positive effects on society.
In recent years, many people trust that influencers are gain overloaded profit and their impact on social media platforms and human s life negative. Despite some people agree with these thoughts but others disagree and believe. They are qualified for the money that they make because of their amazing effects on society and they do […]
New household appliances have resulted in more free time for women and has enabled them to both work and run a home with dependent children. What are the advantages for a family when the mother works?. Do you think the disadvantages outweigh the advantages?.
In a contemporary era, advancement of new technologies, certainly domestic appliances, caused additional leisure time for women to be employed and organize their household appliances with reliant offsprings. I firmly believe that advantages far outweigh any potential disadvantage. This phenomenon has its disadvantages in terms of taking care of children. Some people might say this […]
All large companies should provide sports and community facilities to the local community. To what extent do you agree or disagree with this statement? Give reasons for your answer and include any relevant examples from your own knowledge or experience.
Large companies should take responsibility for providing sports and community facilities, as these efforts benefit both the local population and the companies themselves. Offering such facilities promotes a healthy lifestyle while enhancing the company’s reputation, creating a positive impact on society. One significant reason for supporting this idea is the improvement in community health. Access […]
Economic growth is the best way of ending global poverty but it can also have a negative effect on the environment. Discuss both views and give your own opinion.
It has been a debate about financial growth with poverty.Where some people suggest that economic growth of countries is the best way to tackle global poverty.But,it can cause advirse effect on the environment.In my opinion, i agree with the viewpoint. Both the viewpoint and my opinion is discussed further. To begin with, when a country […]
Plans & Pricing
Saudi Arabia: Unemployment falls to lowest in five years
The drop is partly caused by people dropping out of the workforce altogether, which is not the best news for Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman, who vowed to make job creation for young people a priority.

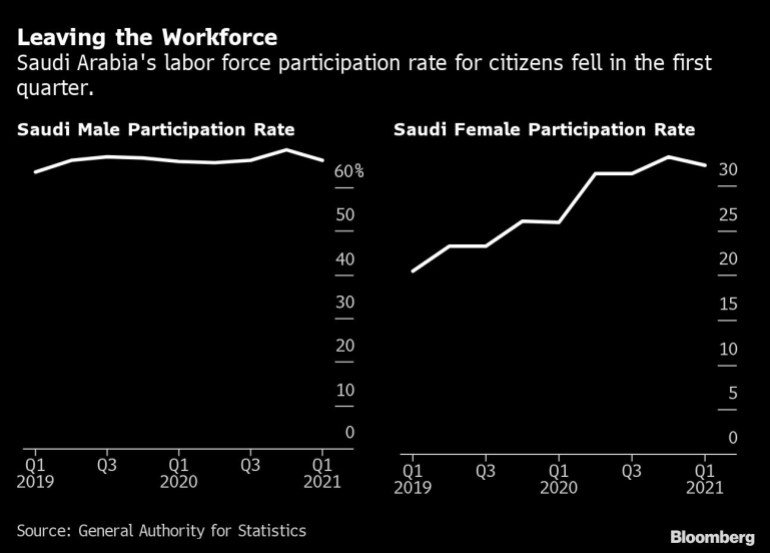
Unemployment among Saudi Arabia’s citizens fell to its lowest level in nearly five years, but the decline was partly driven by people dropping out of the labor force, unwelcome news for a crown prince who has put job creation for a youthful population at the center of his agenda.
The jobless rate decreased to 11.7% in the first quarter compared to 12.6% in the fourth quarter, continuing a strong downward trend after hitting a record at the height of the pandemic, according to data from the General Authority for Statistics. However, labor force participation for citizens also fell, from 51.2% in the fourth quarter to 49.5% in the first three months of the year — the sharpest drop since an economic downturn in 2017.
Job creation is a major consideration for Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman, the country’s de facto leader, as he reshapes an economy dependent on exporting oil and importing foreign labor. The global health emergency exacerbated the scale of the problem, pushing citizen unemployment up to 15.4% during the kingdom’s coronavirus lockdown last year.
Officials have restricted a slew of professions to Saudis only and introduced fees for businesses that hire foreign workers — part of a broader effort to replace employees from Asia, Africa and other parts of the Arab world with citizens. Prince Mohammed is also revamping regulations to try to boost entrepreneurship and attract more foreign investment, hoping both will eventually create more jobs for Saudis.
In a local television interview in April, he predicted the jobless rate would fall below 11% this year, reflecting a “V-shaped recovery,” eventually reaching his goal of 7% by 2030.
Some economists say the prince’s target is unrealistic as a demographic bulge of young people enters the labor market, necessitating the creation of at least 150,000 new jobs each year in order to keep unemployment steady.
In the first quarter, male unemployment increased slightly to 7.2%, while among women the rate fell to 21.2% from 24.4%, following a trend of more women working as social restrictions in the conservative Islamic country loosen.
The data released Wednesday didn’t include the number of employees by sector and nationality — indicators that have been reported by the statistics authority for years — making it difficult to track job creation. In the fourth quarter, the number of Saudis employed in the private sector had fallen even as the number of foreign workers in the sector dropped by over 100,000.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The problem of unemployment in Saudi Arabia began to appear at the beginning of the last century. In 1975, "Saudization" was launched as a way of replacing expatriate with Saudi workers for localization jobs, but after 37 years of unemployment is still one of the important topics of concern to citizen.
Read Sample Unemployment In Saudi Arabia Essays and other exceptional papers on every subject and topic college can throw at you. We can custom-write anything as well! We use cookies to enhance our website for you. Proceed if you agree to this policy or learn more about it. I agree.
Unemployment is one of the main problems facing society in Saudi Arabia, with the jobless rate among Saudi nationals at its highest since records began being recorded in 1999. The Kingdom is ...
This prompts an unemployment issue as a residual problem affecting the economy. Politically, leaders are legislating policies to increase the number of active age group into the workforce. The uncontrolled population has significantly been cited as the primary cause of unemployment. The menace of unemployment irritates many energetic youths.
Read Essays On Unemployment In Saudi Arabia and other exceptional papers on every subject and topic college can throw at you. We can custom-write anything as well! We use cookies to enhance our website for you.
Unemployment is a significant social and economic problem. Not always positive aspects of enterprise development contribute to a decrease in the percentage of unemployed. The negative impact may be cumulative along with phenomena such as inflation external factors, including the pandemic.
Unemployment data provided by the government for the year 2002 showed that the overall unemployment for all gender was pegged at 6.1%, with Saudi male unemployment figure estimated at 8.1% while female unemployment was at 15.8 per cent, almost twice the male unemployment figure (Niblock, 2006. Pp. 115).
The main reasons for unemployment in Saudi Arabia is because of lack of education, lack of schools and industrial colleges. We cannot ignore that Saudi Arabia's unemployment is due to their lack of education and colleges. The problem of unemployment in Saudi Arabia for female is much higher than comparing to the male unemployed rate.
The essay adequately addresses the prompt by identifying causes and suggesting solutions to unemployment. However, the depth of analysis could be improved by providing more specific examples and exploring the complexities of the issue further. The solutions offered are somewhat simplistic. The essay falls short of the required 250 words.
In the first quarter, male unemployment increased slightly to 7.2%, while among women the rate fell to 21.2% from 24.4%, following a trend of more women working as social restrictions in the ...